
Hydrological modelling
Encyclopedia
Hydrologic models are simplified, conceptual representations of a part of the hydrologic cycle. They are primarily used for hydrologic prediction and for understanding hydrologic processes. Two major types of hydrologic models can be distinguished:
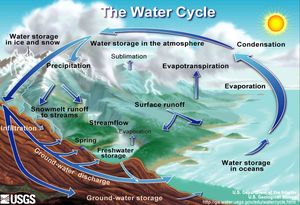 Recent research in hydrologic modelling tries to have a more global approach to the understanding of the behaviour of hydrologic systems
Recent research in hydrologic modelling tries to have a more global approach to the understanding of the behaviour of hydrologic systems
to make better predictions and to face the major challenges in water resources management
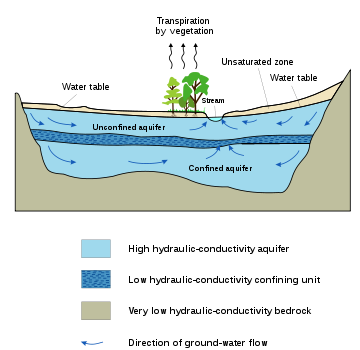
Groundwater models are computer models
of groundwater
flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are employed to simulate and predict aquifer
conditions.
The runoff curve number (also called a curve number or simply CN) is an empirical parameter used in hydrology for predicting direct runoff or infiltration from rainfall excess. It can be used with a unit hydrograph to derive the runoff rate from the direct runoff by convolution
.
.
, MOHID
, WAFLEX
and DSSAM
.
, which is combines an empirical runoff model and a hydrological transport model
. Some models combine elements of surface water models and groundwater models, for example GSSHA
, MIKE SHE
, and WEAP
.
like irrigation
, evapotranspiration
and groundwater flow
to simulate the behavior of the water table
and soil salinization and to assess agricultural engineering measures like watertable control
and soil salinity control by subsurface drains
, drainage by wells
and salt leaching.
SahysMod is a polygonal combination of SaltMod with a groundwater model
.
- Stochastic Models. These models are black box systems, based on data and using mathematical and statistical concepts to link a certain input (for instance rainfall) to the model output (for instance runoffSurface runoffSurface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
). Commonly used techniques are regressionRegression analysisIn statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
, transfer functionTransfer functionA transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
s, neural networksNeural NetworksNeural Networks is the official journal of the three oldest societies dedicated to research in neural networks: International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network Society, published by Elsevier...
and system identificationSystem identificationIn control engineering, the field of system identification uses statistical methods to build mathematical models of dynamical systems from measured data...
. These models are known as stochastic hydrology models. - Process-Based Models. These models try to represent the physical processes observed in the real world. Typically, such models contain representations of surface runoffSurface runoffSurface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
, subsurface flowSubsurface flowSubsurface flow, in hydrology, is the flow of water beneath earth's surface as part of the water cycle.In the water cycle, when precipitation falls on the earth's land, some of the water flows on the surface forming streams and rivers...
, evapotranspirationEvapotranspirationEvapotranspiration is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies...
, and channel flowOpen channel flowOpen-Channel Flow, a branch of Hydraulics, is a type of liquid flow within a conduit with a free surface, known as a channel. The other type of flow within a conduit is pipe flow. These two types of flow are similar in many ways, but differ in one important respect; the free surface...
, but they can be far more complicated. These models are known as deterministic hydrology models. Deterministic hydrology models can be subdivided into single-event models and continuous simulation models.

Behavioral modeling in hydrology
In hydrology, behavioral modeling is a modeling approach that focuses on the modeling of the behavior of hydrological systems.The behavioral modeling approach makes the main assumption that every system, given its environment, has a most probable behavior...
to make better predictions and to face the major challenges in water resources management
Groundwater modelling

Groundwater models are computer models
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
of groundwater
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are employed to simulate and predict aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
conditions.
Runoff model (empirical)
These models use an empirical method to convert rainfall volume into runoff volume. An example is the Curve Number method.The runoff curve number (also called a curve number or simply CN) is an empirical parameter used in hydrology for predicting direct runoff or infiltration from rainfall excess. It can be used with a unit hydrograph to derive the runoff rate from the direct runoff by convolution
Convolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
.
Runoff model (reservoir)
These models describe rainfall-runoff relations using the concept of a (non)linear reservoir. Examples include: VfloVflo
Vflo is a commercially available, physics-based distributed hydrologic model generated by Vflo uses radar rainfall data for hydrologic input to simulate distributed runoff . Vflo employs GIS maps for parameterization via a desktop interface . The model is suited for distributed hydrologic...
.
Hydrological transport model
These models describe the flow and routing of water once it has entered a river/stream system and the transport of dissolved or suspended material and debris in a river/stream. Examples include MIKE 11MIKE 11
MIKE 11 is a computer program that simulates flow and water level, water quality and sediment transport in rivers, flood plains, irrigation canals, reservoirs and other inland water bodies. MIKE 11 is a 1 dimensional river model. It was developed by DHI Water • Environment • Health.MIKE11 has long...
, MOHID
MOHID Water Modelling System
MOHID is short for Modelo Hidrodinâmico which is Hydrodynamic Model in Portuguese. MOHID Water Modelling System is a modular finite volumes water modelling system written in ANSI-Fortran95 using an Object-oriented programming philosophy, integrating diverse mathematical models and supporting...
, WAFLEX
WAFLEX
WAFLEX is a spreadsheet-based model. It can be used to analyse upstream-downstream interactions, dam management options and water allocation and development options.-Structure of the Model:...
and DSSAM
DSSAM Model
The DSSAM Model is a computer simulation developed for the Truckee River to analyze water quality impacts from land use and wastewater management decisions in the Truckee River Basin. This area includes the cities of Reno and Sparks, Nevada as well as the Lake Tahoe Basin...
.
Composite models
Many models combine two of these types, for example HBVHBV hydrology model
The HBV hydrology model, or Hydrologiska Byråns Vattenbalansavdelning model, is a computer simulation used to analyze river discharge and water pollution...
, which is combines an empirical runoff model and a hydrological transport model
Hydrological transport model
An hydrological transport model is a mathematical model used to simulate river or stream flow and calculate water quality parameters. These models generally came into use in the 1960s and 1970s when demand for numerical forecasting of water quality was driven by environmental legislation, and at...
. Some models combine elements of surface water models and groundwater models, for example GSSHA
GSSHA
Gridded Surface/Subsurface Hydrologic Analysis ModelGSSHA is the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Engineer Research and Development Center two-dimensional, physically based, watershed model. GSSHA is a mathematical model that simulates surface and ground water hydrology, erosion and sediment transport...
, MIKE SHE
MIKE SHE
MIKE SHE is an integrated hydrological modelling system for building and simulating surface water flow and groundwater flow. MIKE SHE can simulate the entire land phase of the hydrologic cycle and allows components to be used independently and customized to local needs...
, and WEAP
WEAP
WEAP: the Water Evaluation And Planning system is a Windows-based decision support system for integrated water resources management and policy analysis...
.
Agricultural hydro-salinity modelling
Agricultural hydro-salinity models like SaltMod, Swatre and Drainmod are models integrating hydrological factorsHydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
like irrigation
Surface irrigation
Surface irrigation is defined as the group of application techniques where water is applied and distributed over the soil surface by gravity. It is by far the most common form of irrigation throughout the world and has been practiced in many areas virtually unchanged for thousands of years.Surface...
, evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies...
and groundwater flow
Groundwater flow
Groundwater flow is defined as the "...part of streamflow that has infiltrated the ground, has entered the phreatic zone, and has been discharged into a stream channel, via springs or seepage water". In hydrogeology it is measured by the Groundwater flow equation.- See also :*Subsurface...
to simulate the behavior of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
and soil salinization and to assess agricultural engineering measures like watertable control
Watertable control
Watertable control is the practice of controlling the water table in agricultural land by subsurface drainage with proper criteria to improve the crop production.- Description and definitions :...
and soil salinity control by subsurface drains
Drainage system (Agriculture)
An agricultural drainage system is a system by which the water level on or in the soil is controlled to enhance agricultural crop production.-Classification:Figure 1 classifies the various types of drainage systems...
, drainage by wells
Well drainage
Well drainage means drainage of agricultural lands by wells. Agricultural land is drained by pumped wells to improve the soils by controlling water table levels and soil salinity.-Introduction:...
and salt leaching.
SahysMod is a polygonal combination of SaltMod with a groundwater model
Groundwater model
Groundwater models are computer models of groundwater flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are used to simulate and predict aquifer conditions.-Characteristics:...
.
See also
- Surface runoffSurface runoffSurface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
- Hydrology (agriculture)Hydrology (agriculture)Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
- AquiferAquiferAn aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
- Groundwater modelGroundwater modelGroundwater models are computer models of groundwater flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are used to simulate and predict aquifer conditions.-Characteristics:...
- Watertable controlWatertable controlWatertable control is the practice of controlling the water table in agricultural land by subsurface drainage with proper criteria to improve the crop production.- Description and definitions :...
- Water qualityWater qualityWater quality is the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water. It is a measure of the condition of water relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species and or to any human need or purpose. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which...
- Soil salinity control
- International trade and waterInternational trade and waterInternational trade and water is a term that is used to describe the relationship between international trade and the water being used by humans. The substantial increase in human population during the 20th century combined with rapid increases in overall global economic development has resulted in...

