
Hypsicles
Encyclopedia
This article is about Hypsicles of Alexandria. For the historian, see Hyspicrates (historian)
.
Hypsicles was an ancient Greek
mathematician
and astronomer
known for authoring On Ascensions (Ἀναφορικός) and the spurious Book XIV of Euclid's Elements
.
and uses the results to calculate approximate values for the times required for the signs of the zodiac to rise above the horizon
. It is thought that this is the work from which the division of the circle
into 360 parts
may have been adopted since it divides the day into 360 parts, a division possibly suggested by Babylonian
astronomy.
Hypsicles is more famously known for possibly writing the apocryphal Book XIV of Euclid's Elements. The spurious Book XIV may have been composed on the basis of a treatise by Apollonius
. The book continues Euclid's comparison of regular solids inscribed in spheres
, with the chief result being that the ratio of the surfaces of the dodecahedron and icosahedron inscribed in the same sphere is the same as the ratio
of their volume
s, the ratio being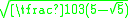 .
.
Hyspicrates (historian)
Hypsicrates the historian was a Greek writer in Rome who flourished in the 1st century BC. His work does not survive, but scholars have conjectures about the writer and his work. He was associated probably with Pontus and wrote a history of the area that was possibly used by Strabo...
.
Hypsicles was an ancient Greek
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
and astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
known for authoring On Ascensions (Ἀναφορικός) and the spurious Book XIV of Euclid's Elements
Euclid's Elements
Euclid's Elements is a mathematical and geometric treatise consisting of 13 books written by the Greek mathematician Euclid in Alexandria c. 300 BC. It is a collection of definitions, postulates , propositions , and mathematical proofs of the propositions...
.
Life and work
Although little is known about the life of Hypsicles, it is believed that he authored the astronomical work On Ascensions (Ἀναφορικός). In this work, Hypsicles proves a number of propositions on arithmetical progressionsArithmetic progression
In mathematics, an arithmetic progression or arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between the consecutive terms is constant...
and uses the results to calculate approximate values for the times required for the signs of the zodiac to rise above the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
. It is thought that this is the work from which the division of the circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
into 360 parts
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
may have been adopted since it divides the day into 360 parts, a division possibly suggested by Babylonian
History of astronomy
Astronomy is the oldest of the natural sciences, dating back to antiquity, with its origins in the religious, mythological, and astrological practices of pre-history: vestiges of these are still found in astrology, a discipline long interwoven with public and governmental astronomy, and not...
astronomy.
Hypsicles is more famously known for possibly writing the apocryphal Book XIV of Euclid's Elements. The spurious Book XIV may have been composed on the basis of a treatise by Apollonius
Apollonius of Perga
Apollonius of Perga [Pergaeus] was a Greek geometer and astronomer noted for his writings on conic sections. His innovative methodology and terminology, especially in the field of conics, influenced many later scholars including Ptolemy, Francesco Maurolico, Isaac Newton, and René Descartes...
. The book continues Euclid's comparison of regular solids inscribed in spheres
SPHERES
The Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient Experimental Satellites experiment is a testbed consisting of three miniaturized satellites that can operate in a variety of environments, including inside the International Space Station...
, with the chief result being that the ratio of the surfaces of the dodecahedron and icosahedron inscribed in the same sphere is the same as the ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of their volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
s, the ratio being
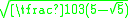 .
.
