
ISS ECLSS
Encyclopedia
International Space Station
The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes...
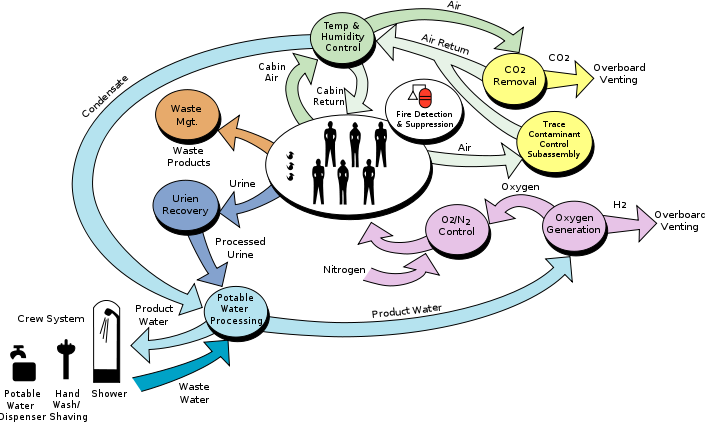
Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) is a life support system
Life support system
In human spaceflight, a life support system is a group of devices that allow a human being to survive in space.US government space agency NASA,and private spaceflight companies...
that provides or controls atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
, fire detection and suppression, oxygen levels, waste management and water supply. The highest priority for the ECLSS is the ISS atmosphere, but the system also collects, processes, and stores waste and water produced and used by the crew—a process that recycles fluid from the sink, shower, toilet, and condensation from the air. The Elektron system aboard Zvezda and a similar system in Destiny generate oxygen aboard the station.
The crew has a backup option in the form of bottled oxygen and Solid Fuel Oxygen Generation
Chemical oxygen generator
A chemical oxygen generator is a device releasing oxygen created by a chemical reaction. The oxygen source is usually an inorganic superoxide, chlorate, or perchlorate. A promising group of oxygen sources are ozonides. The generators are usually ignited mechanically, by a firing pin, and the...
(SFOG) canisters.
Carbon dioxide is removed from the air by the Vozdukh system in Zvezda. Other by-products of human metabolism, such as methane from the intestines and ammonia from sweat, are removed by activated charcoal
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
filters.
Water recovery systems
The ISS has two water recovery systems. Zvezda contains a water recovery system that processes waste water from showers, sinks, and other crew systems and water vapor from the atmosphere that could be used for drinking in an emergency but is normally fed to the Elektron system to produce oxygen. The American segment has a Water Recovery System installed during STS-126STS-126
-Crew notes:Originally scheduled to fly on STS-126 was Joan E. Higginbotham, who was a mission specialist on STS-116. On 21 November 2007, NASA announced a change in the crew manifest due to Higginbotham's decision to leave NASA to take a job in the private sector. Stephen G...
in Destiny that can process water vapour collected from the atmosphere, waste water from showers, sinks, and other crew systems, and also urine into water that is intended for drinking.
The Water Recovery System consists of a Urine Processor Assembly and a Water Processor Assembly.
The Urine Processor Assembly uses a low pressure vacuum distillation process that uses a centrifuge to compensate for the lack of gravity and thus aid in separating liquids and gasses.
Water from the Urine Processor Assembly and from waste water sources are combined to feed the Water Processor Assembly that filters out gasses and solid materials before passing through filter beds and then a high-temperature catalytic reactor assembly. The water is then tested by onboard sensors and unacceptable water is cycled back through the water processor assembly.
The Volatile Removal Assembly flew on STS-89
STS-89
STS-89 was a space shuttle mission to the Mir space station flown by Space Shuttle Endeavour, and launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 22 January 1998.-Crew:-Crew notes:...
in January 1998 to demonstrate the Water Processor Assembly's catalytic reactor in microgravity. A Vapour Compression Distillation Flight Experiment flew, but was destroyed, in STS-107
STS-107
-Mission parameters:*Mass:**Orbiter Liftoff: **Orbiter Landing: **Payload: *Perigee: *Apogee: *Inclination: 39.0°*Period: 90.1 min- Insignia :...
.
The Water Recovery System failed during the first tests and required astronauts to remove several rubber vibration isolators as the way the system was configured when it was first installed caused balance issues with the centrifuge in the vacuum distillation assembly that resulted in it failing with an error code after two hours of use. Six litres of water will be returned with STS-126 to calibrate the on-board analysis and after running successfully for 90 days, the station will be able to support an additional three astronauts.
Atmosphere
Several systems are currently used on board the ISS to maintain the spacecraft's atmosphere, which is similar to the Earth's. Normal air pressure on the ISS is 101.3 kPa (14.7 psiPounds per square inch
The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units...
); the same as at sea level on Earth. An Earth-like atmosphere offers benefits for crew comfort, and is much safer than the alternative, a pure oxygen atmosphere, because of the increased risk of a fire such as that responsible for the deaths of the Apollo 1
Apollo 1
Apollo 1 was scheduled to be the first manned mission of the Apollo manned lunar landing program, with a target launch date of February 21, 1967. A cabin fire during a launch pad test on January 27 at Launch Pad 34 at Cape Canaveral killed all three crew members: Command Pilot Virgil "Gus"...
crew.
Air revitalisation system
Carbon dioxide and trace contaminants are removed by the Air Revitalisation System. This is a NASA rack, to be placed in Tranquillity, designed to provide a Carbon Dioxide Removal Assembly (CDRA), a Trace Contaminant Control Subassembly (TCCS) to remove hazardous trace contamination from the atmosphere and a Major Constituent Analyser (MCA) to monitor NitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, Oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, Methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, and water vapour. The Air Revitalization System was flown to the station aboard STS-128
STS-128
-Crew notes:Nicole Stott was originally scheduled to return aboard Soyuz TMA-15, but a change in the flight plan was made due to the possible flight delays in future shuttle missions, which may extend Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk's mission beyond the six-month duration preferred for station...
and was temporarily installed in the Japanese Experiment Module
Japanese Experiment Module
The Japanese Experiment Module , also known with the nickname , is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on space shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124...
Pressurised Module. The system is scheduled to be transferred to Tranquillity now that the module has arrived and was installed during Space Shuttle Endeavour
Space Shuttle Endeavour
Space Shuttle Endeavour is one of the retired orbiters of the Space Shuttle program of NASA, the space agency of the United States. Endeavour was the fifth and final spaceworthy NASA space shuttle to be built, constructed as a replacement for Challenger...
mission STS-130
STS-130
STS-130 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station . 's primary payloads were the Tranquility module and the Cupola, a robotic control station with six windows around its sides and another in the center, providing a 360-degree view around the station...
.
Oxygen generating system
The Oxygen Generating System (OGS) is a NASA rack designed to electrolyse water from the Water Recovery System to produce oxygen and hydrogen. The oxygen is delivered to the cabin atmosphere and the hydrogen is vented overboard. The unit is installed in the DestinyDestiny Laboratory Module
The Destiny module is the primary operating facility for U.S. research payloads aboard the International Space Station . It was berthed to the Unity module and activated over a period of five days in February, 2001...
module. During one of the spacewalks conducted by STS-117
STS-117
- Crew Notes :The initial crew manifest before the Columbia accident was:Astronaut Mark Polansky was originally slated to pilot this mission, but was moved to STS-116, which he commanded...
astronauts, a hydrogen vent valve required to begin using the system was installed. The system became operational on 12 July 2007.
In 2011, American news outlet CBS news and news magazine spaceflightnow reported "The OGA over the past six months has not been running well because the water that's been fed to it is just slightly too acidic," said station Flight Director Chris Edelen. "For the past several months, the station crew has been using oxygen brought up aboard visiting Progress supply ships, a European cargo craft and the Russian Elektron oxygen generator while awaiting delivery of the OGA repair equipment. The OGA, like the Elektron, uses electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. "
Elektron
Elektron is a RussiaRussia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n oxygen generator, also used on Mir
Mir
Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the...
, which uses electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
to produce oxygen. This process splits water molecules reclaimed from other uses on board the station into oxygen and hydrogen via electrolysis. The oxygen is vented into the cabin and the hydrogen is vented into space. Nasa claims the three Elektron oxygen generators on board the International Space Station have been 'plagued with problems', sometimes forcing the crew to use backup sources of bottled oxygen and Solid Fuel Oxygen Generation (SFOG) canisters. Each canister can supply the oxygen needs of one crewmember for one day. NASA delivered a similar American-built system with Discovery flight STS-121
STS-121
STS-121 was a space shuttle mission to the International Space Station flown by Space Shuttle Discovery. The main purposes of the mission were to test new safety and repair techniques introduced following the Columbia disaster of February 2003 as well as to deliver supplies, equipment and...
, to supplement the Russian Elektron oxygen system and eventually support a crew of six. It became operational in 2007.
This was the first time Americans had reprocessed the atmosphere of any spacecraft. From 2001, the US orbital segment had used oxygen in a pressurized storage tank on the Quest airlock module, or from the Russian service module.
In 2004, the Elektron unit shut down mysteriously. Two weeks of troubleshooting resulted in the unit starting up again, then immediately shutting down. The cause was eventually traced to gas bubbles in the unit, which remained non-functional until a Progress
Progress spacecraft
The Progress is a Russian expendable freighter spacecraft. The spacecraft is an unmanned resupply spacecraft during its flight but upon docking with a space station, it allows astronauts inside, hence it is classified manned by the manufacturer. It was derived from the Soyuz spacecraft, and is...
resupply mission in October 2004. In 2005 ISS personnel tapped into the oxygen supply of the recently-arrived Progress resupply ship, when the Elektron unit failed. In 2006 fumes from a malfunctioning Elektron unit prompted NASA flight engineers to declare a "spacecraft emergency". A burning smell led the ISS crew to suspect another Elektron fire, but the unit was only "very hot". A leak of corrosive, odorless potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
forced the ISS crew to don gloves and face masks. It has been conjectured that the smell came from overheated rubber seals. The incident occurred shortly after STS-115
STS-115
Note:The P3/P4 Truss segment and batteries were so heavy that the crew count was reduced from seven to six.-Crew notes:...
left and just before arrival of a resupply mission (including space tourist
Space tourism
Space Tourism is space travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. A number of startup companies have sprung up in recent years, hoping to create a space tourism industry...
Anousheh Ansari
Anousheh Ansari
Anousheh Ansari is an engineer and the Iranian-American co-founder and chairman of Prodea Systems. Her previous business accomplishments include serving as co-founder and CEO of Telecom Technologies, Inc. . The Ansari family is also the title sponsor of the Ansari X Prize. On September 18, 2006,...
). The Elektron did not come back online until November 2006, after new valves and cables arrived on the October 2006 Progress resupply vessel. The ERPTC (Electrical Recovery Processing Terminal Current) was inserted into the ISS to prevent harm to the systems.
Vika
A backup to the temperamental Elektron system used on both the ISS and Mir is the Vika solid-fuel oxygen generator (SFOG), which contains a replaceable cartridge, a thin walled steel tube with a three-part block of oxygen-releasing mixture based on lithium perchlorateLithium perchlorate
Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate.-Uses:...
. Two parts are tablets of the chemical mixture and the third one is the igniter tablet with a flash igniter. The igniter is struck by a firing pin when the device is activated. One cartridge releases 600 litres (158.5 US gal) of oxygen and burns for 5–20 minutes at 450–500 °C (842–932 F) The oxygen is cooled and filtered from dust and odours, and released into the space station atmosphere.
On 23 February 1997, during the exchange of an air filter, a failed chemical oxygen generator spewed a torch-like jet of a molten metal and sparks across one of the Mir
Mir
Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the...
space station
Space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
modules, burning for 14 minutes and blocking the escape route to one of the Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz , Union) is a series of spacecraft initially designed for the Soviet space programme by the Korolyov Design Bureau in the 1960s, and still in service today...
. The accident was caused by a leak of the lithium perchlorate from one of the canisters.

