Ileus
Encyclopedia
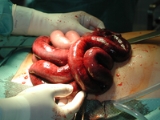
Ileus ˈɪliːəs is a disruption of the normal propulsive ability of the gastrointestinal tract
.
Ileus is commonly defined simply as bowel obstruction
. However, authoritative sources define it as decreased motor activity of the GI tract due to non-mechanical causes. In such sense, this does not include motility disorders that result from structural abnormalities, and, therefore, some mechanical obstructions are misnomers, such as gallstone ileus and meconium ileus, and are not true examples of ileus.
Paralytic ileus is a common side effect of some types of surgery, in these cases it is commonly called postsurgical ileus. It can also result from certain drugs and from various injuries and illnesses, i.e. acute pancreatitis
. Paralytic ileus causes constipation and bloating. On listening to the abdomen with a stethoscope, no bowel sounds are heard because the bowel is inactive.
A temporary paralysis of a portion of the intestines occurs typically after an abdominal surgery. Since the intestinal content of this portion is unable to move forward, food or drink should be avoided until peristaltic sound is heard from auscultation of the area where this portion lies.
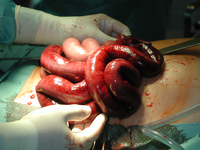 Intestinal atony or paralysis may be caused by inhibitory neural reflexes, inflammation or other implication of neurohumoral peptides.
Intestinal atony or paralysis may be caused by inhibitory neural reflexes, inflammation or other implication of neurohumoral peptides.
was considered to be mandatory in all cases, but now it is recognised that gentle feeding by enteral feeding tube
may help to restore motility by triggering the gut's normal feedback signals, so this is the recommended management initially. When the patient has severe, persistent signs that motility is completely disrupted, nasogastric suction
and parenteral
nutrition may be required until passage is restored. In such cases, continuing aggressive enteral feeding causes a risk of perforating the gut.
There are several options in the case of paralytic ileus. Most treatment is supportive. If caused by medication, the offending agent is discontinued or reduced. Bowel movements may be stimulated by prescribing lactulose
, erythromycin
or, in severe cases that are thought to have a neurological component (such as Ogilvie's syndrome), neostigmine
. There is also evidence that sham feeding, such as chewing gum, may stimulate gastrointestinal motility in the post-operative period .
If possible the underlying cause is corrected (e.g. replace electrolytes).
formation, because intestinal segments have more prolonged contact, allowing fibrous adhesions to form, and intestinal distention causes serosal injury and ischemia. Intestinal distention has been shown to cause adhesions in foals. Some respondents also mentioned the importance of walking horses postoperatively to stimulate motility. Repeat celiotomy to decompress chronically distended small intestine and remove fibrinous adhesions is also a useful method of treating ileus and reducting adhesions, and it has been associated with a good outcome
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
.
Ileus is commonly defined simply as bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines, preventing the normal transit of the products of digestion. It can occur at any level distal to the duodenum of the small intestine and is a medical emergency...
. However, authoritative sources define it as decreased motor activity of the GI tract due to non-mechanical causes. In such sense, this does not include motility disorders that result from structural abnormalities, and, therefore, some mechanical obstructions are misnomers, such as gallstone ileus and meconium ileus, and are not true examples of ileus.
Types
Decreased propulsive ability may be broadly classified as caused either by bowel obstruction or intestinal atony or paralysis. However, there are instances where there are symptoms and signs of a bowel obstruction, but with absence of a mechanical obstruction, mainly in acute colonic pseudoobstruction, also known as Ogilvie's syndrome.Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction is generally a mechanical obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract.Intestinal atony or paralysis
Paralysis of the intestine is often termed paralytic ileus. To be termed "paralytic ileus," the intestinal paralysis need not be complete, but it must be sufficient to prohibit the passage of food through the intestine and lead to intestinal blockage.Paralytic ileus is a common side effect of some types of surgery, in these cases it is commonly called postsurgical ileus. It can also result from certain drugs and from various injuries and illnesses, i.e. acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis or acute pancreatic necrosis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment...
. Paralytic ileus causes constipation and bloating. On listening to the abdomen with a stethoscope, no bowel sounds are heard because the bowel is inactive.
A temporary paralysis of a portion of the intestines occurs typically after an abdominal surgery. Since the intestinal content of this portion is unable to move forward, food or drink should be avoided until peristaltic sound is heard from auscultation of the area where this portion lies.

Symptoms
Symptoms of ileus include, but are not limited to:- moderate, diffuse abdominal discomfort
- constipationConstipationConstipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
- abdominal distensionAbdominal distensionAbdominal distension is a sensation of elevated abdominal pressure and volume. It is estimated that close to 25% of the US population has some degree of abdominal distension on a regular basis. Some describe it as belching, others claim they feel nausea and yet others say they pass excessive gas...
- nauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
/vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, especially after meals - lack of bowel movement and/or flatulenceFlatulenceFlatulence is the expulsion through the rectum of a mixture of gases that are byproducts of the digestion process of mammals and other animals. The medical term for the mixture of gases is flatus, informally known as a fart, or simply gas...
- excessive belching
Risk factors
- gastrointestinal surgeryLower gastrointestinal surgeryDigestive system surgery can be divided into upper GI surgery and lower GI surgery.Upper gastrointestinal surgery, often referred to as upper GI surgery, refers to a practise of surgery that focuses on the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract...
or other GI procedures - electrolyte imbalance
- diabetic ketoacidosisDiabetic ketoacidosisDiabetic ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening complication in patients with diabetes mellitus. It happens predominantly in those with type 1 diabetes, but it can occur in those with type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances...
(DKA), and other causes of metabolic acidosisMetabolic acidosisIn medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the... - hypothyroidismHypothyroidismHypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide but it can be caused by other causes such as several conditions of the thyroid gland or, less commonly, the pituitary gland or...
- medications (e.g. opiates or antimuscarinics)
- severe illnessIllnessIllness is a state of poor health. Illness is sometimes considered another word for disease. Others maintain that fine distinctions exist...
(Inflammation with peritonitis) - spinal cord injury (SCI), those with injury above thoracic vertebrae 5 (T5) will have hypomotility problems within the bowel
Treatment in humans
Traditionally, nil by mouthNil per os
Nil per os is a medical instruction meaning to withhold oral food and fluids from a patient for various reasons. It is a Latin phrase which translates as "nothing through the mouth". In the United Kingdom it is translated as nil by mouth .Typical reasons for NPO instructions are the prevention...
was considered to be mandatory in all cases, but now it is recognised that gentle feeding by enteral feeding tube
Feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to patients who cannot obtain nutrition by swallowing. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral feeding or tube feeding...
may help to restore motility by triggering the gut's normal feedback signals, so this is the recommended management initially. When the patient has severe, persistent signs that motility is completely disrupted, nasogastric suction
Nasogastric intubation
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the nose, past the throat, and down into the stomach.-Uses:...
and parenteral
Parenteral
Parenteral is a route of administration that involves piercing the skin or mucous membrane. Parenteral nutrition refers to providing nutrition via the veins.-Etymology:...
nutrition may be required until passage is restored. In such cases, continuing aggressive enteral feeding causes a risk of perforating the gut.
There are several options in the case of paralytic ileus. Most treatment is supportive. If caused by medication, the offending agent is discontinued or reduced. Bowel movements may be stimulated by prescribing lactulose
Lactulose
Lactulose is a synthetic, non-digestible sugar used in the treatment of chronic constipation and hepatic encephalopathy, a complication of liver disease. It is a disaccharide formed from one molecule each of the simple sugars fructose and galactose...
, erythromycin
Erythromycin
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often used for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including mycoplasma and...
or, in severe cases that are thought to have a neurological component (such as Ogilvie's syndrome), neostigmine
Neostigmine
Neostigmine is a parasympathomimetic that acts as a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.- Synthesis :Neostigmine was first synthesized by Aeschlimann and Reinert in 1931....
. There is also evidence that sham feeding, such as chewing gum, may stimulate gastrointestinal motility in the post-operative period .
If possible the underlying cause is corrected (e.g. replace electrolytes).
Complications
Ileus may increase adhesionAdhesion (medicine)
Adhesions are fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery. They may be thought of as internal scar tissue that connect tissues not normally connected.-Pathophysiology:...
formation, because intestinal segments have more prolonged contact, allowing fibrous adhesions to form, and intestinal distention causes serosal injury and ischemia. Intestinal distention has been shown to cause adhesions in foals. Some respondents also mentioned the importance of walking horses postoperatively to stimulate motility. Repeat celiotomy to decompress chronically distended small intestine and remove fibrinous adhesions is also a useful method of treating ileus and reducting adhesions, and it has been associated with a good outcome

