Illusion
Encyclopedia
An illusion is a distortion of the sense
s, revealing how the brain
normally organizes and interprets sensory stimulation. While illusions distort reality, they are generally shared by most people.
Illusions may occur with more of the human senses than vision, but visual illusions, optical illusion
s, are the most well known and understood. The emphasis on visual illusions occurs because vision
often dominates the other senses. For example, individuals watching a ventriloquist will perceive the voice is coming from the dummy since they are able to see the dummy mouth the words.
Some illusions are based on general assumptions the brain makes during perception
. These assumptions are made using organizational principles, like Gestalt
, an individual's ability of depth perception
and motion perception, and perceptual constancy
. Other illusions occur because of biological sensory structures within the human body
or conditions outside of the body within one’s physical environment.
The term illusion refers to a specific form of sensory distortion. Unlike a hallucination
, which is a distortion in the absence of a stimulus, an illusion describes a misinterpretation of a true sensation. For example, hearing voices regardless of the environment would be a hallucination, whereas hearing voices in the sound of running water (or other auditory source) would be an illusion.
Mimes are known for a repertoire of illusions that are created by physical means. The mime artist
creates an illusion of acting upon or being acted upon by an unseen object. These illusions exploit the audience's assumptions about the physical world. Well known examples include "walls", "climbing stairs", "leaning", "descending ladders", "pulling and pushing" etc.
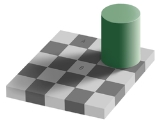
An optical illusion
is always characterized by visually perceived
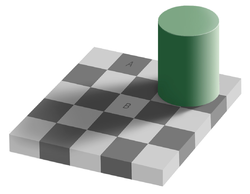
images that, at least in common sense terms, are deceptive or misleading. Therefore, the information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain to give, on the face of it, a percept that does not tally with a physical measurement of the stimulus source. A conventional assumption is that there are physiological illusions that occur naturally and cognitive illusions that can be demonstrated by specific visual tricks that say something more basic about how human perceptual systems work.
The human brain constructs a world inside our head based on what it samples from the surrounding environment. However sometimes it tries to organise this information it thinks best while other times it fills in the gaps. This way in which our brain works is the basis of an illusion.
is an illusion of hearing
, the sound
equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or "impossible" sounds. In short, audio illusions highlight areas where the human ear and brain, as organic, makeshift tools, differ from perfect audio receptors (for better or for worse). One example of an auditory illusion is a Shepard tone
.
, the thermal grill illusion
, the cutaneous rabbit illusion
and a curious illusion that occurs when the crossed index and middle fingers are run along the bridge of the nose with one finger on each side, resulting in the perception of two separate noses. Interestingly, the brain areas activated during illusory tactile perception are similar to those activated during actual tactile stimulation. Tactile illusions can also be elicited through haptic technology. These "illusory" tactile objects can be used to create "virtual objects".
the word "illusion" is used to denote different aspects in Hindu Philosophy (Maya
). Many Monist philosophies clearly demarcate illusion from truth and falsehood. As per Hindu advaita philosophy, Illusion is something which is not true and not false. Whereas in general usage it is common to assume that illusion is false, Hindu philosophy makes a distinction between Maya (illusion) and falsehood. In terms of this philosophy maya is true in itself but it is not true in comparison with the truth. As per this philosophy, illusion is not the opposite of truth or reality. Based on these assumptions Vedas declare that the world as humans normally see is illusion (Maya). It does not mean the world is not real. The world is only so much real as the image of a person in a mirror. The world is not real/true when compared to the reality. But the world is also not false. Falsehood is something which does not exist. if we apply this philosophy to the above example, the illusion is not actually illusion but is false. This is because in general usage people tend to consider lllusion to be the same as falsehood.
As per adishankar's a guru of monist teachings the world we think is not true but is an illusion (not true not false). The truth of the world is something which can only be experienced by removing the identity (ego).
Sense
Senses are physiological capacities of organisms that provide inputs for perception. The senses and their operation, classification, and theory are overlapping topics studied by a variety of fields, most notably neuroscience, cognitive psychology , and philosophy of perception...
s, revealing how the brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
normally organizes and interprets sensory stimulation. While illusions distort reality, they are generally shared by most people.
Illusions may occur with more of the human senses than vision, but visual illusions, optical illusion
Optical illusion
An optical illusion is characterized by visually perceived images that differ from objective reality. The information gathered by the eye is processed in the brain to give a perception that does not tally with a physical measurement of the stimulus source...
s, are the most well known and understood. The emphasis on visual illusions occurs because vision
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
often dominates the other senses. For example, individuals watching a ventriloquist will perceive the voice is coming from the dummy since they are able to see the dummy mouth the words.
Some illusions are based on general assumptions the brain makes during perception
Perception
Perception is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information. All perception involves signals in the nervous system, which in turn result from physical stimulation of the sense organs...
. These assumptions are made using organizational principles, like Gestalt
Gestalt
Die Gestalt is a German word for form or shape. It is used in English to refer to a concept of 'wholeness'. Gestalt may also refer to:* Gestalt psychology , a theory of mind and brain, describing the Gestalt effect....
, an individual's ability of depth perception
Depth perception
Depth perception is the visual ability to perceive the world in three dimensions and the distance of an object. Depth sensation is the ability to move accurately, or to respond consistently, based on the distances of objects in an environment....
and motion perception, and perceptual constancy
Subjective constancy
Subjective constancy or perceptual constancy is the perception of an object or quality as constant under changing conditions.-Vision:There are several types of perceptual constancies in Visual perception:-* Shape constancy* Size constancy...
. Other illusions occur because of biological sensory structures within the human body
Human body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
or conditions outside of the body within one’s physical environment.
The term illusion refers to a specific form of sensory distortion. Unlike a hallucination
Hallucination
A hallucination, in the broadest sense of the word, is a perception in the absence of a stimulus. In a stricter sense, hallucinations are defined as perceptions in a conscious and awake state in the absence of external stimuli which have qualities of real perception, in that they are vivid,...
, which is a distortion in the absence of a stimulus, an illusion describes a misinterpretation of a true sensation. For example, hearing voices regardless of the environment would be a hallucination, whereas hearing voices in the sound of running water (or other auditory source) would be an illusion.
Mimes are known for a repertoire of illusions that are created by physical means. The mime artist
Mime artist
A mime artist is someone who uses mime as a theatrical medium or as a performance art, involving miming, or the acting out a story through body motions, without use of speech. In earlier times, in English, such a performer was referred to as a mummer...
creates an illusion of acting upon or being acted upon by an unseen object. These illusions exploit the audience's assumptions about the physical world. Well known examples include "walls", "climbing stairs", "leaning", "descending ladders", "pulling and pushing" etc.
Optical illusions

An optical illusion
Optical illusion
An optical illusion is characterized by visually perceived images that differ from objective reality. The information gathered by the eye is processed in the brain to give a perception that does not tally with a physical measurement of the stimulus source...
is always characterized by visually perceived
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
images that, at least in common sense terms, are deceptive or misleading. Therefore, the information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain to give, on the face of it, a percept that does not tally with a physical measurement of the stimulus source. A conventional assumption is that there are physiological illusions that occur naturally and cognitive illusions that can be demonstrated by specific visual tricks that say something more basic about how human perceptual systems work.
The human brain constructs a world inside our head based on what it samples from the surrounding environment. However sometimes it tries to organise this information it thinks best while other times it fills in the gaps. This way in which our brain works is the basis of an illusion.
Auditory illusions
An auditory illusionAuditory illusion
An auditory illusion is an illusion of hearing, the aural equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or "impossible" sounds...
is an illusion of hearing
Hearing (sense)
Hearing is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations through an organ such as the ear. It is one of the traditional five senses...
, the sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or "impossible" sounds. In short, audio illusions highlight areas where the human ear and brain, as organic, makeshift tools, differ from perfect audio receptors (for better or for worse). One example of an auditory illusion is a Shepard tone
Shepard tone
A Shepard tone, named after Roger Shepard, is a sound consisting of a superposition of sine waves separated by octaves. When played with the base pitch of the tone moving upward or downward, it is referred to as the Shepard scale. This creates the auditory illusion of a tone that continually...
.
Tactile illusions
Examples of tactile illusions include phantom limbPhantom limb
A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached to the body and is moving appropriately with other body parts. 2 out of 3 combat veterans report this feeling. Approximately 60 to 80% of individuals with an amputation experience phantom sensations in their...
, the thermal grill illusion
Thermal grill illusion
The thermal grill illusion is a sensory illusion originally demonstrated in 1896 by T. Thunberg. The illusion is created by an interlaced grill of warm and cool bars. When someone presses a hand against the grill, he or she experiences the illusion of burning heat...
, the cutaneous rabbit illusion
Cutaneous rabbit illusion
The cutaneous rabbit illusion is a tactile illusion evoked by tapping two separate regions of the skin. Many experiments demonstrating the effect have been carried out on the forearm...
and a curious illusion that occurs when the crossed index and middle fingers are run along the bridge of the nose with one finger on each side, resulting in the perception of two separate noses. Interestingly, the brain areas activated during illusory tactile perception are similar to those activated during actual tactile stimulation. Tactile illusions can also be elicited through haptic technology. These "illusory" tactile objects can be used to create "virtual objects".
Other senses
Illusions can occur with the other senses including that of taste and smell. It was discovered that even if some portion of the taste receptor on the tongue became damaged that illusory taste could be produced by tactile stimulation. Evidence of olfactory (smell) illusions occurred when positive or negative verbal labels were given prior to olfactory stimulation.Disorders
Some illusions occur as result of an illness or a disorder. While these types of illusions are not shared with everyone, they are typical of each condition. For example migraine sufferers often report Fortification illusions.Philosophy and Illusion
Just like many other words often used in a different sense in spiritualitySpirituality
Spirituality can refer to an ultimate or an alleged immaterial reality; an inner path enabling a person to discover the essence of his/her being; or the “deepest values and meanings by which people live.” Spiritual practices, including meditation, prayer and contemplation, are intended to develop...
the word "illusion" is used to denote different aspects in Hindu Philosophy (Maya
Maya (illusion)
Maya , in Indian religions, has multiple meanings, usually quoted as "illusion", centered on the fact that we do not experience the environment itself but rather a projection of it, created by us. Maya is the principal deity that manifests, perpetuates and governs the illusion and dream of duality...
). Many Monist philosophies clearly demarcate illusion from truth and falsehood. As per Hindu advaita philosophy, Illusion is something which is not true and not false. Whereas in general usage it is common to assume that illusion is false, Hindu philosophy makes a distinction between Maya (illusion) and falsehood. In terms of this philosophy maya is true in itself but it is not true in comparison with the truth. As per this philosophy, illusion is not the opposite of truth or reality. Based on these assumptions Vedas declare that the world as humans normally see is illusion (Maya). It does not mean the world is not real. The world is only so much real as the image of a person in a mirror. The world is not real/true when compared to the reality. But the world is also not false. Falsehood is something which does not exist. if we apply this philosophy to the above example, the illusion is not actually illusion but is false. This is because in general usage people tend to consider lllusion to be the same as falsehood.
As per adishankar's a guru of monist teachings the world we think is not true but is an illusion (not true not false). The truth of the world is something which can only be experienced by removing the identity (ego).
External links
- Universal Veiling Techniques
- Best Rotating Illusions Video
- Make own Illusion video
- Illusion Database Daily Illusions
- What is an Illusion? by J.R. Block.
- Optical illusions and visual phenomena by Michael Bach
- Auditory illusions
- Haptic Perception of Shape - touch illusions, forces and the geometry of objects, by Gabriel Robles-De-La-Torre.
- Illusions of taste
- Get High Now (a science site with audio and visual illusions)
- Silencing awareness of visual change by motion
- Illusion Mini Keelboat

