Image rectification
Encyclopedia
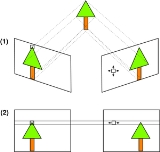
Image rectification is a transformation process used to project two-or-more images onto a common image plane. It corrects image distortion by transforming the image into a standard coordinate system.
 Stereo vision uses triangulation based on epipolar geometry
Stereo vision uses triangulation based on epipolar geometry
to determine distance to an object.
Between two cameras there is a problem of finding a corresponding point viewed by one camera in the image of the other camera (known as the correspondence problem
). In most camera configurations, finding correspondences requires a search in two-dimensions. However, if the two cameras are aligned to be coplanar, the search is simplified to one dimension - a horizontal line parallel to the baseline
between the cameras. Furthermore, if the location of a point in the left image is known, it can be searched for in the right image by searching left of this location along the line, and vice versa (see binocular disparity
). Image rectification is an equivalent (and more often used) alternative to perfect camera alignment. Image rectification is usually performed regardless of camera precision due to
. X & Y rotation puts the images on the same plane, scaling makes the image frames be the same size and Z rotation & skew adjustments make the image pixel rows directly line up. The rigid alignment of the cameras needs to be known (by calibration) and the calibration coefficients are used by the transform.
In performing the transform, if the cameras themselves are calibrated for internal parameters, an essential matrix provides the relationship between the cameras. The more general case (without camera calibration) is represented by the fundamental matrix. If the fundamental matrix is not known, it is necessary to find preliminary point correspondences between stereo images to facilitate its extraction.
Stereo images can also be taken with a single camera in motion. In this case the relationship of the images can have significant forward-motion components, and a linear transformation may produce severely warped images or very large images. Non-linear transformation techniques can be used to manage this difficulty.
Primary difficulties in the process occur
The maps that are used with rectified images are non-topographical. However, the images to be used may contain distortion from terrain. Image orthorectification additionally removes these effects.
Image rectification is a standard feature available with commercial GIS software packages.
- It is used in computer stereo visionComputer stereo visionComputer stereo vision is the extraction of 3D information from digital images, such as obtained by a CCD camera. By comparing information about a scene from two vantage points, 3D information can be extracted by examination of the relative positions of objects in the two panels...
to simplify the problem of finding matching points between images. - It is used in geographic information systemGeographic Information SystemA geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
s to merge images taken from multiple perspectives into a common map coordinate system.
Computer stereo vision

Epipolar geometry
Epipolar geometry is the geometry of stereo vision. When two cameras view a 3D scene from two distinct positions, there are a number of geometric relations between the 3D points and their projections onto the 2D images that lead to constraints between the image points...
to determine distance to an object.
Between two cameras there is a problem of finding a corresponding point viewed by one camera in the image of the other camera (known as the correspondence problem
Correspondence problem
The correspondence problem tries to figure out which parts of an image correspond to which parts of another image, after the camera has moved, time has elapsed, and/or the objects have moved around.-Overview:...
). In most camera configurations, finding correspondences requires a search in two-dimensions. However, if the two cameras are aligned to be coplanar, the search is simplified to one dimension - a horizontal line parallel to the baseline
Baseline
A baseline is a line that is a base for measurement or for construction; see datum or point of reference .The word baseline may refer to:...
between the cameras. Furthermore, if the location of a point in the left image is known, it can be searched for in the right image by searching left of this location along the line, and vice versa (see binocular disparity
Binocular disparity
Binocular disparity refers to the difference in image location of an object seen by the left and right eyes, resulting from the eyes' horizontal separation. The brain uses binocular disparity to extract depth information from the two-dimensional retinal images in stereopsis...
). Image rectification is an equivalent (and more often used) alternative to perfect camera alignment. Image rectification is usually performed regardless of camera precision due to
- impracticality or impossibility of perfectly aligning cameras
- perfectly aligned cameras may become misaligned over time
Transformation
If the images to be rectified are taken from camera pairs without geometric distortion, this calculation can easily be made with a linear transformationLinear transformation
In mathematics, a linear map, linear mapping, linear transformation, or linear operator is a function between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. As a result, it always maps straight lines to straight lines or 0...
. X & Y rotation puts the images on the same plane, scaling makes the image frames be the same size and Z rotation & skew adjustments make the image pixel rows directly line up. The rigid alignment of the cameras needs to be known (by calibration) and the calibration coefficients are used by the transform.
In performing the transform, if the cameras themselves are calibrated for internal parameters, an essential matrix provides the relationship between the cameras. The more general case (without camera calibration) is represented by the fundamental matrix. If the fundamental matrix is not known, it is necessary to find preliminary point correspondences between stereo images to facilitate its extraction.
Stereo images can also be taken with a single camera in motion. In this case the relationship of the images can have significant forward-motion components, and a linear transformation may produce severely warped images or very large images. Non-linear transformation techniques can be used to manage this difficulty.
Algorithms
There are basically three algorithms for image rectification: planar rectification , cylindrical rectification and polar rectification.Geographic information system
Image rectification in GIS converts images to a standard map coordinate system. This is done by matching ground control points (GCP) in the mapping system to points in the image. These GCPs calculate necessary image transforms.Primary difficulties in the process occur
- when the accuracy of the map points are not well known
- when the images lack clearly identifiable points to correspond to the maps.
The maps that are used with rectified images are non-topographical. However, the images to be used may contain distortion from terrain. Image orthorectification additionally removes these effects.
Image rectification is a standard feature available with commercial GIS software packages.
See also
- Binocular disparityBinocular disparityBinocular disparity refers to the difference in image location of an object seen by the left and right eyes, resulting from the eyes' horizontal separation. The brain uses binocular disparity to extract depth information from the two-dimensional retinal images in stereopsis...
- Correspondence problemCorrespondence problemThe correspondence problem tries to figure out which parts of an image correspond to which parts of another image, after the camera has moved, time has elapsed, and/or the objects have moved around.-Overview:...
- Epipolar geometryEpipolar geometryEpipolar geometry is the geometry of stereo vision. When two cameras view a 3D scene from two distinct positions, there are a number of geometric relations between the 3D points and their projections onto the 2D images that lead to constraints between the image points...
- Geographic information systemGeographic Information SystemA geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
- Stereo cameraStereo cameraA stereo camera is a type of camera with two or more lenses with a separate image sensor or film frame for each lens. This allows the camera to simulate human binocular vision, and therefore gives it the ability to capture three-dimensional images, a process known as stereo photography. Stereo...
- Stereo vision
- Structure from motionStructure from motionIn computer vision structure from motion refers to the process of finding the three-dimensional structure of an object by analyzing local motion signals over time....

