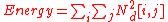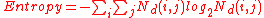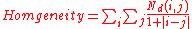Image texture
Encyclopedia
An image texture is a set of metrics calculated in image processing designed to quantify the perceived texture of an image. Image Texture gives us information about the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or selected region of an image.
Image textures can be artificially created or found in natural scenes captured in an image. Image textures are one way that can be used to help in Segmentation (image processing)
or classification of images. To analyze an image texture in computer graphics, there are two ways to approach the issue: Structured Approach and Statistical Approach.
in some regular or repeated pattern. This works well when analyzing artificial textures.
To obtain a structured description a characterization of the spatial relationship of the texels is gathered by using Voronoi tessellation of the texels.
to determine the number of edge pixels in a specified region helps determine a characteristic of texture complexity. After edges have been found the direction of the edges can also be applied as a characteristic of texture and can be useful in determining patterns in the texture. These directions can be represented as an average or in a histogram.
Consider a region with N pixels. the gradient-based edge detector is applied to this region by producting two outputs for each pixel p: the gradient magnitude Mag(p) and the gradient direction Dir(p). The edgeness per unit area is can be defined by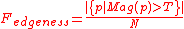 for some threshold T.
for some threshold T.
To include orientation with edgeness we can use histograms for both gradient magnitude and gradient direction. Let Hmag(R) denote the normalized histogram of gradient magnitudes of region R, and let Hdir denote the normalized histogram of gradient orientations of region R. Both are normalized according to the size NR Then is quantitative texture description of region R.
is quantitative texture description of region R.
can caputure properties of a texture, though they are not directly useful for further analysis. Numeric features computed from co-occurrence matrices can be used to represent and compare textures. The following are standard features derivable from a normalized co-occurrence matrix:
L5 (Level) = [1 4 6 4 1]
E5 (Edge) = [-1 -2 0 2 1]
S5 (Spot) = [-1 0 2 0 1]
R5 (Ripple) = [1 -4 6 -4 1]
based on image texture, region based and boundary based. Though image texture is not a perfect measure for segmentation
it is used along with other measure, such as color, that helps solve segmenting in image.
Image textures can be artificially created or found in natural scenes captured in an image. Image textures are one way that can be used to help in Segmentation (image processing)
Segmentation (image processing)
In computer vision, segmentation refers to the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments . The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze...
or classification of images. To analyze an image texture in computer graphics, there are two ways to approach the issue: Structured Approach and Statistical Approach.
Structured Approach
A structured approach sees an image texture as a set of primitive texelsTexel (graphics)
A texel, or texture element is the fundamental unit of texture space, used in computer graphics. Textures are represented by arrays of texels, just as pictures are represented by arrays of pixels....
in some regular or repeated pattern. This works well when analyzing artificial textures.
To obtain a structured description a characterization of the spatial relationship of the texels is gathered by using Voronoi tessellation of the texels.
Statistical Approach
A statistical approach sees an image texture as a quantitative measure of the arrangement of intensities in a region. In general this approach is easier to compute and is more widely used, since natural textures are made of patterns of irregular subelements.Edge Detection
The use of edge detectionEdge detection
Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aim at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities...
to determine the number of edge pixels in a specified region helps determine a characteristic of texture complexity. After edges have been found the direction of the edges can also be applied as a characteristic of texture and can be useful in determining patterns in the texture. These directions can be represented as an average or in a histogram.
Consider a region with N pixels. the gradient-based edge detector is applied to this region by producting two outputs for each pixel p: the gradient magnitude Mag(p) and the gradient direction Dir(p). The edgeness per unit area is can be defined by
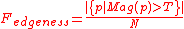 for some threshold T.
for some threshold T.To include orientation with edgeness we can use histograms for both gradient magnitude and gradient direction. Let Hmag(R) denote the normalized histogram of gradient magnitudes of region R, and let Hdir denote the normalized histogram of gradient orientations of region R. Both are normalized according to the size NR Then
 is quantitative texture description of region R.
is quantitative texture description of region R.Co-occurrence Matrices
Co-occurrence matrixCo-occurrence matrix
A co-occurrence matrix or co-occurrence distribution is a matrix or distribution that is defined over an image to be the distribution of co-occurring values at a given offset...
can caputure properties of a texture, though they are not directly useful for further analysis. Numeric features computed from co-occurrence matrices can be used to represent and compare textures. The following are standard features derivable from a normalized co-occurrence matrix:
Laws Texture Energy Measures
Another approach to generate texture features is to use local masks to detect various types of textures. Convolution masks of 5x5 are used to compute the energy of texture which is then represented by a nine element vector for each pixel. The masks are generated from the following vectors:L5 (Level) = [1 4 6 4 1]
E5 (Edge) = [-1 -2 0 2 1]
S5 (Spot) = [-1 0 2 0 1]
R5 (Ripple) = [1 -4 6 -4 1]
Autocorrelation and Power Spectrum
The autocorrelation function of an image can be used to detect repetitive patterns of textures.Texture Segmentation
The use of image texture can be used as a description for regions into segments. There are two main types of segmentationSegmentation (image processing)
In computer vision, segmentation refers to the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments . The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze...
based on image texture, region based and boundary based. Though image texture is not a perfect measure for segmentation
Segmentation (image processing)
In computer vision, segmentation refers to the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments . The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze...
it is used along with other measure, such as color, that helps solve segmenting in image.