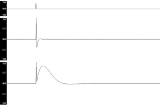
Impulse response
Overview
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse
Dirac delta function
The Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change. In both cases, the impulse response describes the reaction of the system as a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
of time (or possibly as a function of some other independent variable
Independent variable
The terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
that parameterizes the dynamic behavior of the system).
For example, the dynamic system might be a planetary system
Planetary system
A planetary system consists of the various non-stellar objects orbiting a star such as planets, dwarf planets , asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and cosmic dust...
in orbit around a star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
; the external influence in this case might be another massive object arriving from elsewhere in the galaxy; the impulse response is the change in the motion of the planetary system caused by interaction with the new object.
In all these cases, the 'dynamic system' and its 'impulse response' may refer to actual physical objects, or to a mathematical system of equations describing these objects.
Mathematically, how the impulse is described depends on whether the system is modeled in discrete or continuous time.

