Influenza-like illness
Encyclopedia
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
of possible influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
or other illness causing a set of common symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s, with SARI referring to Severe Acute Respiratory Infection.
Symptoms commonly include fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, shivering
Shivering
Shivering is a bodily function in response to early hypothermia in warm-blooded animals. When the core body temperature drops, the shivering reflex is triggered to maintain homeostasis. Muscle groups around the vital organs begin to shake in small movements in an attempt to create warmth by...
, chills, malaise
Malaise
Malaise is a feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness, of being "out of sorts", often the first indication of an infection or other disease. Malaise is often defined in medicinal research as a "general feeling of being unwell"...
, dry cough, loss of appetite
Appetite
The appetite is the desire to eat food, felt as hunger. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Decreased desire to eat is...
, body aches and nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, typically in connection with a sudden onset of illness. In most cases, the symptoms are caused by cytokines released by immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
activation.
Common causes of ILI include the common cold
Common cold
The common cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system, caused primarily by rhinoviruses and coronaviruses. Common symptoms include a cough, sore throat, runny nose, and fever...
and influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
, which tends to be less common but more severe than the common cold. Still less common causes include side effects
Adverse effect (medicine)
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
of many drugs
DRUGS
Destroy Rebuild Until God Shows are an American post-hardcore band formed in 2010. They released their debut self-titled album on February 22, 2011.- Formation :...
and manifestations of many other diseases.
Causes
The causes of influenza-like illness range from benign self-limited illnesses such as gastroenteritisGastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is marked by severe inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract involving both the stomach and small intestine resulting in acute diarrhea and vomiting. It can be transferred by contact with contaminated food and water...
, rhinoviral disease, and influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
, to severe, life-threatening diseases such as meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
, sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
, and leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
.
Influenza
Technically, any clinicalPhysical examination
Physical examination or clinical examination is the process by which a doctor investigates the body of a patient for signs of disease. It generally follows the taking of the medical history — an account of the symptoms as experienced by the patient...
diagnosis of influenza is a diagnosis of ILI, not of influenza. This distinction usually is of no great concern because, regardless of cause, most cases of ILI are mild and self-limiting. Furthermore, except perhaps during the peak of a major outbreak of influenza, most cases of ILI are not due to influenza. ILI is very common: in the United States each adult can average 1–3 episodes per year and each child can average 3–6 episodes per year.
Influenza in humans
Human flu
Human flu is a term used to refer to influenza cases caused by Orthomyxoviridae that are endemic to human populations . It is an arbitrary categorization scheme, and is not associated with phylogenetics-based taxonomy...
is subject to clinical surveillance
Clinical surveillance
Clinical surveillance refers to the surveillance of health data about a clinical syndrome that has a significant impact on public health, which is then used to drive decisions about health policy and health education...
by a global network of more than 110 National Influenza Centers
National Influenza Centers
National Influenza Centers are institutions which are formally recognized as such by the World Health Organization ."The WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network was established in 1952...
. These centers receive samples obtained from patients diagnosed with ILI, and test the samples for the presence of an influenza virus. Not all patients diagnosed with ILI are tested, and not all test results are reported. Samples are selected for testing based on severity of ILI, and as part of routine sampling, and at participating surveillance clinics and laboratories. The United States has a general surveillance program, a border surveillance program, and a hospital surveillance program, all devoted to finding new outbreaks of influenza.
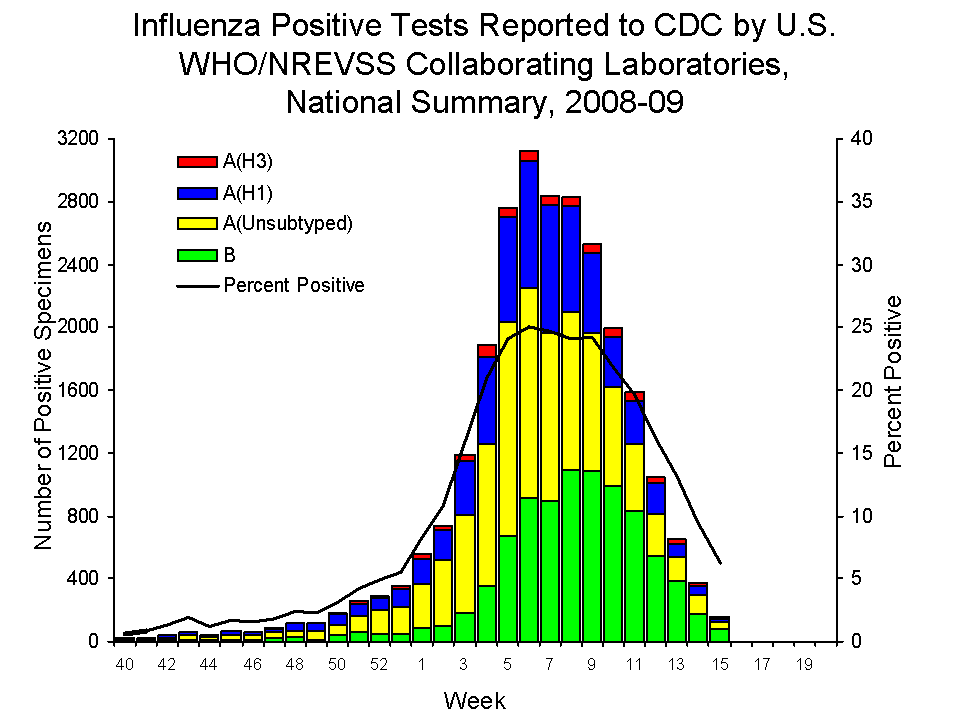
In most years, in the majority of samples tested, the influenza virus is not present (see figure). In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
during the 2008–9 influenza season through April 18, out of 183,839 samples tested and reported to the CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
, only 25,925 (14.1%) were positive for influenza. The percent positive reached a maximum of about 25%. The percent positive increases with the incidence
Incidence (epidemiology)
Incidence is a measure of the risk of developing some new condition within a specified period of time. Although sometimes loosely expressed simply as the number of new cases during some time period, it is better expressed as a proportion or a rate with a denominator.Incidence proportion is the...
of infection, peaking with the peak incidence of influenza (see figure). During an epidemic
Epidemic
In epidemiology, an epidemic , occurs when new cases of a certain disease, in a given human population, and during a given period, substantially exceed what is expected based on recent experience...
, 60-70% of patients with a clear influenza-like illness actually have influenza.
Samples are respiratory samples, usually collected by a physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
, nurse, or assistant, and sent to a hospital laboratory for preliminary testing. There are several methods of collecting a respiratory sample, depending on requirements of the laboratory that will test the sample. A sample may be obtained from around the nose
Human nose
The visible part of the human nose is the protruding part of the face that bears the nostrils. The shape of the nose is determined by the ethmoid bone and the nasal septum, which consists mostly of cartilage and which separates the nostrils...
simply by wiping with a dry cotton swab
Cotton swab
Cotton swabs or cotton buds or ear buds consist of a small wad of cotton wrapped around one or both ends of a short rod, usually made of either wood, rolled paper, or plastic...
.
Other causes
Infectious diseases causing ILI include malariaMalaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
, acute HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
infection, herpes, hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease primarily affecting the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus . The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years...
, Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is an emerging infectious disease caused by at least three species of bacteria belonging to the genus Borrelia. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto is the main cause of Lyme disease in the United States, whereas Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii cause most...
, rabies
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes acute encephalitis in warm-blooded animals. It is zoonotic , most commonly by a bite from an infected animal. For a human, rabies is almost invariably fatal if post-exposure prophylaxis is not administered prior to the onset of severe symptoms...
, myocarditis
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of heart muscle . It resembles a heart attack but coronary arteries are not blocked.Myocarditis is most often due to infection by common viruses, such as parvovirus B19, less commonly non-viral pathogens such as Borrelia burgdorferi or Trypanosoma cruzi, or as a...
, Q fever
Q fever
Q fever is a disease caused by infection with Coxiella burnetii, a bacterium that affects humans and other animals. This organism is uncommon but may be found in cattle, sheep, goats and other domestic mammals, including cats and dogs...
, dengue fever
Dengue fever
Dengue fever , also known as breakbone fever, is an infectious tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash that is similar to measles...
, poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis, is an acute viral infectious disease spread from person to person, primarily via the fecal-oral route...
, and many others.
Pharmaceutical drugs that may cause ILI include many biologics such as interferon
Interferon
Interferons are proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens—such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites—or tumor cells. They allow communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that eradicate pathogens or tumors.IFNs belong to...
s or monoclonal antibodies. Chemotherapeutic agents also commonly cause flu-like symptoms. Other drugs associated with a flu-like syndrome include bisphosphonates, caspofungin
Caspofungin
Caspofungin is an antifungal drug, the first of a new class termed the echinocandins from Merck & Co., Inc. It shows activity against infections with Aspergillus and Candida, and works by inhibiting the enzyme β-D-Glucan synthase and thereby disturbing the integrity of the fungal cell wall...
or levamisole
Levamisole
Levamisole is an anthelminthic and immunomodulator belonging to a class of synthetic imidazothiazole derivatives. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1966...
. A flu-like syndrome can also be caused by an influenza vaccine or other vaccines, and by opioid withdrawal in addicts.
Diagnosis
Influenza-like illness is a nonspecific respiratory illness characterized by feverFever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, fatigue, cough
Cough
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
, and other symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s that stop within a few days. Most cases of ILI are caused not by influenza but by other viruses (e.g., rhinovirus
Rhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
es and respiratory syncytial virus, adenoviruses, and parainfluenza viruses). Less common causes of ILI include bacteria such as Legionella
Legionella
Legionella is a pathogenic Gram negative bacterium, including species that cause legionellosis or Legionnaires' disease, most notably L. pneumophila. It may be readily visualized with a silver stain....
, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a very small bacterium in the class Mollicutes.It causes the disease mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia, and is related to cold agglutinin disease.-Cell wall/Treatment:...
, and Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. A significant human pathogenic bacterium, S...
. Influenza, RSV, and certain bacterial infections are particularly important causes of ILI because these infections can lead to serious complications requiring hospitalization. Physicians who examine persons with ILI can use a combination of epidemiologic and clinical data (information about recent other patients and the individual patient) and, if necessary, laboratory and radiographic tests to determine the cause of the ILI.
During the 2009 swine flu outbreak many thousands of cases of ILI were reported in the media as suspected swine flu
Swine flu
Swine influenza, also called pig influenza, swine flu, hog flu and pig flu, is an infection by any one of several types of swine influenza virus. Swine influenza virus or S-OIV is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs...
. Most were false alarms. A differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
of probable swine flu requires not only symptoms but also a high likelihood of swine flu due to the person's recent history. During the 2009 swine flu outbreak in the United States, the CDC advised physicians to "consider swine influenza infection in the differential diagnosis of patients with acute febrile respiratory illness who have either been in contact with persons with confirmed swine flu, or who were in one of the five U.S. states that have reported swine flu cases or in Mexico during the 7 days preceding their illness onset." A diagnosis of confirmed swine flu required laboratory testing of a respiratory sample (a simple nose and throat swab).
In rare cases
If a person with ILI also has either a history of exposure or an occupational or environmental risk of exposure to Bacillus anthracis (anthraxAnthrax
Anthrax is an acute disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Most forms of the disease are lethal, and it affects both humans and other animals...
), then a differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
requires distinguishing between ILI and anthrax. Other rare causes of ILI include leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
and metal fume fever
Metal fume fever
Metal fume fever also known as brass founders' ague, brass shakes, zinc shakes, Galvie Flu, or Monday morning fever is an illness caused primarily by exposure to certain fumes...
.
In other animals
ILI occurs in some horses after intramuscular injectionIntramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection is the injection of a substance directly into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several alternative methods for the administration of medications . It is used for particular forms of medication that are administered in small amounts...
of vaccine
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
s. For these horses, light exercise speeds resolution of the ILI. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
s (NSAIDs) may be given with the vaccine.

