Common cold
Encyclopedia
The common cold is a viral infectious disease
of the upper respiratory system
, caused primarily by rhinovirus
es and coronavirus
es. Common symptoms include a cough
, sore throat
, runny nose
, and fever
. There is no cure for the common cold, but symptoms usually resolve in 7 to 10 days, with some symptoms possibly lasting for up to three weeks.
The common cold is the most frequent infectious disease in humans with the average adult contracting two to four infections a year and the average child contracting between 6 and 12.
Collectively, colds, influenza
, and other upper respiratory tract infection
s (URTI) with similar symptoms are included in the diagnosis of influenza-like illness
.
, sore throat
, runny nose, and nasal congestion
; sometimes this may be accompanied by conjunctivitis
(pink eye), muscle aches
, fatigue, headache
s, shivering
, and loss of appetite
. Fever
is often present thus creating a symptom picture which overlaps with influenza
. The symptoms of influenza however are usually more severe.
Those suffering from colds often report a sensation of chilliness even though the cold is not generally accompanied by fever, and although chills
are generally associated with fever, the sensation may not always be caused by actual fever. In one study, 60% of those suffering from a sore throat and upper respiratory tract infection reported headaches, often due to nasal congestion
.
The first indication of an upper respiratory virus is often a sore or scratchy throat
. Other common symptoms are runny nose
, congestion
, and sneezing
. These are sometimes accompanied by muscle aches
, fatigue, malaise
, headache
, weakness
, or loss of appetite
. Cough and fever generally indicate influenza
rather than an upper respiratory virus with a positive predictive value of around 80%.
Symptoms may be more severe in infants and young children, and in these cases it may include fever and hives
. Upper respiratory viruses may also be more severe in smokers.
-caused colds more than other colds. Rhinovirus-caused colds are most infectious during the first three days of symptoms. They become much less infectious after those three days.
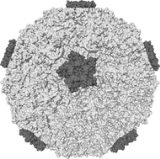
 The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. The most commonly implicated virus is a rhinovirus
The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. The most commonly implicated virus is a rhinovirus
(30–50%), a type of picornavirus
with 99 known serotypes. Others include: coronavirus
(10–15%), influenza
(5–15%), human parainfluenza viruses
, human respiratory syncytial virus
, adenoviruses
, enterovirus
es, and metapneumovirus
.
In total over 200 serologically different viral types cause colds. Coronaviruses are particularly implicated in adult colds. Of over 30 coronaviruses, 3 or 4 cause infections in humans, but they are difficult to grow in the laboratory and their significance is thus less well-understood. Due to the many different types of viruses and their tendency for continuous mutation, it is impossible to gain complete immunity to the common cold.
(inflammation of the throat). In the common cold, the inflammation is caused by a viral infection in the uppermost part of the throat (the nasopharynx
), which runs from behind the nose down to the mouth.
The common cold virus is transmitted mainly from contact with saliva or nasal secretions of an infected person, either directly, when a healthy person breathes in the virus-laden aerosol
generated when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or by touching a contaminated surface and then touching the nose or eyes.
Symptoms are not necessary for viral shedding or transmission, as a percentage of asymptomatic subjects exhibit viruses in nasal swabs. It is generally not possible to identify the virus type through symptoms, although influenza can be distinguished by its sudden onset, fever, and cough.
The major entry point for the virus is normally the nose, but can also be the eyes (in this case drainage into the nasopharynx
would occur through the nasolacrimal duct
). From there, it is transported to the back of the nose and the adenoid
area. The virus then attaches to a receptor, ICAM-1
, which is located on the surface of cells
of the lining of the nasopharynx. The receptor fits into a docking port on the surface of the virus. Large amounts of virus receptor are present on cells of the adenoid. After attachment to the receptor, virus is taken into the cell, where it starts an infection, and increases ICAM-1 production, which in turn helps the immune response against the virus. Rhinovirus colds do not generally cause damage to the nasal epithelium
. Macrophage
s trigger the production of cytokines, which in combination with mediators cause the symptoms. Cytokines cause the systemic effects. The mediator bradykinin
plays a major role in causing the local symptoms such as sore throat and nasal irritation.
The common cold is self-limiting, and the host's immune system
effectively deals with the infection. Within a few days, the body's humoral immune response begins producing specific antibodies that can prevent the virus from infecting cells. Additionally, as part of the cell-mediated immune response, leukocytes destroy the virus through phagocytosis and destroy infected cells to prevent further viral replication. In healthy, immunocompetent individuals, the common cold resolves in seven days on average.
Regular hand washing
is recommended to reduce transmission of cold viruses and other pathogens via direct contact
. Virus can be recovered from the hands of ∼40% of adults with rhinovirus colds, and the quantity of virus recovered from the hands is also generally greater than that recovered in coughs and sneezes. Washing of the hands reduces virus count on the skin.
Randomized controlled trial
s have shown that hand washing using different combinations of cleaning agents resulted in a reduction in the incidence of rhinovirus infections.
In two studies at day care facilities, increased handwashing of caregivers reduced the incidence of colds in children by up to 20%. However, scheduled handwashing at an elementary school has been shown to reduce the incidence of all communicable illnesses and gastrointestinal illnesses in particular, but was not shown to prevent respiratory ailments.
Cleaning contaminated surfaces such as coffee cup handles with a mixed alcohol/phenol disinfectant has been shown to almost halve the chance of transmission via direct contact.
Efforts to develop a vaccine
against the common cold have been unsuccessful. Common colds are produced by a large variety of rapidly mutating viruses; successful creation of a broadly effective vaccine is highly improbable.
Exposure to cold temperatures and dry weather have been found to facilitate viral infection, explaining why colds and flu are more prevalent in winter outside of tropical areas. Cold weather may make the mucous lining of the respiratory tract more sluggish, taking longer to sweep any inhaled virus particles away. This allows more time for the virus to establish infection and means an individual is infectious (exhaling virus particles) for longer. In humidity above 80%, droplets containing viruses fall out of the air.
However, whilst it creates a better environment for the virus, cold weather itself does not directly cause colds and neither is there evidence supporting the idea that cold weather weakens the cells involved in the immune response.
 There are currently no medications or herbal remedies which have been conclusively demonstrated to shorten the duration of infection in all people with cold symptoms.
There are currently no medications or herbal remedies which have been conclusively demonstrated to shorten the duration of infection in all people with cold symptoms.
Treatment comprises symptomatic support usually via analgesics for fever, headache, sore muscles, and sore throat.
s such as ibuprofen
and acetaminophen / paracetamol
. Evidence does not show that cough medicine
is any more effective than simple analgesics and is not recommended for use in children due to a lack of evidence supporting its effectiveness and the potential for harm.
Symptoms of a runny nose can be reduced by a first generation antihistamine; however, it can cause drowsiness and other side effects. Other decongestant
s such as pseudoephedrine
are effective in adults but there is insufficient evidence to support their use in children. Anticholinergics such as Ipratropium
nasal spray can reduce the symptoms of runny nose with less side effects.
One study has found chest vapor rub to be effective at providing some symptomatic relief of nocturnal cough, congestion, and sleep difficulty.
Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling
with warm salt water, are reasonable conservative measures. Due to lack of studies, it is not currently known whether increased fluid intake improves symptoms or shortens respiratory illness and a similar lack of data exists for the use of heated humidified air. Saline nasal drops may help alleviate nasal congestion.
s for the common cold even though some preliminary research has shown benefit.
may be a more effective treatment in decreasing cough and improving sleep in children than no treatment or dextromethorphan
. However, honey should not be given to a child younger than one year old because of the risk of infant botulism. The benefits versus risk of nasal irrigation
are currently unclear and therefore it is not recommended.
Zinc
may inhibit rhinovirus replication and reduce inflammation. Trials have found that zinc supplements can somewhat reduce the severity and duration of common cold symptoms when taken by otherwise healthy adults within 24 hours of onset of symptoms.
Vitamin C
's effect on the common cold has been extensively researched. It has not been shown effective in prevention or treatment of the common cold, except in limited circumstances (specifically, individuals exercising vigorously in cold environments). Routine vitamin C supplementation does not reduce the incidence or severity of the common cold in the general population, though it may reduce the duration of illness.
Evidence about the usefulness of echinacea
supplements, a popular herbal remedy, is contradictory. Well-conducted research studies tend to have negative results at a much higher rate than poorly conducted studies. Different types of echinacea supplements may vary in their effectiveness. Generally, those studies that show supportive results indicate that echinacea might reduce the likelihood of developing cold symptoms upon inoculation with a virus by about half.
 The name "common cold" came into use in the 16th century, due to the similarity between its symptoms and those of exposure to cold weather. Norman Moore relates in his history of the Study of Medicine that James I
The name "common cold" came into use in the 16th century, due to the similarity between its symptoms and those of exposure to cold weather. Norman Moore relates in his history of the Study of Medicine that James I
continually suffered from nasal colds, which were then thought to be caused by polypi
, sinus
trouble, or autotoxaemia.
In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin
considered the causes and prevention of the common cold. After several years of research he concluded: "People often catch cold from one another when shut up together in small close rooms, coaches, etc. and when sitting near and conversing so as to breathe in each other's transpiration." Although viruses had not yet been discovered, Franklin hypothesized that the common cold was passed between people through the air. He recommended exercise, bathing, and moderation in food and drink consumption to avoid the common cold. Franklin's theory on the transmission of the cold was confirmed some 150 years later.
, the Common Cold Unit
was set up by the Medical Research Council
in 1946. The unit worked with volunteers who were infected with various viruses. The rhinovirus
was discovered there. In the late 1950s, researchers were able to grow one of these cold viruses in a tissue culture
, as it would not grow in fertilized chicken eggs, the method used for many other viruses. In the 1970s, the CCU demonstrated that treatment with interferon
during the incubation phase of rhinovirus infection protects somewhat against the disease, but no practical treatment could be developed. The unit was closed in 1989, two years after it completed research of zinc gluconate lozenges in the prophylaxis and treatment of rhinovirus colds, the only successful treatment in the history of the unit.
 In the United States, the common cold leads to 75 to 100 million physician visits annually at a conservative cost estimate of $7.7 billion per year. Americans spend $2.9 billion on over-the-counter drugs and another $400 million on prescription medicines for symptomatic relief.
In the United States, the common cold leads to 75 to 100 million physician visits annually at a conservative cost estimate of $7.7 billion per year. Americans spend $2.9 billion on over-the-counter drugs and another $400 million on prescription medicines for symptomatic relief.
More than one-third of patients who saw a doctor received an antibiotic prescription, which has implications for antibiotic resistance
from overuse of such drugs.
An estimated 22 to 189 million school days are missed annually due to a cold. As a result, parents missed 126 million workdays to stay home to care for their children. When added to the 150 million workdays missed by employees suffering from a cold, the total economic impact of cold-related work loss exceeds $20 billion per year. This accounts for 40% of time lost from work.
weather such as rain or winter conditions, which is where the disease got its name. Common colds are seasonal in temperate latitudes, with more occurring during winter. The experimental evidence for this effect is uneven: many experiments have failed to produce evidence that short-term exposure to cold weather or direct chilling increases susceptibility to infection, implying that the seasonal variation is instead due to a change in behaviors such as increased time spent indoors at close proximity to others. However, other experiments do find such an effect for both body chilling and cold air exposure, and a number of mechanisms by which lower temperatures could compromise the immune system have been suggested, while other experiments have shown that exposure to cold temperatures may instead stimulate the immune system.
are developing a drug, currently known as BTA798, which targets rhinovirus
. In 2009, the drug has completed Phase IIA clinical trials.
ViroPharma
and Schering-Plough
are developing an antiviral drug, pleconaril, that targets picornaviruses, the viruses that cause the majority of common colds. Pleconaril has been shown to be effective in an oral
form.
Schering-Plough
is developing an intra-nasal
formulation that may have fewer adverse effects.
Researchers from University of Maryland, College Park
and University of Wisconsin–Madison
have mapped the genome
for all known virus strains that cause the common cold.
Naturally produced antibodies can accompany virus particles into cells. This has raised hopes of a drug that could boost this process, thus providing a medication that could combat not only the common cold, but other infections caused by similar viruses.
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
of the upper respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
, caused primarily by rhinovirus
Rhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
es and coronavirus
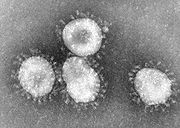
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are species in the genera of virus belonging to the subfamily Coronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae. Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a helical symmetry. The genomic size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 16 to 31...
es. Common symptoms include a cough
Cough
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
, sore throat
Sore throat
A sore throat or throat pain is a common physical symptom usually caused by acute pharyngitis, or throat inflammation, though it also occurs in a number of other situations, such as post trauma and in diphtheria. It can cause mild to extreme pain....
, runny nose
Rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea or rhinorrhoea is a condition where the nasal cavity is filled with a significant amount of mucous fluid. The condition, commonly known as "runny nose", occurs relatively frequently and is not usually considered dangerous. Rhinorrhea is a common symptom of allergies or certain diseases,...
, and fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
. There is no cure for the common cold, but symptoms usually resolve in 7 to 10 days, with some symptoms possibly lasting for up to three weeks.
The common cold is the most frequent infectious disease in humans with the average adult contracting two to four infections a year and the average child contracting between 6 and 12.
Collectively, colds, influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
, and other upper respiratory tract infection
Upper respiratory tract infection
Upper respiratory tract infections are the illnesses caused by an acute infection which involves the upper respiratory tract: nose, sinuses, pharynx or larynx...
s (URTI) with similar symptoms are included in the diagnosis of influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness , also known as acute respiratory infection and flu-like syndrome, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms, with SARI referring to Severe Acute Respiratory Infection.Symptoms commonly include fever, shivering, chills,...
.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms are coughCough
A cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
, sore throat
Sore throat
A sore throat or throat pain is a common physical symptom usually caused by acute pharyngitis, or throat inflammation, though it also occurs in a number of other situations, such as post trauma and in diphtheria. It can cause mild to extreme pain....
, runny nose, and nasal congestion
Nasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the blockage of the nasal passages usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflamed blood vessels. It is also known as nasal blockage, nasal obstruction, blocked nose, stuffy nose, or stuffed up nose.Nasal congestion has many causes and can range from a...
; sometimes this may be accompanied by conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis refers to inflammation of the conjunctiva...
(pink eye), muscle aches
Myalgia
Myalgia means "muscle pain" and is a symptom of many diseases and disorders. The most common causes are the overuse or over-stretching of a muscle or group of muscles. Myalgia without a traumatic history is often due to viral infections...
, fatigue, headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
s, shivering
Shivering
Shivering is a bodily function in response to early hypothermia in warm-blooded animals. When the core body temperature drops, the shivering reflex is triggered to maintain homeostasis. Muscle groups around the vital organs begin to shake in small movements in an attempt to create warmth by...
, and loss of appetite
Anorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
. Fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
is often present thus creating a symptom picture which overlaps with influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
. The symptoms of influenza however are usually more severe.
Those suffering from colds often report a sensation of chilliness even though the cold is not generally accompanied by fever, and although chills
Rigor (medicine)
Rigor is a shaking occurring during a high fever. It occurs because cytokines and prostaglandins are released as part of an immune response and increase the set point for body temperature in the hypothalamus....
are generally associated with fever, the sensation may not always be caused by actual fever. In one study, 60% of those suffering from a sore throat and upper respiratory tract infection reported headaches, often due to nasal congestion
Nasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the blockage of the nasal passages usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflamed blood vessels. It is also known as nasal blockage, nasal obstruction, blocked nose, stuffy nose, or stuffed up nose.Nasal congestion has many causes and can range from a...
.
Progression
The viral replication begins 2 to 6 hours after initial contact. Symptoms usually begin 2 to 5 days after initial infection but occasionally occur in as little as 10 hours. Symptoms peak 2–3 days after symptom onset, whereas influenza symptom onset is constant and immediate. The symptoms usually resolve spontaneously in 7 to 10 days but some can last for up to three weeks. In children the cough lasts for more than 10 days in 35–40% of cases and continues for more than 25 days in 10%.The first indication of an upper respiratory virus is often a sore or scratchy throat
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
. Other common symptoms are runny nose
Rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea or rhinorrhoea is a condition where the nasal cavity is filled with a significant amount of mucous fluid. The condition, commonly known as "runny nose", occurs relatively frequently and is not usually considered dangerous. Rhinorrhea is a common symptom of allergies or certain diseases,...
, congestion
Nasal congestion
Nasal congestion is the blockage of the nasal passages usually due to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from inflamed blood vessels. It is also known as nasal blockage, nasal obstruction, blocked nose, stuffy nose, or stuffed up nose.Nasal congestion has many causes and can range from a...
, and sneezing
Sneeze
A sneeze is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa...
. These are sometimes accompanied by muscle aches
Myalgia
Myalgia means "muscle pain" and is a symptom of many diseases and disorders. The most common causes are the overuse or over-stretching of a muscle or group of muscles. Myalgia without a traumatic history is often due to viral infections...
, fatigue, malaise
Malaise
Malaise is a feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness, of being "out of sorts", often the first indication of an infection or other disease. Malaise is often defined in medicinal research as a "general feeling of being unwell"...
, headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
, weakness
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness or myasthenia is a lack of muscle strength. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness...
, or loss of appetite
Anorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
. Cough and fever generally indicate influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
rather than an upper respiratory virus with a positive predictive value of around 80%.
Symptoms may be more severe in infants and young children, and in these cases it may include fever and hives
Urticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
. Upper respiratory viruses may also be more severe in smokers.
Infectious period
Researchers have studied rhinovirusRhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
-caused colds more than other colds. Rhinovirus-caused colds are most infectious during the first three days of symptoms. They become much less infectious after those three days.
Viruses

Rhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
(30–50%), a type of picornavirus
Picornavirus
A picornavirus is a virus belonging to the family Picornaviridae. Picornaviruses are non-enveloped, positive-stranded RNA viruses with an icosahedral capsid. The genome RNA is unusual because it has a protein on the 5' end that is used as a primer for transcription by RNA polymerase...
with 99 known serotypes. Others include: coronavirus
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are species in the genera of virus belonging to the subfamily Coronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae. Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a helical symmetry. The genomic size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 16 to 31...
(10–15%), influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
(5–15%), human parainfluenza viruses
Human parainfluenza viruses
Human parainfluenza viruses are a group of four distinct serotypes of enveloped single-stranded RNA viruses belonging to the paramyxovirus family.Parainfluenza viruses can be detected via cell culture, immunofluorescent microscopy, and PCR....
, human respiratory syncytial virus
Human respiratory syncytial virus
Human respiratory syncytial virus is a virus that causes respiratory tract infections. It is the major cause of lower respiratory tract infections and hospital visits during infancy and childhood. A prophylactic medication exists for preterm birth infants and infants with a congenital heart...
, adenoviruses
Adenoviridae
Adenoviruses are medium-sized , nonenveloped icosahedral viruses composed of a nucleocapsid and a double-stranded linear DNA genome...
, enterovirus
Enterovirus
Enteroviruses are a genus of ssRNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Serologic studies have distinguished 66 human enterovirus serotypes on the basis of antibody neutralization tests. Additional antigenic variants have been defined within several of the serotypes on the...
es, and metapneumovirus
Metapneumovirus
Human metapneumovirus is a negative single-stranded RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae and is closely related to the avian metapneumovirus subgroup C. It was isolated for the first time in 2001 in the Netherlands by using the RAP-PCR technique for identification of unknown viruses growing...
.
In total over 200 serologically different viral types cause colds. Coronaviruses are particularly implicated in adult colds. Of over 30 coronaviruses, 3 or 4 cause infections in humans, but they are difficult to grow in the laboratory and their significance is thus less well-understood. Due to the many different types of viruses and their tendency for continuous mutation, it is impossible to gain complete immunity to the common cold.
Risk factors
- Touching eyes, nose, or mouth with contaminated fingers. This behavior increases the likelihood of transferring viruses from the surface of the hands, where they are harmless, into the upper respiratory tract, where they can infect the tissues. It has been demonstrated that cold viruses can be spread by touching contaminated objects and surfaces, or by brief contact of hands.
- Spending time in an enclosed area with an infected person or in close contact with an infected person. Common colds are droplet-borne infections, which means that they can be transmitted through breathing in tiny particles that the infected person emits when he or she coughs or sneezes. In one study, the virus was recovered in 1/13 of sneezes and 0/8 coughs generated by adults with natural rhinovirus (cold) infections.
- The role of body cooling in causing the common cold is controversial. It is the most commonly offered folk explanation for the disease, and it has received some experimental evidence. One study showed that exposure to the cold causes cold symptoms in about 10% of those exposed, and that the subjects experiencing this effect report far more colds overall than those who do not. However, a variety of other studies do not show such an effect.
- A history of smoking extends the duration of illness by about three days.
- Getting fewer than seven hours of sleepSleepSleep is a naturally recurring state characterized by reduced or absent consciousness, relatively suspended sensory activity, and inactivity of nearly all voluntary muscles. It is distinguished from quiet wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimuli, and is more easily reversible than...
per night has been associated with a risk three times higher of developing an infection when exposed to a rhinovirus, compared to those who sleep more than eight hours per night. - Common colds are seasonal, occurring more frequently during winter outside of tropical zones. Some argue that this is partly due to a change in behaviors such as increased time spent indoors, which puts infected people in close proximity to other people, rather than the exposure to cold temperatures.
- Low humidity increases viral transmission rates. One theory is that dry air causes evaporation of water, thus allowing small viral droplets to disperse farther and stay in the air longer.
- Counterintuitively, people with stronger immune systems are more likely to develop symptomatic colds. This is because the symptoms of a cold are directly due to the strong immune response to the virus, not the virus itself. People with less active immune systems—about a quarter of adults—get infected with the viruses, but the relatively weak immunological response produces no significant or identifiable symptoms. These people are asymptomatic carrierAsymptomatic carrierAn asymptomatic carrier is a person or other organism that has contracted an infectious disease, but who displays no symptoms. Although unaffected by the disease themselves, carriers can transmit it to others...
s and can unknowingly spread the virus to other people. Because strong immune responses cause cold symptoms, "boosting" the immune system increases cold symptoms.
Pathophysiology
The common cold is a type of pharyngitisPharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
(inflammation of the throat). In the common cold, the inflammation is caused by a viral infection in the uppermost part of the throat (the nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
The nasopharynx is the uppermost part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate; it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx in that its cavity always remains patent .-Lateral:On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal ostium of the...
), which runs from behind the nose down to the mouth.
The common cold virus is transmitted mainly from contact with saliva or nasal secretions of an infected person, either directly, when a healthy person breathes in the virus-laden aerosol
Aerosol
Technically, an aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas. Examples are clouds, and air pollution such as smog and smoke. In general conversation, aerosol usually refers to an aerosol spray can or the output of such a can...
generated when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or by touching a contaminated surface and then touching the nose or eyes.
Symptoms are not necessary for viral shedding or transmission, as a percentage of asymptomatic subjects exhibit viruses in nasal swabs. It is generally not possible to identify the virus type through symptoms, although influenza can be distinguished by its sudden onset, fever, and cough.
The major entry point for the virus is normally the nose, but can also be the eyes (in this case drainage into the nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
The nasopharynx is the uppermost part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate; it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx in that its cavity always remains patent .-Lateral:On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal ostium of the...
would occur through the nasolacrimal duct
Nasolacrimal duct
The nasolacrimal duct carries tears from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity. Excess tears flow through nasolacrimal duct which drains into the inferior nasal meatus...
). From there, it is transported to the back of the nose and the adenoid
Adenoid
Adenoids are a mass of lymphoid tissue situated posterior to the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat....
area. The virus then attaches to a receptor, ICAM-1
ICAM-1
ICAM-1 also known as CD54 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ICAM1 gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is typically expressed on endothelial cells and cells of the immune system...
, which is located on the surface of cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
of the lining of the nasopharynx. The receptor fits into a docking port on the surface of the virus. Large amounts of virus receptor are present on cells of the adenoid. After attachment to the receptor, virus is taken into the cell, where it starts an infection, and increases ICAM-1 production, which in turn helps the immune response against the virus. Rhinovirus colds do not generally cause damage to the nasal epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
. Macrophage
Macrophage
Macrophages are cells produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. Human macrophages are about in diameter. Monocytes and macrophages are phagocytes. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms of vertebrate animals...
s trigger the production of cytokines, which in combination with mediators cause the symptoms. Cytokines cause the systemic effects. The mediator bradykinin
Bradykinin
Bradykinin is a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate , and therefore causes blood pressure to lower. A class of drugs called ACE inhibitors, which are used to lower blood pressure, increase bradykinin further lowering blood pressure...
plays a major role in causing the local symptoms such as sore throat and nasal irritation.
The common cold is self-limiting, and the host's immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
effectively deals with the infection. Within a few days, the body's humoral immune response begins producing specific antibodies that can prevent the virus from infecting cells. Additionally, as part of the cell-mediated immune response, leukocytes destroy the virus through phagocytosis and destroy infected cells to prevent further viral replication. In healthy, immunocompetent individuals, the common cold resolves in seven days on average.
Prevention
The best prevention for the common cold is staying away from people who are infected, and places where infected individuals have been.Regular hand washing
Hand washing
Hand washing for hand hygiene is the act of cleaning the hands with or without the use of water or another liquid, or with the use of soap, for the purpose of removing soil, dirt, and/or microorganisms....
is recommended to reduce transmission of cold viruses and other pathogens via direct contact
Direct Contact
Direct Contact is a direct-to-DVD film starring Dolph Lundgren. The production company is Nu Image. The movie was filmed in Bulgaria, and stars Swedish actor Dolph Lundgren and Michael Paré...
. Virus can be recovered from the hands of ∼40% of adults with rhinovirus colds, and the quantity of virus recovered from the hands is also generally greater than that recovered in coughs and sneezes. Washing of the hands reduces virus count on the skin.
- Hand washing with plain soap and water is recommended. The mechanical action of hand rubbing with plain soap, rinsing, and drying physically removes the virus particles from the hands.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers kill viruses, but are not as demonstrably effective in preventing respiratory illness as they are in preventing gastrointestinal illness. A 2001 study found that use of an alcohol-free instant hand sanitizer reduced elementary school absences related to respiratory illnesses by 50%.
- Because the common cold is caused by a virus instead of a bacterium, anti-bacterial soaps are no better than regular soap for removing the virus from skin or other surfaces.
- Aqueous iodineIodineIodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
has been found to reliably eliminate the cold virus on human skin; however, iodine is not acceptable for general use as a virucidal hand treatment because it discolors and dries the skin.
Randomized controlled trial
Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
s have shown that hand washing using different combinations of cleaning agents resulted in a reduction in the incidence of rhinovirus infections.
In two studies at day care facilities, increased handwashing of caregivers reduced the incidence of colds in children by up to 20%. However, scheduled handwashing at an elementary school has been shown to reduce the incidence of all communicable illnesses and gastrointestinal illnesses in particular, but was not shown to prevent respiratory ailments.
Cleaning contaminated surfaces such as coffee cup handles with a mixed alcohol/phenol disinfectant has been shown to almost halve the chance of transmission via direct contact.
Efforts to develop a vaccine
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
against the common cold have been unsuccessful. Common colds are produced by a large variety of rapidly mutating viruses; successful creation of a broadly effective vaccine is highly improbable.
Exposure to cold temperatures and dry weather have been found to facilitate viral infection, explaining why colds and flu are more prevalent in winter outside of tropical areas. Cold weather may make the mucous lining of the respiratory tract more sluggish, taking longer to sweep any inhaled virus particles away. This allows more time for the virus to establish infection and means an individual is infectious (exhaling virus particles) for longer. In humidity above 80%, droplets containing viruses fall out of the air.
However, whilst it creates a better environment for the virus, cold weather itself does not directly cause colds and neither is there evidence supporting the idea that cold weather weakens the cells involved in the immune response.
Management

Treatment comprises symptomatic support usually via analgesics for fever, headache, sore muscles, and sore throat.
Symptomatic
Treatments that help alleviate symptoms include simple analgesics and antipyreticAntipyretic
Antipyretics ; an-tee-pahy-ret-iks; from the Greek anti, against, and pyreticus, are drugs or herbs that reduce fever. Normally, they will not lower body temperature if one does not have a fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override an interleukin-induced increase in temperature...
s such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
and acetaminophen / paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
. Evidence does not show that cough medicine
Cough medicine
A cough medicine is a medicinal drug used in an attempt to treat coughing and related conditions. For dry coughs, treatment with cough suppressants may be attempted to suppress the body's urge to cough...
is any more effective than simple analgesics and is not recommended for use in children due to a lack of evidence supporting its effectiveness and the potential for harm.
Symptoms of a runny nose can be reduced by a first generation antihistamine; however, it can cause drowsiness and other side effects. Other decongestant
Decongestant
A decongestant or nasal decongestant is a type of drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion.-Pharmacology:The vast majority of decongestants act via enhancing norepinephrine and epinephrine or adrenergic activity by stimulating the α-adrenergic receptors...
s such as pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is used as a nasal/sinus decongestant and stimulant, or as a wakefulness-promoting agent....
are effective in adults but there is insufficient evidence to support their use in children. Anticholinergics such as Ipratropium
Ipratropium
Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic drug used for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and acute asthma. It blocks the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the smooth muscles of the bronchi in the lungs, opening the bronchi...
nasal spray can reduce the symptoms of runny nose with less side effects.
One study has found chest vapor rub to be effective at providing some symptomatic relief of nocturnal cough, congestion, and sleep difficulty.
Getting plenty of rest, drinking fluids to maintain hydration, and gargling
Gargling
Gargling is the act in which one bubbles a liquid in one's mouth. It usually requires that the head be tilted back, allowing a mouthful of liquid to sit in the upper throat. The head can be tilted by extending either the neck or the back, depending on what is comfortable for the gargler...
with warm salt water, are reasonable conservative measures. Due to lack of studies, it is not currently known whether increased fluid intake improves symptoms or shortens respiratory illness and a similar lack of data exists for the use of heated humidified air. Saline nasal drops may help alleviate nasal congestion.
Antibiotics and antivirals
Antibiotics have no effect against viral infections and thus have no effect against the viruses that cause the common cold and due to their side effects cause overall harm. There are no approved antiviral drugAntiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used specifically for treating viral infections. Like antibiotics for bacteria, specific antivirals are used for specific viruses...
s for the common cold even though some preliminary research has shown benefit.
Alternative treatments
While many alternative treatments are used there is insufficient scientific evidence to support the use of most. HoneyHoney
Honey is a sweet food made by bees using nectar from flowers. The variety produced by honey bees is the one most commonly referred to and is the type of honey collected by beekeepers and consumed by humans...
may be a more effective treatment in decreasing cough and improving sleep in children than no treatment or dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan is an antitussive drug. It is one of the active ingredients in many over-the-counter cold and cough medicines, such as Robitussin, NyQuil, Dimetapp, Vicks, Coricidin, Delsym, and others, including generic labels. Dextromethorphan has also found other uses in medicine, ranging...
. However, honey should not be given to a child younger than one year old because of the risk of infant botulism. The benefits versus risk of nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation or nasal lavage or nose douche is the personal hygiene practice in which the nasal cavity is washed to flush out excess mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses. The practice is well-tolerated and beneficial with only minor side effects...
are currently unclear and therefore it is not recommended.
Zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
may inhibit rhinovirus replication and reduce inflammation. Trials have found that zinc supplements can somewhat reduce the severity and duration of common cold symptoms when taken by otherwise healthy adults within 24 hours of onset of symptoms.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
's effect on the common cold has been extensively researched. It has not been shown effective in prevention or treatment of the common cold, except in limited circumstances (specifically, individuals exercising vigorously in cold environments). Routine vitamin C supplementation does not reduce the incidence or severity of the common cold in the general population, though it may reduce the duration of illness.
Evidence about the usefulness of echinacea
Echinacea
Echinacea is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the daisy family, Asteraceae. The nine species it contains are commonly called purple coneflowers. They are endemic to eastern and central North America, where they are found growing in moist to dry prairies and open wooded areas. They have...
supplements, a popular herbal remedy, is contradictory. Well-conducted research studies tend to have negative results at a much higher rate than poorly conducted studies. Different types of echinacea supplements may vary in their effectiveness. Generally, those studies that show supportive results indicate that echinacea might reduce the likelihood of developing cold symptoms upon inoculation with a virus by about half.
Epidemiology
Upper respiratory tract infections are the most common infectious diseases among adults, who have two to four respiratory infections annually. Children may have six to ten colds a year (and up to 12 colds a year for school children). In the United States, the incidence of colds is higher in the fall (autumn) and winter, with most infections occurring between September and April. The seasonality may be due to the start of the school year, or due to people spending more time indoors (thus in closer proximity with each other) increasing the chance of transmission of the virus.History

James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
continually suffered from nasal colds, which were then thought to be caused by polypi
Polyp (medicine)
A polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated. If no stalk is present, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, sinus, urinary bladder...
, sinus
Sinus (anatomy)
Sinus is Latin for "bay", "pocket", "curve", or "bosom". In anatomy, the term is used in various contexts.A sinus is a sack or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue...
trouble, or autotoxaemia.
In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin
Dr. Benjamin Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat...
considered the causes and prevention of the common cold. After several years of research he concluded: "People often catch cold from one another when shut up together in small close rooms, coaches, etc. and when sitting near and conversing so as to breathe in each other's transpiration." Although viruses had not yet been discovered, Franklin hypothesized that the common cold was passed between people through the air. He recommended exercise, bathing, and moderation in food and drink consumption to avoid the common cold. Franklin's theory on the transmission of the cold was confirmed some 150 years later.
Common Cold Unit
In the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, the Common Cold Unit
Common Cold Unit
In Britain, the Common Cold Unit , also known as the Common Cold Research Unit , was set up by the civilian Medical Research Council in 1946 on the site of a former military hospital, the Harvard Hospital, at Harnham Down near Salisbury in Wiltshire...
was set up by the Medical Research Council
Medical Research Council (UK)
The Medical Research Council is a publicly-funded agency responsible for co-ordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is one of seven Research Councils in the UK and is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills...
in 1946. The unit worked with volunteers who were infected with various viruses. The rhinovirus
Rhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
was discovered there. In the late 1950s, researchers were able to grow one of these cold viruses in a tissue culture
Tissue culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissues or cells separate from the organism. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar...
, as it would not grow in fertilized chicken eggs, the method used for many other viruses. In the 1970s, the CCU demonstrated that treatment with interferon
Interferon
Interferons are proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens—such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites—or tumor cells. They allow communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that eradicate pathogens or tumors.IFNs belong to...
during the incubation phase of rhinovirus infection protects somewhat against the disease, but no practical treatment could be developed. The unit was closed in 1989, two years after it completed research of zinc gluconate lozenges in the prophylaxis and treatment of rhinovirus colds, the only successful treatment in the history of the unit.
Economics

More than one-third of patients who saw a doctor received an antibiotic prescription, which has implications for antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
from overuse of such drugs.
An estimated 22 to 189 million school days are missed annually due to a cold. As a result, parents missed 126 million workdays to stay home to care for their children. When added to the 150 million workdays missed by employees suffering from a cold, the total economic impact of cold-related work loss exceeds $20 billion per year. This accounts for 40% of time lost from work.
Legal
Canada in 2009 restricted the use of over-the-counter cough and cold medication in children 6 years and under due to concerns regarding risks and unproven benefits.Cold weather
The traditional folk theory is that a cold can be "caught" by prolonged exposure to coldCold
Cold describes the condition of low temperature.Cold may also refer to:*Common cold, a contagious viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease...
weather such as rain or winter conditions, which is where the disease got its name. Common colds are seasonal in temperate latitudes, with more occurring during winter. The experimental evidence for this effect is uneven: many experiments have failed to produce evidence that short-term exposure to cold weather or direct chilling increases susceptibility to infection, implying that the seasonal variation is instead due to a change in behaviors such as increased time spent indoors at close proximity to others. However, other experiments do find such an effect for both body chilling and cold air exposure, and a number of mechanisms by which lower temperatures could compromise the immune system have been suggested, while other experiments have shown that exposure to cold temperatures may instead stimulate the immune system.
Research
Biota HoldingsBiota Holdings
Biota is an Australian antiviral drug development company listed on the Australian Stock Exchange .In 1989 Biota discovered the drug Zanamivir, which acts as a neuraminidase inhibitor for the treatment and prevention of influenza. This drug is licensed to GlaxoSmithKline and marketed as Relenza....
are developing a drug, currently known as BTA798, which targets rhinovirus
Rhinovirus
Human rhinoviruses are the most common viral infective agents in humans and are the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures between 33–35 °C , and this may be why it occurs primarily in the nose...
. In 2009, the drug has completed Phase IIA clinical trials.
ViroPharma
ViroPharma
ViroPharma Incorporated, a pharmaceutical company, develops and sells drugs that address serious diseases treated by physician specialists and in hospital settings...
and Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough Corporation was a United States-based pharmaceutical company. It was founded in 1851 by Ernst Christian Friedrich Schering as Schering AG in Germany. In 1971, the Schering Corporation merged with Plough to form Schering-Plough. On November 4, 2009 Merck & Co...
are developing an antiviral drug, pleconaril, that targets picornaviruses, the viruses that cause the majority of common colds. Pleconaril has been shown to be effective in an oral
Route of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.-Classification:Routes of administration are usually classified by application location...
form.
Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough Corporation was a United States-based pharmaceutical company. It was founded in 1851 by Ernst Christian Friedrich Schering as Schering AG in Germany. In 1971, the Schering Corporation merged with Plough to form Schering-Plough. On November 4, 2009 Merck & Co...
is developing an intra-nasal
Route of administration
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.-Classification:Routes of administration are usually classified by application location...
formulation that may have fewer adverse effects.
Researchers from University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park is a top-ranked public research university located in the city of College Park in Prince George's County, Maryland, just outside Washington, D.C...
and University of Wisconsin–Madison
University of Wisconsin–Madison
The University of Wisconsin–Madison is a public research university located in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1848, UW–Madison is the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. It became a land-grant institution in 1866...
have mapped the genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
for all known virus strains that cause the common cold.
Naturally produced antibodies can accompany virus particles into cells. This has raised hopes of a drug that could boost this process, thus providing a medication that could combat not only the common cold, but other infections caused by similar viruses.
External links
- Cold and flu symptom checker (NHS Direct - UK Only)
- Summer Cold (Common Cold Centre, Cardiff University)

