
Initial mass function
Encyclopedia
The initial mass function (IMF) is an empirical
function that describes the mass distribution
(the histogram of stellar masses) of a population of stars in terms of their theoretical initial mass (the mass they were formed with). The properties and evolution of a star are closely related to its mass, so the IMF is an important diagnostic tool for astronomers studying large quantities of stars. The IMF is relatively invariant from one group of stars to another.
s, where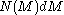 (sometimes also represented as
(sometimes also represented as 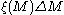 ), the number of stars with masses in the range
), the number of stars with masses in the range  to
to 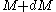 within a specified volume of space, is proportional to
within a specified volume of space, is proportional to 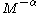 , where
, where  is a dimensionless exponent. The IMF can be
is a dimensionless exponent. The IMF can be
inferred from the present day stellar luminosity function
by using the stellar mass-luminosity relation together with a model of how the star formation rate varies with time.
The IMF of stars more massive than our sun was first quantified by Edwin Salpeter in 1955. His work favoured an exponent of . This form of the
. This form of the
IMF is called the Salpeter function or a Salpeter IMF. It shows that the number of stars in each mass range decreases rapidly with increasing mass. The Salpeter Initial Mass Function is
Later authors extended the work below one solar mass. Glenn E. Miller and John M. Scalo suggested that the IMF "flattened" (approached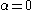 ) below one solar mass. Pavel Kroupa
) below one solar mass. Pavel Kroupa
kept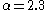 above half a solar mass, but introduced
above half a solar mass, but introduced 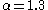 between 0.08-0.5 solar masses and
between 0.08-0.5 solar masses and 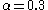 below 0.08 solar masses.
below 0.08 solar masses.
Commonly used forms of the IMF are the Kroupa 2001 broken power law and the Chabrier 2003 lognormal.
Chabrier 2003 for individual stars:

Chabrier 2003 for stellar systems:
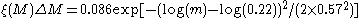
Kroupa 2001:
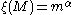
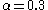 for
for 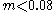 ,
,
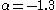 for
for 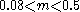 ,
,
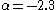 for
for 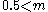
There are large uncertainties concerning the substellar region
.
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
function that describes the mass distribution
Mass distribution
Mass distribution is a term used in physics and mechanics and describes the spatial distribution of mass within a solid body. In principle, it is relevant also for gases or liquids, but on earth their mass distribution is almost homogeneous.-Astronomy:...
(the histogram of stellar masses) of a population of stars in terms of their theoretical initial mass (the mass they were formed with). The properties and evolution of a star are closely related to its mass, so the IMF is an important diagnostic tool for astronomers studying large quantities of stars. The IMF is relatively invariant from one group of stars to another.
Form of the IMF
The IMF is often stated in terms of a series of power lawPower law
A power law is a special kind of mathematical relationship between two quantities. When the frequency of an event varies as a power of some attribute of that event , the frequency is said to follow a power law. For instance, the number of cities having a certain population size is found to vary...
s, where
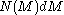 (sometimes also represented as
(sometimes also represented as 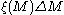 ), the number of stars with masses in the range
), the number of stars with masses in the range  to
to 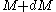 within a specified volume of space, is proportional to
within a specified volume of space, is proportional to 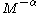 , where
, where  is a dimensionless exponent. The IMF can be
is a dimensionless exponent. The IMF can beinferred from the present day stellar luminosity function
Luminosity function (astronomy)
In astronomy, the luminosity function gives the number of stars or galaxies per luminosity interval. Luminosity functions are used to study the properties of large groups or classes of objects, such as the stars in clusters or the galaxies in the Local Group....
by using the stellar mass-luminosity relation together with a model of how the star formation rate varies with time.
The IMF of stars more massive than our sun was first quantified by Edwin Salpeter in 1955. His work favoured an exponent of
 . This form of the
. This form of theIMF is called the Salpeter function or a Salpeter IMF. It shows that the number of stars in each mass range decreases rapidly with increasing mass. The Salpeter Initial Mass Function is

Later authors extended the work below one solar mass. Glenn E. Miller and John M. Scalo suggested that the IMF "flattened" (approached
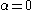 ) below one solar mass. Pavel Kroupa
) below one solar mass. Pavel KroupaPavel Kroupa
Pavel Kroupa is an Australian astrophysicist and professor at the University of Bonn.- Biography and career:...
kept
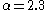 above half a solar mass, but introduced
above half a solar mass, but introduced 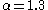 between 0.08-0.5 solar masses and
between 0.08-0.5 solar masses and 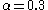 below 0.08 solar masses.
below 0.08 solar masses.Commonly used forms of the IMF are the Kroupa 2001 broken power law and the Chabrier 2003 lognormal.
Chabrier 2003 for individual stars:

Chabrier 2003 for stellar systems:
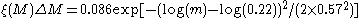
Kroupa 2001:
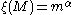
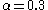 for
for 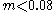 ,
,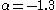 for
for 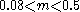 ,
,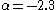 for
for 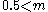
There are large uncertainties concerning the substellar region
Brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are sub-stellar objects which are too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, which is characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs have fully convective surfaces and interiors, with no chemical differentiation by depth...
.

