
Luminosity function (astronomy)
Encyclopedia
In astronomy
, the luminosity function gives the number of stars
or galaxies
per luminosity
interval. Luminosity functions are used to study the properties of large groups or classes of objects, such as the star
s in cluster
s or the galaxies
in the Local Group
.
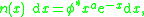
where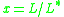 , and
, and  is a characteristic galaxy luminosity where the power-law form of the function cuts off. The parameter
is a characteristic galaxy luminosity where the power-law form of the function cuts off. The parameter 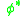 has units of number density and provides the normalization. The galaxy luminosity function may have different parameters for different populations and environments; it is not a universal function. One measurement from field galaxies is
has units of number density and provides the normalization. The galaxy luminosity function may have different parameters for different populations and environments; it is not a universal function. One measurement from field galaxies is  .
.
stars with a given luminosity. As this is determined by the rates at which these stars form and cool, it is of interest for the information it gives about the physics
of white dwarf cooling and the age and history of the Galaxy
.
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, the luminosity function gives the number of stars
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
or galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
per luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
interval. Luminosity functions are used to study the properties of large groups or classes of objects, such as the star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s in cluster
Star cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
s or the galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
in the Local Group
Local Group
The Local Group is the group of galaxies that includes Earth's galaxy, the Milky Way. The group comprises more than 30 galaxies , with its gravitational center located somewhere between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy...
.
Schechter luminosity function
The Schechter luminosity function gives the space density of galaxies within a luminosity bin. The form of the function is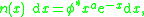
where
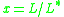 , and
, and  is a characteristic galaxy luminosity where the power-law form of the function cuts off. The parameter
is a characteristic galaxy luminosity where the power-law form of the function cuts off. The parameter 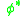 has units of number density and provides the normalization. The galaxy luminosity function may have different parameters for different populations and environments; it is not a universal function. One measurement from field galaxies is
has units of number density and provides the normalization. The galaxy luminosity function may have different parameters for different populations and environments; it is not a universal function. One measurement from field galaxies is 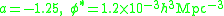 .
.White dwarf luminosity function
The white dwarf luminosity function (WDLF) gives the number of white dwarfWhite dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
stars with a given luminosity. As this is determined by the rates at which these stars form and cool, it is of interest for the information it gives about the physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
of white dwarf cooling and the age and history of the Galaxy
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
.

