
Inter frame
Encyclopedia
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of Inter frame prediction. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage from temporal redundancy between neighboring frames allowing to achieve higher compression rates.
. This process is done by a block matching algorithm
. If the encoder succeeds on its search, the block could be encoded by a vector, known as motion vector
, which points to the position of the matching block at the reference frame. The process of motion vector determination is called motion estimation
.
In most cases the encoder will succeed, but the block found is likely not an exact match to the block it is encoding. This is why the encoder will compute the differences between them. Those residual values are known as the prediction error and need to be transformed and sent to the decoder.
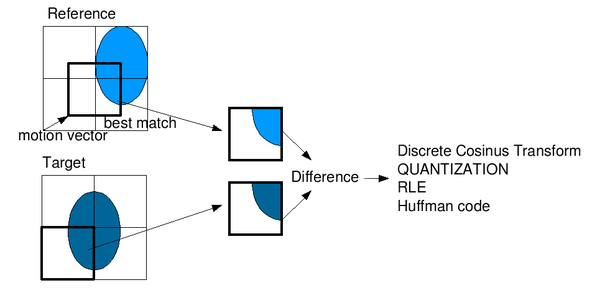
To sum up, if the encoder succeeds to find a matching block on a reference frame, it will obtain a motion vector pointing to the matched block and a prediction error. Using both elements, the decoder will be able to recover the raw pixels of the block. The following image shows the whole process graphically:
 This kind of prediction has some pros and cons:
This kind of prediction has some pros and cons:
These drawbacks stress out the need of a reliable and time periodic reference frame for this technique to be efficient and useful. That reference frame is known as I-frame, which is strictly intra coded -every block is coded using raw pixel values-, so it can always be decoded without additional information.
In most designs, there are two types of inter frames: P-frames and B-frames. These two kinds of frames and the I-frames (Intra-coded pictures) usually join in a GOP
(Group Of Pictures). The I-frame doesn't need additional information to be decoded and it can be used as a reliable reference. This structure also allows to achieve an I-frame periodicity, needed for decoder synchronization.
The amount of data needed for doing this prediction consist of motion vectors and transform coefficients describing prediction correction. It involves the use of motion compensation
.
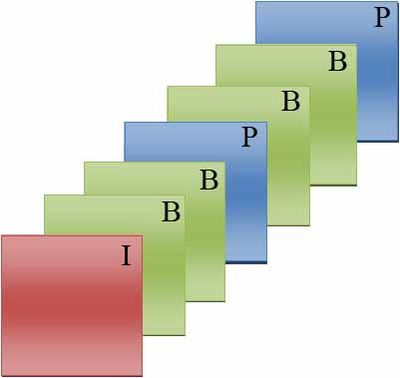 This structure suggests a problem because the fourth frame (a P-frame) is needed in order to predict the second and the third (B-frames). So we need to transmit the P-frame before the B-frames and it will delay the transmission (it will be necessary to keep the P-frame).
This structure suggests a problem because the fourth frame (a P-frame) is needed in order to predict the second and the third (B-frames). So we need to transmit the P-frame before the B-frames and it will delay the transmission (it will be necessary to keep the P-frame).
This structure has strong points:
But it has weak points:
), 16 x 8, 8 x 16, 8 x 8. Last case allows divide the block in new blocks of 4 x 8, 8 x 4, 4 x 4.
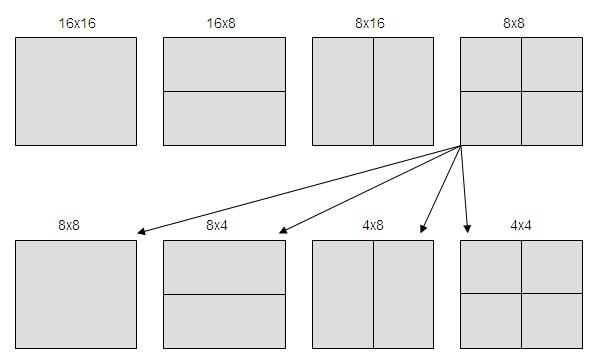
The frame to be coded is divided in block of equal size as some blocks shown in the picture above. Each block prediction will be blocks of same size as reference pictures, by a small displacement.
H=[1 -5 20 20 -5 1]
For example:
b=A - 5B + 20C + 20D - 5E + F
Pixels at quarter-pixel position are obtained by bilinear interpolation.
While MPEG-2
allowed a ½ pixel resolution, Inter frame allows up to ½ pixel resolution. That means that it is possible to search a block in the frame to be coded in other reference frames, or we can interpolate nonexistent pixels to find blocks that are even better suited to the current block. If motion vector is an integer number of units of samples, that means it is possible to find in reference pictures the compensated block in motion. If motion vector is not an integer, the prediction will be obtained from interpolated pixels by an interpolator filter to horizontal and vertical directions.

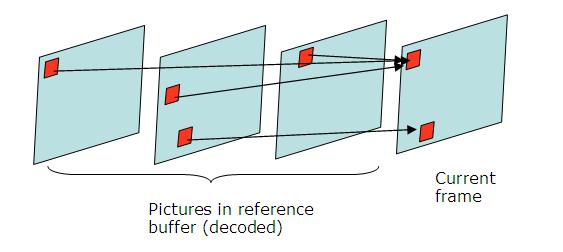
There are two ways to deduce the motion:
It uses the block motion vector from List 1 frame, located at the same position to deduce the motion vector. List 1 block uses a List 0 block as reference.

It predicts the movement from neighbour macroblocks in same frame. A possible criterion could be to copy the motion vector from a neighboring block. These modes are used in uniform zones of the picture where there is not much movement.
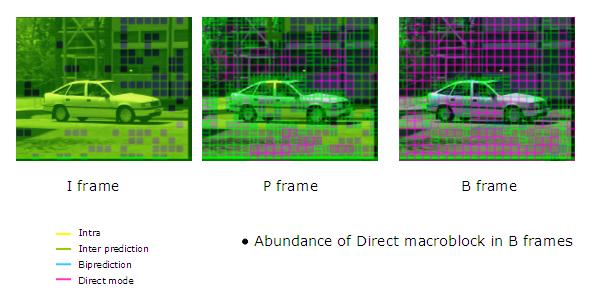
In the figure above, pink blocks are Direct/Skip Mode coded blocks. As we can see, they are used very frequently, mainly in B-frames.
s for video coding by MPEG and VCEG
) a more general concept is applied by using the word "picture" rather than "frame", where a picture can either be a complete frame or a single interlaced field.
Video
codecs such as MPEG-2
, H.264 or Ogg
Theora
reduce the amount of data in a stream by following key frames with one or more inter frames. These frames can typically be encoded using a lower bit rate
than is needed for key frames because much of the image is ordinarily similar, so only the changing parts need to be coded.
Inter frame prediction
An inter coded frame is divided into blocks known as macroblocks. After that, instead of directly encoding the raw pixel values for each block, the encoder will try to find a block similar to the one it is encoding on a previously encoded frame, referred to as a reference frameReference frame (video)
Reference frames are frames of a compressed video that are used to define future frames. As such, they are only used in inter-frame compression techniques. In older video encoding standards, such as MPEG-2, only one reference frame – the previous frame – was used for P-frames...
. This process is done by a block matching algorithm
Block-matching algorithm
A Block Matching Algorithm is a way of locating matching blocks in a sequence of digital video frames for the purposes of motion estimation....
. If the encoder succeeds on its search, the block could be encoded by a vector, known as motion vector
Motion vector
In video compression, a motion vector is the key element in the motion estimation process. It is used to represent a macroblock in a picture based on the position of this macroblock in another picture, called the reference picture....
, which points to the position of the matching block at the reference frame. The process of motion vector determination is called motion estimation
Motion estimation
Motion estimation is the process of determining motion vectors that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion is in three dimensions but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D...
.
In most cases the encoder will succeed, but the block found is likely not an exact match to the block it is encoding. This is why the encoder will compute the differences between them. Those residual values are known as the prediction error and need to be transformed and sent to the decoder.
To sum up, if the encoder succeeds to find a matching block on a reference frame, it will obtain a motion vector pointing to the matched block and a prediction error. Using both elements, the decoder will be able to recover the raw pixels of the block. The following image shows the whole process graphically:

- If everything goes fine, the algorithm will be able to find a matching block with little prediction error so that, once transformed, the overall size of motion vector plus prediction error is lower than the size of a raw encoding.
- If the block matching algorithm fails to find a suitable match the prediction error will be considerable. Thus the overall size of motion vector plus prediction error will be greater than the raw encoding. In this case the encoder would make an exception and send a raw encoding for that specific block.
- If the matched block at the reference frame has also been encoded using Inter frame prediction, the errors made for its encoding will be propagated to the next block. If every frame was encoded using this technique, there would be no way for a decoder to synchronize to a video stream because it would be impossible to obtain the reference images.
These drawbacks stress out the need of a reliable and time periodic reference frame for this technique to be efficient and useful. That reference frame is known as I-frame, which is strictly intra coded -every block is coded using raw pixel values-, so it can always be decoded without additional information.
In most designs, there are two types of inter frames: P-frames and B-frames. These two kinds of frames and the I-frames (Intra-coded pictures) usually join in a GOP
Group of pictures
In Video coding, a group of pictures, or GOP structure, specifies the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. The GOP is a group of successive pictures within a coded video stream. Each coded video stream consists of successive GOPs...
(Group Of Pictures). The I-frame doesn't need additional information to be decoded and it can be used as a reliable reference. This structure also allows to achieve an I-frame periodicity, needed for decoder synchronization.
Frame types
The difference between P-frames and B-frames is the reference frame they are allowed to use.P-frame
P-frame is the name to define the forward Predicted pictures. The prediction is made from an earlier picture, mainly an I-frame, so that require less coding data (≈50% when compared to I-frame size).The amount of data needed for doing this prediction consist of motion vectors and transform coefficients describing prediction correction. It involves the use of motion compensation
Motion compensation
Motion compensation is an algorithmic technique employed in the encoding of video data for video compression, for example in the generation of MPEG-2 files. Motion compensation describes a picture in terms of the transformation of a reference picture to the current picture. The reference picture...
.
B-frame
B-frame is the term for bidirectionally predicted pictures. This kind of prediction method occupies less coding data than P-frames (≈25% when compared to I-frame size) because they can be predicted or interpolated from an earlier and/or later frame. Similar to P-frames, B-frames are expressed as motion vectors and transform coefficients. In order to avoid a growing propagation error, B-frames are not used as a reference to make further predictions in most encoding standards. However, in newer encoding methods (such as AVC), B-frames may used as reference.Typical Group Of Pictures (GOP) structure
The typical Group Of Pictures (GOP) structure is IBBPBBP... The I-frame is used to predict the first P-frame and these two frames are also used to predict the first and the second B-frame. The second P-frame is predicted using the first P-frame and they join to predict the third and fourth B-frames. The scheme is shown in the next picture:
This structure has strong points:
- It minimizes the problem of possible uncovered areas.
- P-frames and B-frames need less data than I-frames, so less data is transmitted.
But it has weak points:
- It increases the complexity of the decoder, which can mean more memory is needed to rearrange the frames.
- The interpolated frames (namely B-frames) require more motion vectors which means an increased bit rate.
H.264 Inter frame prediction improvements
The most important improvements of this technique in regard to previous H.264 standard are:- More flexible block partition
- Resolution of up to ¼ pixel motion compensation
- Multiple references
- Enhanced Direct/Skip Macroblock
More flexible block partition
Luminance block partition of 16 x 16(MPEG-2MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
), 16 x 8, 8 x 16, 8 x 8. Last case allows divide the block in new blocks of 4 x 8, 8 x 4, 4 x 4.

The frame to be coded is divided in block of equal size as some blocks shown in the picture above. Each block prediction will be blocks of same size as reference pictures, by a small displacement.
Resolution of up to ¼ pixel motion compensation
Pixels at half-pixel position are obtained by applying a filter of length 6.H=[1 -5 20 20 -5 1]
For example:
b=A - 5B + 20C + 20D - 5E + F
Pixels at quarter-pixel position are obtained by bilinear interpolation.
While MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
allowed a ½ pixel resolution, Inter frame allows up to ½ pixel resolution. That means that it is possible to search a block in the frame to be coded in other reference frames, or we can interpolate nonexistent pixels to find blocks that are even better suited to the current block. If motion vector is an integer number of units of samples, that means it is possible to find in reference pictures the compensated block in motion. If motion vector is not an integer, the prediction will be obtained from interpolated pixels by an interpolator filter to horizontal and vertical directions.

Multiple references
Multiple references to motion estimation allows finding the best reference in 2 possible buffers (List 0 to past pictures, List 1 to future pictures) which contain up to 16 frames each. Block prediction is done by a weighted sum of blocks from the reference picture. It allows enhanced picture quality in scenes where there are changes of plane, zoom, or when new objects are revealed.
Enhanced Direct/Skip Macroblock
Skip and Direct Mode are very frequently used, especially with B-frames. They significantly reduce the number of bits to be coded. These modes are referred to when a block is coded without sending residual error or motion vectors. The encoder will only record that it is a Skip Macroblock. The decoder will deduce the motion vector of Direct/Skip Mode coded block from other blocks already decoded.There are two ways to deduce the motion:
- TEMPORAL:
It uses the block motion vector from List 1 frame, located at the same position to deduce the motion vector. List 1 block uses a List 0 block as reference.

- SPATIAL:
It predicts the movement from neighbour macroblocks in same frame. A possible criterion could be to copy the motion vector from a neighboring block. These modes are used in uniform zones of the picture where there is not much movement.

In the figure above, pink blocks are Direct/Skip Mode coded blocks. As we can see, they are used very frequently, mainly in B-frames.
Additional information
Although the use of the term "frame" is common in informal usage, in many cases (such as in international standardInternational standard
International standards are standards developed by international standards organizations. International standards are available for consideration and use, worldwide...
s for video coding by MPEG and VCEG
VCEG
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group is the informal name of Question 6 of Working Party 3 of Study Group 16 of the ITU-T. Its abbreviated title is ITU-T Q.6/SG 16...
) a more general concept is applied by using the word "picture" rather than "frame", where a picture can either be a complete frame or a single interlaced field.
Video
Video
Video is the technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing, transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes in motion.- History :...
codecs such as MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
, H.264 or Ogg
Ogg
Ogg is a free, open container format maintained by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The creators of the Ogg format state that it is unrestricted by software patents and is designed to provide for efficient streaming and manipulation of high quality digital multimedia.The Ogg container format can multiplex...
Theora
Theora
Theora is a free lossy video compression format. It is developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and distributed without licensing fees alongside their other free and open media projects, including the Vorbis audio format and the Ogg container....
reduce the amount of data in a stream by following key frames with one or more inter frames. These frames can typically be encoded using a lower bit rate
Bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
than is needed for key frames because much of the image is ordinarily similar, so only the changing parts need to be coded.

