
MPEG-2
Encyclopedia
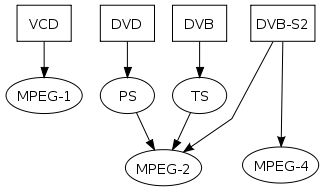
Main characteristics
MPEG-2 is widely used as the format of digital televisionDigital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
signals that are broadcast by terrestrial
Terrestrial television
Terrestrial television is a mode of television broadcasting which does not involve satellite transmission or cables — typically using radio waves through transmitting and receiving antennas or television antenna aerials...
(over-the-air), cable
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
, and direct broadcast satellite
Direct broadcast satellite
Direct broadcast satellite is a term used to refer to satellite television broadcasts intended for home reception.A designation broader than DBS would be direct-to-home signals, or DTH. This has initially distinguished the transmissions directly intended for home viewers from cable television...
TV
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
systems. It also specifies the format of movies and other programs that are distributed on DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
and similar discs. As such, TV stations, TV receivers, DVD players, and other equipment are often designed to this standard. MPEG-2 was the second of several standards developed by the Moving Pictures Expert Group (MPEG) and is an international standard (ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
/IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
13818). Parts 1 and 2 of MPEG-2 were developed in a joint collaborative team with ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
, and they have a respective catalog number in the ITU-T Recommendation Series.
While MPEG-2 is the core of most digital television and DVD formats, it does not completely specify them. Regional institutions can adapt it to their needs by restricting and augmenting aspects of the standard. See Video profiles and levels.
Systems
MPEG-2 includes a Systems section, part 1, that defines two distinct, but related, container formats. One is the MPEG transport stream, designed to carry digital video and audio over possibly lossy media, where the beginning and the end of the stream may not be identified, such as broadcasting or magnetic tape, examples of which include ATSC, DVB, SBTVDSBTVD
ISDB-T International or SBTVD, short for Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital is a technical standard for digital television broadcast used in Brazil, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Venezuela, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Philippines, Bolivia, Nicaragua and Uruguay, based on the Japanese ISDB-T...
and HDV
HDV
HDV is a format for recording of high-definition video on DV cassette tape. The format was originally developed by JVC and supported by Sony, Canon and Sharp...
. MPEG-2 Systems also defines the MPEG program stream, a container format designed for file-based media such as hard disk drives, optical disc
Optical disc
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc is a flat, usually circular disc which encodes binary data in the form of pits and lands on a special material on one of its flat surfaces...
s and flash memory
Flash memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and must be erased in fairly large blocks before these can be rewritten with new data...
.
MPEG-2 Systems is formally known as ISO/IEC 13818-1 and as ITU-T Rec. H.222.0. ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
authorized the "SMPTE Registration Authority, LLC" as the registration authority for MPEG-2 format identifiers. The registration descriptor of MPEG-2 transport is provided by ISO 13818-1 in order to enable users of the standard to unambiguously carry data when its format is not necessarily a recognized international standard. This provision will permit the MPEG-2 transport standard to carry all types of data while providing for a method of unambiguous identification of the characteristics of the underlying private data.
Video
The Video section, part 2 of MPEG-2, is similar to the previous MPEG-1MPEG-1
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become...
standard, but also provides support for interlaced video, the format used by analog broadcast TV systems. MPEG-2 video is not optimized for low bit-rates, especially less than 1 Mbit/s at standard definition resolutions. All standards-compliant MPEG-2 Video decoders are fully capable of playing back MPEG-1 Video streams conforming to the Constrained Parameters Bitstream syntax. MPEG-2/Video is formally known as ISO/IEC 13818-2 and as ITU-T Rec. H.262
H.262
H.262 or MPEG-2 Part 2 is a digital video compression and encoding standard developed and maintained jointly by ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group and ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group . It is the second part of the ISO/IEC MPEG-2 standard...
.
With some enhancements, MPEG-2 Video and Systems are also used in some HDTV
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
transmission systems.
MPEG-2 Part 3
The MPEG-2 Audio section, defined in Part 3 (ISO/IEC 13818-3) of the standard, enhances MPEG-1
MPEG-1
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become...
's audio by allowing the coding of audio programs with more than two channel
Surround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
s, up to 5.1 multichannel. This method is backwards-compatible (also known as MPEG-2 BC), allowing MPEG-1 audio decoders to decode the two main stereo components of the presentation. MPEG-2 part 3 also defined additional bit rates and sample rates for MPEG-1 Audio Layer I
MPEG-1 Audio Layer I
MPEG-1 Audio Layer I, commonly abbreviated to MP1, is one of three audio formats included in the MPEG-1 standard. While supported by most media players, the codec is considered largely outdated, and replaced by MP2 or MP3....
, II
MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
MPEG-1 Audio Layer II or MPEG-2 Audio Layer II is a lossy audio compression format defined by ISO/IEC 11172-3 alongside MPEG-1 Audio Layer I and MPEG-1 Audio Layer III...
and III.
MPEG-2 BC (backward compatible with MPEG-1 audio formats)
- low bitrate encoding with halved sampling rate (MPEG-1 Layer 1/2/3 LSF - a.k.a. MPEG-2 LSF - "Low Sampling Frequencies")
- multichannel encoding with up to 5.1 channels, a.k.a. MPEG MultichannelMPEG MultichannelMPEG Multichannel is an extension to the MPEG-1 Layer II audio compression specification, as defined in the MPEG-2 Audio standard , which allows it provide up to 5.1-channels of audio...
MPEG-2 Part 7
Part 7 (ISO/IEC 13818-7) of the MPEG-2 standard specifies a rather different, non-backwards-compatible audio format (also known as MPEG-2 NBC). Part 7 is referred to as MPEG-2 AAC
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
. AAC
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
is more efficient than the previous MPEG audio standards, and is in some ways less complicated than its predecessor, MPEG-1 Audio, Layer 3, in that it does not have the hybrid filter bank. It supports from 1 to 48 channels at sampling rates of 8 to 96 kHz, with multichannel, multilingual, and multiprogram capabilities. Advanced Audio is also defined in Part 3 of the MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
standard.
MPEG-2 NBC (Non-Backward Compatible)
- MPEG-2 AACAdvanced Audio CodingAdvanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
- multichannel encoding with up to 48 channels
ISO/IEC 13818
MPEG-2 standards were published as parts of ISO/IEC 13818. Each part covers a certain aspect of the whole specification.Part 1: Systems – describes synchronization and multiplexing of video and audio. (It is also known as ITU-T Rec. H.222.0.) See MPEG transport stream and MPEG program stream.
Part 2: Video – compression codec for interlaced and non-interlaced video signals (Also known as ITU-T Rec. H.262
H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2
H.262 or MPEG-2 Part 2 is a digital video compression and encoding standard developed and maintained jointly by ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group and ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group . It is the second part of the ISO/IEC MPEG-2 standard...
).
Part 3: Audio – compression codec for perceptual coding of audio signals. A multichannel-enabled extension and extension of bit rates and sample rates for MPEG-1 Audio Layer I, II and III of MPEG-1 audio.
Part 4: Describes procedures for testing compliance.
Part 5: Describes systems for Software simulation.
Part 6: Describes extensions for DSM-CC (Digital Storage Media Command and Control).
Part 7: Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
(AAC).
Part 9: Extension for real time interfaces.
Part 10: Conformance extensions for DSM-CC.
Part 11: Intellectual property management (IPMP)
(Part 8: 10-bit video extension. Primary application was studio video. Part 8 has been withdrawn due to lack of interest by industry.)
| Part | Number | First public release date (First edition) | Latest public release date (edition) | Latest amend- ment | Identical ITU-T Rec. | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | ISO/IEC 13818-1 | 1996 | 2007 | 2009 (2011 or 2012) | H.222.0 | Systems | |
| Part 2 | ISO/IEC 13818-2 | 1996 | 2000 | 2010(2011) | H.262 | Video | |
| Part 3 | ISO/IEC 13818-3 | 1995 | 1998 | Audio | MPEG-2 BC - backwards compatible with MPEG-1 Audio | ||
| Part 4 | ISO/IEC 13818-4 | 1998 | 2004 | 2009 | Conformance testing | ||
| Part 5 | ISO/IEC TR 13818-5 | 1997 | 2005 | Software simulation | |||
| Part 6 | ISO/IEC 13818-6 | 1998 | 1998 | 2001 | Extensions for DSM-CC | extensions for Digital Storage Media Command and Control | |
| Part 7 | ISO/IEC 13818-7 | 1997 | 2006 | 2007 | Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) | MPEG-2 NBC Audio - Non-Backwards Compatible with MPEG-1 Audio | |
| Part 8 | dropped | 10-Bit Video | The work was terminated because of low industry's interest. It was started in recognition of the need to support studio-quality video signals quantized with 10 bits per component. | ||||
| Part 9 | ISO/IEC 13818-9 | 1996 | 1996 | Extension for real time interface for systems decoders | |||
| Part 10 | ISO/IEC 13818-10 | 1999 | 1999 | Conformance extensions for Digital Storage Media Command and Control (DSM-CC) | |||
| Part 11 | ISO/IEC 13818-11 | 2004 | 2004 | IPMP on MPEG-2 systems | Intellectual Property Management and Protection on the MPEG-2 system (XML IPMP messages are also defined in ISO/IEC 23001-3) |
History
MPEG-2 evolved out of the shortcomings of MPEG-1.MPEG-1's known weaknesses:
- an audio compression system limited to two channels (stereo.)
- no standardized support for interlaced video with poor compression when used for interlaced video
- only one standardized "profile" (Constrained Parameters Bitstream) which was unsuited for higher resolution video. MPEG-1 could support 4k video but there was no easy way to encode video for higher resolutions, and identify hardware capable of supporting it, as the limitations of such hardware were not defined.
- Support for only one color space, 4:2:0.
Filename extensions
.mpg, .mpeg, m2v, .mp2, mp3 are some of a number of filename extensions used for MPEG-1MPEG-1
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become...
or MPEG-2 audio and video file formats.
DVD-Video
The DVD-VideoDVD-Video
DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVD discs, and is currently the dominant consumer video format in Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and a MPEG-2 decoder...
standard uses MPEG-2 video, but imposes some restrictions:
- Allowed Dimensions
- 720 × 480, 704 × 480, 352 × 480, 352 × 240 pixel (NTSC)
- 720 × 576, 704 × 576, 352 × 576, 352 × 288 pixel (PAL)
- Allowed Aspect ratiosAspect ratio (image)The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
(Display AR)- 4:3
- 16:9 (1.85:1 and 2.35:1, among others, are often listed as valid DVD aspect ratios, but are actually a "letterboxed" 16:9 image)
- Allowed Frame rates
- 29.97 frame/s (NTSC)
- 25 frame/s (PAL)
- Note: By using a pattern of REPEAT_FIRST_FIELD flags on the headers of encoded pictures, pictures can be displayed for either two or three fields and almost any picture display rate (minimum ⅔ of the frame rate) can be achieved. This is most often used to display 23.976 (approximately film rate) video on NTSC.
- Audio+video bitrate
- Video peak 9.8 Mbit/s
- Total peak 10.08 Mbit/s
- Minimum 300 kbit/s
- YUV 4:2:0Chroma subsamplingChroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance....
- Additional subtitles possible
- Closed captioning (NTSC only)
- Audio
- Linear Pulse Code ModulationLPCMLinear pulse-code modulation is a method of encoding audio information digitally. The term also refers collectively to formats using this method of encoding...
(LPCM): 48 kHz or 96 kHz; 16- or 24-bit; up to six channels (not all combinations possible due to bitrate constraints) - MPEG Layer 2 (MP2): 48 kHz, up to 5.1 channels (required in PAL players only)
- Dolby DigitalDolby DigitalDolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. It was originally called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994. Except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints...
(DD, also known as AC-3): 48 kHz, 32–448 kbit/s, up to 5.1 channels - Digital Theater Systems (DTS): 754 kbit/s or 1510 kbit/s (not required for DVD player compliance)
- NTSC DVDs must contain at least one LPCM or Dolby Digital audio track.
- PAL DVDs must contain at least one MPEG Layer 2, LPCM, or Dolby Digital audio track.
- Players are not required to play back audio with more than two channels, but must be able to downmixDownmixingDownmixing is a general term used for manipulating audio where a number of distinct audio channels are mixed together to produce a lower number of channels...
multichannel audio to two channels.
- Linear Pulse Code Modulation
- GOP structure (Group Of Pictures)
- Sequence header must be present at the beginning of every GOP
- Maximum frames per GOP: 18 (NTSC) / 15 (PAL), i.e. 0.6 seconds both
- Closed GOP required for multi-angle DVDs
- Audio+video bitrate
HDV
HDV is a format for recording and playback of high-definition MPEG-2 video on a DV cassette tape.MOD and TOD
MOD and TOD are recording formats for use in consumer digital file-based camcorders.DVB
Application-specific restrictions on MPEG-2 video in the DVB standard:Allowed resolutions for SDTV:
- 720, 640, 544, 528, 480 or 352 × 480 pixel, 24/1.001, 24, 30/1.001 or 30 frame/s
- 352 × 240 pixel, 24/1.001, 24, 30/1.001 or 30 frame/s
- 720, 704, 544, 528, 480 or 352 × 576 pixel, 25 frame/s
- 352 × 288 pixel, 25 frame/s
For HDTV:
- 720 x 576 x 50 frame/s progressive (576p50)
- 1280 x 720 x 25 or 50 frame/s progressive (720p50)
- 1440 or 1920 x 1080 x 25 frame/s progressive (1080p25 = film mode)
- 1440 or 1920 x 1080 x 25 frame/s interlace (1080i50)
ATSC
The ATSC A/53 standard used in the United States, uses MPEG-2 video at the Main Profile @ High Level, with additional restrictions such as the maximum bitrate of 19.4 Mbit/s for broadcast television and 38.8 Mbit/s for cable television, 4:2:0 chroma subsamplingChroma subsampling
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance....
format, and mandatory colorimetry information.
ATSC allows the following video resolutions, aspect ratios, and frame/field rates:
- 1920 × 1080 pixel (16:9, square pixels), at 30p, 29.97p, 24p, 23.976p, 60i, 59.94i.
- 1280 × 720 pixel (16:9, square pixels), at 60p, 59.94p, 30p, 29.97p, 24p, or 23.976p
- 704 × 480 pixel (4:3 or 16:9, non-square pixels), at 60p, 59.94p, 30p, 29.97p, 24p, 23.976p, 60i, or 59.94i
- 640 × 480 pixel (4:3, square pixels), at 60p, 59.94p, 30p, 29.97p, 24p, 23.976p, 60i, or 59.94i
ATSC standard A/63 defines additional resolutions and aspect rates for 50 Hz (PAL) signal.
The ATSC specification and MPEG-2 allow the use of progressive frames, even within an interlaced video sequence. For example, a station that transmits 1080i60 video sequence can use a coding method where those 60 fields are coded with 24 progressive frames and metadata instructs the decoder to interlace them and perform 3:2 pulldown before display. This allows broadcasters to switch between 60 Hz interlaced (news, soap operas) and 24 Hz progressive (prime-time) content without ending the MPEG-2 sequence and introducing a several seconds of delay as the TV switches formats. This is the reason why 1080p30 and 1080p24 sequences allowed by the ATSC specification are not used in practice.
The 1080-line formats are encoded with 1920 × 1088 pixel luma matrices and 960 × 540 chroma matrices, but the last 8 lines are discarded by the MPEG-2 decoding and display process.
ATSC A/72 is the newest revision of ATSC standards for digital television which allows the use of H.264/AVC codec and 1080p60 signal.
MPEG-2 audio was a contender for the ATSC standard during the DTV
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
"Grand Alliance
Grand Alliance (HDTV)
The Grand Alliance was a consortium created in 1993 at the behest of the Federal Communications Commission to develop the American digital television and HDTV specification, with the aim of pooling the best work from different companies...
" shootout, but lost out to Dolby AC-3.
ISDB-T
Technical features of MPEG-2 in ATSC are also valid for ISDB-T, except that in the main TS has aggregated a second program for mobile devices compressed in MPEG-4MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
H.264 AVC for video and AAC
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
-LC for audio, mainly known as 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
.
Patent holders
MPEG Licensing Authority, a private patent licensing organization, has acquired rights from over 20 corporations and one university to license a patent poolPatent pool
In patent law, a patent pool is a consortium of at least two companies agreeing to cross-license patents relating to a particular technology. The creation of a patent pool can save patentees and licensees time and money, and, in case of blocking patents, it may also be the only reasonable method...
of approximately 640 worldwide patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s, which it claims are the "essential" to use of MPEG-2 technology, although many of the patents have since expired. Where software patent
Software patent
Software patent does not have a universally accepted definition. One definition suggested by the Foundation for a Free Information Infrastructure is that a software patent is a "patent on any performance of a computer realised by means of a computer program".In 2005, the European Patent Office...
ability is upheld, the use of MPEG-2 requires the payment of licensing fees to the patent holders. Other patents are licensed by Audio MPEG, Inc. The development of the standard itself took less time than the patent negotiations. Patent pooling between essential and peripheral patent holders in the MPEG-2 pool is the subject of a study by the University of Wisconsin.
MPEG-2 patents (U.S. only)
| Patent | Filed | Granted | First File | Expiration | Summary | Notes | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4833543 | 24 dec 1986 | 23 May 1989 | 24 dec 1986 | 24 dec 2006 | Image processing system and phaselocked loop used therein | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4833543 file+20: [2006, 12, 24] grant+17:[2006, 5, 23] | Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent is a global telecommunications corporation, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It provides telecommunications solutions to service providers, enterprises, and governments around the world, enabling these customers to deliver voice, data, and video services... |
| 4970590 | 21 dec 1989 | 13 nov 1990 | 21 dec 1989 | 21 dec 2009 | System and device for package multiplexing in transmission of many data flows generated by a sole algorithm | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4970590 file+20: [2009, 12, 21] grant+17:[2007, 11, 13] | Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent is a global telecommunications corporation, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It provides telecommunications solutions to service providers, enterprises, and governments around the world, enabling these customers to deliver voice, data, and video services... |
| 5453790 | 26 mar 1993 | 26 sep 1995 | 26 mar 1993 | 26 mar 2013 | Video decoder having asynchronous operation with respect to a video display | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5453790 file+20: [2013, 3, 26] grant+17:[2012, 9, 26] | Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent is a global telecommunications corporation, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It provides telecommunications solutions to service providers, enterprises, and governments around the world, enabling these customers to deliver voice, data, and video services... |
| 5291284 | 23 jul 1991 | 01 mar 1994 | 12 dec 1989 | 01 mar 2011 | Predictive coding and decoding with error drift reduction | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5291284 file+20: [2011, 7, 23] pct_file+20:[2009, 12, 12] grant+17:[2011, 3, 1] | British Telecommunications plc |
| 4982270 | 03 feb 1989 | 01 jan 1991 | 03 feb 1989 | 03 feb 2009 | Video data transmitting system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4982270 file+20: [2009, 2, 3] grant+17:[2008, 1, 1] | Canon Inc. Canon Inc. is a Japanese multinational corporation that specialises in the manufacture of imaging and optical products, including cameras, camcorders, photocopiers, steppers and computer printers. Its headquarters are located in Ōta, Tokyo, Japan.-Origins:... |
| 5068724 | 15 jun 1990 | 26 nov 1991 | 15 jun 1990 | 15 jun 2010 | Adaptive motion compensation for digital television | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5068724 file+20: [2010, 6, 15] grant+17:[2008, 11, 26] | CIF LICENSING, LLC |
| 5091782 | 09 apr 1990 | 25 feb 1992 | 09 apr 1990 | 09 apr 2010 | Apparatus and method for adaptively compressing successive blocks of digital video | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5091782 file+20: [2010, 4, 9] grant+17:[2009, 2, 25] | CIF LICENSING, LLC |
| 5093720 | 20 aug 1990 | 03 mar 1992 | 20 aug 1990 | 20 aug 2010 | Motion compensation for interlaced digital television signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5093720 file+20: [2010, 8, 20] grant+17:[2009, 3, 3] | CIF LICENSING, LLC |
| RE35093 | 03 dec 1990 | 09 mar 1993 | 03 dec 1990 | 03 dec 2010 | Systems and methods for coding even fields of interlaced video sequences | Reissue of 05193004 filed 09 dec 1994 granted 21 nov 1995 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE35093 file+20: [2010, 12, 3] related_patent+20:[2010, 12, 32] grant+17:[2010, 3, 9] Case Text: .Iadd.This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/218,970, filed on Mar. 25, 1994, now abandoned, and is a reissue of U.S. Pat. No. 5,193,004. .Iaddend. | Columbia University Columbia University Columbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the... |
| 4796087 | 01 jun 1987 | 03 jan 1989 | 01 jun 1987 | 01 jun 2007 | Process for coding by transformation for the transmission of picture signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4796087 file+20: [2007, 6, 1] grant+17:[2006, 1, 3] | France Télécom France Télécom France Telecom S.A. is the main telecommunications company in France, the third-largest in Europe and one of the largest in the world. It currently employs about 180,000 people and has 192.7 million customers worldwide . In 2010 the group had revenue of €45.5 billion... |
| 5235618 | 06 nov 1990 | 10 aug 1993 | 06 nov 1990 | 06 nov 2010 | Video signal coding apparatus, coding method used in the video signal coding apparatus and video signal coding transmission system having the video signal coding apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5235618 file+20: [2010, 11, 6] grant+17:[2010, 8, 10] | Fujitsu Fujitsu is a Japanese multinational information technology equipment and services company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is the world's third-largest IT services provider measured by revenues.... |
| 4706260 | 07 nov 1986 | 10 nov 1987 | 07 nov 1986 | 07 nov 2006 | DPCM system with rate-of-fill control of buffer occupancy | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4706260 file+20: [2006, 11, 7] grant+17:[2004, 11, 10] | General Electric General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 4813056 | 08 dec 1987 | 14 mar 1989 | 08 dec 1987 | 08 dec 2007 | Modified statistical coding of digital signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4813056 file+20: [2007, 12, 8] grant+17:[2006, 3, 14] | General Electric General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 4394774 | 26 jun 1981 | 19 jul 1983 | 15 dec 1978 | 19 jul 2000 | Digital video compression system and methods utilizing scene adaptive coding with rate buffer feedback | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4394774 file+20: [2001, 6, 26] related_patent+20:[1998, 12, 15] grant+17:[2000, 7, 19] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 969,991, filed Dec. 15, 1978, now U.S. Pat. No. 4,302,775. | General Instrument General Instrument General Instrument was an electronics manufacturer based in Horsham, PA specializing in semiconductors and cable television equipment. The company was active until 1997, when it split into which was later acquired by Vishay Intertechnology in 2001, CommScope and NextLevel Systems General... |
| 4698672 | 27 oct 1986 | 06 oct 1987 | 27 oct 1986 | 27 oct 2006 | Coding system for reducing redundancy | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4698672 file+20: [2006, 10, 27] grant+17:[2004, 10, 6] | General Instrument General Instrument General Instrument was an electronics manufacturer based in Horsham, PA specializing in semiconductors and cable television equipment. The company was active until 1997, when it split into which was later acquired by Vishay Intertechnology in 2001, CommScope and NextLevel Systems General... |
| 5426464 | 18 oct 1994 | 20 jun 1995 | 32 jan 1993 | 32 jan 2013 | Field elimination apparatus for a video compression/decompression system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5426464 file+20: [2014, 10, 18] related_patent+20:[2013, 1, 32] grant+17:[2012, 6, 20] Case Text: This is a divisional application of Ser. No. 08/004,753, filed 14 Jan. 1993 . | GE General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 5486864 | 13 May 1993 | 23 jan 1996 | 13 May 1993 | 13 May 2013 | Differential time code method and apparatus as for a compressed video signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5486864 file+20: [2013, 5, 13] grant+17:[2013, 1, 23] | GE General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 5491516 | 14 jan 1993 | 13 feb 1996 | 14 jan 1993 | 13 feb 2013 | Field elimination apparatus for a video compression/decompression system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5491516 file+20: [2013, 1, 14] grant+17:[2013, 2, 13] | GE General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 5600376 | 20 mar 1995 | 04 feb 1997 | 32 jan 1993 | 04 feb 2014 | Field elimination apparatus for a video compression/decompression system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5600376 file+20: [2015, 3, 20] related_patent+20:[2013, 1, 32] grant+17:[2014, 2, 4] Case Text: This is a divisional application Ser. No. 08/324,558, filed 18 Oct. 1994, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,426,464 which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/004,753 filed 14 Jan. 1993 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,491,516. | GE General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 5796743 | 23 May 1996 | 18 aug 1998 | 30 nov 1993 | 18 aug 2015 | Data word indicator in a system for assembling transport data packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5796743 file+20: [2016, 5, 23] pct_file+20:[2013, 11, 30] grant+17:[2015, 8, 18] | GE General Electric General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States... |
| 5867501 | 07 jun 1995 | 02 feb 1999 | 17 dec 1992 | 02 feb 2016 | Encoding for communicating data and commands | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5867501 file+20: [2015, 6, 7] related_patent+20:[2012, 12, 17] grant+17:[2016, 2, 2] Case Text: This application is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 07/992,944, filed Dec. 17, 1992 now abandoned. The disclosed invention is related to the commonly assigned, co-pending applications Ser. Nos. 08/485,217, 08/482,618, 08/474,772, 08/485,053, 08/473,541, 08/474,770 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,675,579, issued Oct. 7, 1997, 08/472,222 now abandoned in favor of Ser. No. 08/762,653, filed Dec. 9, 1996, 08/481,749 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,675,807, issued Oct. 7, 1997, 08/484,281, 08/482,628 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,574,849, issued Nov. 12, 1996, 08/479,473, 08/485,062, 08/485,446 now abandoned, and 08/485,055 filed concurrently herewith. | Hewlett-Packard Company |
| 4849812 | 24 feb 1988 | 18 jul 1989 | 24 feb 1988 | 24 feb 2008 | Television system in which digitized picture signals subjected to a transform coding are transmitted from an encoding station to a decoding station | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4849812 file+20: [2008, 2, 24] grant+17:[2006, 7, 18] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 4901075 | 11 sep 1987 | 13 feb 1990 | 11 sep 1987 | 11 sep 2007 | Method and apparatus for bit rate reduction | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4901075 file+20: [2007, 9, 11] grant+17:[2007, 2, 13] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5021879 | 24 sep 1990 | 04 jun 1991 | 25 apr 1988 | 04 jun 2008 | System for transmitting video pictures | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5021879 file+20: [2010, 9, 24] related_patent+20:[2008, 4, 25] grant+17:[2008, 6, 4] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 442,475, filed Nov. 22, 1989 which is a continuation of Ser. No. 185,608 filed Apr. 25, 1988, now abandoned. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5027206 | 13 sep 1989 | 25 jun 1991 | 13 sep 1989 | 13 sep 2009 | High-definition television systems | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5027206 file+20: [2009, 9, 13] grant+17:[2008, 6, 25] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5128758 | 02 jun 1989 | 07 jul 1992 | 02 jun 1989 | 07 jul 2009 | Method and apparatus for digitally processing a high definition television augmentation signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5128758 file+20: [2009, 6, 2] grant+17:[2009, 7, 7] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5179442 | 26 nov 1990 | 12 jan 1993 | 02 jun 1989 | 12 jan 2010 | Method and apparatus for digitally processing a high definition television augmentation signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5179442 file+20: [2010, 11, 26] related_patent+20:[2009, 6, 2] grant+17:[2010, 1, 12] Case Text: This application is a continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 361,523 filed Jun. 2, 1989, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,128,758. The contents of this application is specifically incorporated herein by reference. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5333135 | 01 feb 1993 | 26 jul 1994 | 01 feb 1993 | 01 feb 2013 | Identification of a data stream transmitted as a sequence of packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5333135 file+20: [2013, 2, 1] grant+17:[2011, 7, 26] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5606539 | 31 aug 1994 | 25 feb 1997 | 05 jun 1991 | 25 feb 2014 | Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio and/or video signal, and a record carrier for use with such apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5606539 file+20: [2014, 8, 31] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] grant+17:[2014, 2, 25] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation of Application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of Application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5608697 | 18 mar 1996 | 04 mar 1997 | 05 jun 1991 | 05 jun 2011 | Record carrier containing an audio and/or video signal which has been encoded and includes a decoder delay time parameter indicating a time delay for one or more portions of the signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5608697 file+20: [2016, 3, 18] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a division of application Ser. No. 08/299,027, filed on Aug. 31, 1994, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5740310 | 28 jun 1994 | 14 apr 1998 | 32 May 1991 | 14 apr 2015 | Method of maintaining display continuity from a CD with slow-motion or freeze capability | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5740310 file+20: [2014, 6, 28] related_patent+20:[2011, 5, 32] grant+17:[2015, 4, 14] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/707,527, filed May 30, 1991, now abandoned. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 5844867 | 09 sep 1996 | 01 dec 1998 | 05 jun 1991 | 05 jun 2011 | Methods and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio and/or video signal, and a record carrier used therewith or produced therefrom | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5844867 file+20: [2016, 9, 9] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/299,027, filed on Aug. 31, 1994, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,606,539, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 6181712 | 11 oct 1995 | 30 jan 2001 | 23 feb 1995 | 30 jan 2018 | Method and device for transmitting data packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6181712 file+20: [2015, 10, 11] pct_file+20:[2015, 2, 23] grant+17:[2018, 1, 30] | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| 6792001 | 21 sep 2000 | 14 sep 2004 | 21 sep 2000 | 21 dec 2022 | Method and device for transmitting data packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6792001 file+20: [2020, 9, 21] term extension 821 days Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/537,701, filed Oct. 11, 1995 now U.S. Pat. No. 6,181,712 which is a 371 of PCT/IB95/00116 filed Feb. 23, 1995. | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. |
| RE37057 | 14 nov 1994 | 21 May 1996 | 14 nov 1994 | 14 nov 2014 | Apparatus and method for converting an HDTV signal to a non-HDTV signal | Reissue of 05519446 filed 18 May 1998 granted 20 feb 2001 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE37057 file+20: [2014, 11, 14] related_patent+20:[2014, 11, 32] grant+17:[2013, 5, 21] | LG Electronics LG Electronics LG Electronics is a global electronics and telecommunications company headquartered in Yeouido, Seoul, South Korea. The company operates its business through five divisions: mobile communications, home entertainment, home appliance, air conditioning and business solution... |
| RE37568 | 30 nov 1993 | 01 apr 1997 | 30 nov 1993 | 01 apr 2014 | Inverse Quantizer | Reissue of 05617094 filed 31 mar 1999 granted 05 mar 2002 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE37568 file+20: [2013, 11, 30] related_patent+20:[2013, 11, 32] grant+17:[2014, 4, 1] | LG Electronics LG Electronics LG Electronics is a global electronics and telecommunications company headquartered in Yeouido, Seoul, South Korea. The company operates its business through five divisions: mobile communications, home entertainment, home appliance, air conditioning and business solution... |
| RE35910 | 11 May 1990 | 12 May 1992 | 11 May 1990 | 11 May 2010 | Moving image signal encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus | Reissue of 05113255 filed 12 May 1994 granted 29 sep 1998 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE35910 file+20: [2010, 5, 11] related_patent+20:[2010, 5, 32] grant+17:[2009, 5, 12] | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| RE36015 | 27 mar 1992 | 08 mar 1994 | 27 mar 1992 | 27 mar 2012 | Apparatus and method for processing groups of fields in a video data compression system | Reissue of 05293229 filed 02 oct 1995 granted 29 dec 1998 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE36015 file+20: [2012, 3, 27] related_patent+20:[2012, 3, 32] grant+17:[2011, 3, 8] | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| RE36507 | 27 mar 1992 | 08 mar 1994 | 27 mar 1992 | 27 mar 2012 | Apparatus and method for processing groups of fields in a video data compression system to encode a single frame as an I-field and a P-field | Reissue of 05293229 filed 21 oct 1997 granted 18 jan 2000 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE36507 file+20: [2012, 3, 27] related_patent+20:[2012, 3, 27] grant+17:[2011, 3, 8] Case Text: .Iadd.Application Ser. No 08/538,101, filed Oct. 2, 1995, now U.S. Pat. No. RE 36,015, and application Ser. No. 08/954,916, filed Oct. 21, 1997, are reissue applications of U.S. Pat. No. 5,293,229, which issues from application Ser. No. 07/859,145, filed Mar. 27, 1992..Iaddend. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| RE39276 | 20 jul 1994 | 28 apr 1998 | 02 nov 1992 | 28 apr 2015 | Method for determining motion compensation | Reissue of 05745182 filed 27 apr 2000 granted 12 sep 2006 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE39276 file+20: [2014, 7, 20] related_patent+20:[2012, 11, 2] grant+17:[2015, 4, 28] Case Text: This is a .Iadd.reissue of U.S. Pat. No. 5,745,182 which is a .Iaddend.division of application Ser. No. 07/970,046 filed Nov. 2, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,369,449. .Iadd.This application has the following co-pending related reissue applications: Ser. No. 09/833,680 filed Apr. 13, 2001, Ser. No. 09/833,769 filed Apr. 13, 2001, Ser. No. 09/833,770 filed Apr. 13, 2001, Ser. No. 09/866,811 filed May 30, 2001 and Ser. No. 10/895,283 filed Jul. 21, 2004..Iaddend. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| RE39278 | 20 jul 1994 | 28 apr 1998 | 02 nov 1992 | 28 apr 2015 | Method for determining motion compensation | Reissue of 05745182 filed 13 apr 2001 granted 12 sep 2006 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE39278 file+20: [2014, 7, 20] related_patent+20:[2012, 11, 2] grant+17:[2015, 4, 28] Case Text: This is a .Iadd.reissue of U.S. Pat. No. 5,745,182 which is a .Iaddend.division of application Ser. No. 07/970,046 filed Nov. 2, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,369,449. .Iadd.This application is a division of reissue application No. 09/559,627, filed Apr. 27, 2000 and has the following co-pending related reissue applications: 09/833,680 filed Apr. 13, 2001; 09/833,770 filed Apr. 13, 2001, 09/866,811 filed May 30, 2001, and 10/895,283 filed Jul. 21, 2004. .Iaddend. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| RE39280 | 20 jul 1994 | 28 apr 1998 | 02 nov 1992 | 28 apr 2015 | Method for determining motion compensation | Reissue of 05745182 filed 30 May 2001 granted 12 sep 2006 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE39280 file+20: [2014, 7, 20] related_patent+20:[2012, 11, 2] grant+17:[2015, 4, 28] Case Text: This is a .Iadd.reissue of U.S. Pat. No. 5,745,182 which is a .Iaddend.division of application Ser. No. 07/970,046 filed Nov. 2, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,369,449. .Iadd.This application is a division of reissue application Ser. No. 09/559,627, filed Apr. 27, 2000 and has the following co-pending related reissue applications: Ser. No. 09/833,680 filed Apr. 13, 2001, Ser. No. 09/833,769 filed Apr. 13, 2001, Ser. No. 09/833,770 filed Apr. 13, 2001, and Ser. No. 10/895,283 filed Jul. 21, 2004..Iaddend. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| 5223949 | 17 apr 1992 | 29 jun 1993 | 17 apr 1992 | 17 apr 2012 | Coding means for a signal processing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5223949 file+20: [2012, 4, 17] grant+17:[2010, 6, 29] | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| 5412430 | 4 May 1994 | 2 May 1995 | 31 jul 1992 | 31 jul 2012 | Image coding method and image coding apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5412430 file+20: [2014, 5, 4] related_patent+20:[2012, 7, 31] grant+17:[2012, 5, 2] Case Text: This application is a Continuation of now abandoned application, Ser. No. 07/922,772, filed Jul. 31, 1992, now abandoned. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| 5784107 | 23 jan 1996 | 21 jul 1998 | 21 apr 1992 | 21 apr 2012 | Method and apparatus for picture coding and method and apparatus for picture decoding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5784107 file+20: [2016, 1, 23] related_patent+20:[2012, 4, 21] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/157,627 filed Nov. 24, 1993 which is a continuation-in-part of Ser. No. 871,697, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,347,309 filed Apr. 21, 1992, now abandoned. | Matsushita Matsushita Matsushita is a Japanese place name and surname which means "below the pine tree" and may refer to:-Companies:*Matsushita Electric Industrial, now Panasonic Corporation, a multinational electronics corporation based in Kadoma, Japan... |
| 4954892 | 04 oct 1989 | 04 sep 1990 | 04 oct 1989 | 04 oct 2009 | Buffer controlled picture signal encoding and decoding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4954892 file+20: [2009, 10, 4] grant+17:[2007, 9, 4] | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5072295 | 20 aug 1990 | 10 dec 1991 | 20 aug 1990 | 20 aug 2010 | Adaptive quantization coder/decoder with limiter circuitry | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5072295 file+20: [2010, 8, 20] grant+17:[2008, 12, 10] | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5268846 | 10 apr 1991 | 07 dec 1993 | 10 apr 1991 | 10 apr 2011 | Method and apparatus for nonsequential multimedia data interchange in a data processing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5268846 file+20: [2011, 4, 10] grant+17:[2010, 12, 7] | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5949489 | 31 jul 1998 | 07 sep 1999 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5949489 file+20: [2018, 7, 31] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235, filed on Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed on Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a division of application Ser. No. 07/962,299, filed on Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5963258 | 31 jul 1998 | 05 oct 1999 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5963258 file+20: [2018, 7, 31] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235, filed on Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed on Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/962,299, filed on Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5970175 | 26 oct 1998 | 19 oct 1999 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5970175 file+20: [2018, 10, 26] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235 filed on Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 07/962,299 filed Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 5990960 | 09 dec 1998 | 23 nov 1999 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5990960 file+20: [2018, 12, 9] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235, filed on Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220 which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 07/962,299 filed Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442, the entire contents of which is hereby incorporated by reference. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 6002439 | 27 May 1999 | 14 dec 1999 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6002439 file+20: [2019, 5, 27] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of co-pending application Ser. No. 09/207,919, filed on Dec. 9, 1998, now allowed, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/803,235, filed Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 07/962,299, filed Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 6097759 | 22 nov 1999 | 01 aug 2000 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6097759 file+20: [2019, 11, 22] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/207,919, filed on Dec. 9, 1998, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,990,960, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235, filed on Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293, filed on Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 07/962,299, filed on Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 6188794 | 20 May 1999 | 13 feb 2001 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6188794 file+20: [2019, 5, 20] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/178,619 filed Oct. 26, 1998 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,427,678, now allowed, which is a Div. of Ser. No. 08/803,235 filed Feb. 20, 1997, U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220, which is a Cont. of Ser. No. 08/121,293 filed Sep. 13, 1993, U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a Div. of Ser. No. 07/962,299 filed Oct. 16, 1992, U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 6307973 | 04 dec 2000 | 23 oct 2001 | 16 oct 1992 | 16 oct 2012 | Image signal coding system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6307973 file+20: [2020, 12, 4] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 16] term extension 0 days Case Text: This application is a divisional application under 37 C.F.R. .sctn. 1.53(b) of prior application Ser. No. 09/315,038 filed May 20, 1999, now U.S. Pat. No. 6,188,794 which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/178,619 filed Oct. 26, 1998, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,970,175, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/803,235 filed Feb. 20, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,867,220 which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/121,293 filed Sep. 13, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,638,127, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 07/962,299 filed Oct. 16, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,274,442, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 7362805 | 02 mar 2006 | 22 apr 2008 | 29 jan 1993 | 29 jan 2013 | High efficiency encoder and video information recording/reproducing apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7362805 file+20: [2026, 3, 2] related_patent+20:[2013, 1, 29] term extension 0 days Case Text: This application is a divisional of co-pending application Ser. No. 10/372,212 filed on Feb. 25, 2003, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/271,458, filed on Mar. 18, 1999, now U.S. Pat. No. 6,870,884 B1, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/113,287, filed Jul. 10, 1998, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,909,252, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/559,488, filed Nov. 15, 1995, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,841,474, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/011,243, filed on Jan. 29, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,479,264, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference and for which priority is claimed under 35 U.S.C. .sctn. 120; and this application claims priority of Application No. 4-013719, 4-037599, 4-037821, and 4-043075 filed in Japan on Jan. 29, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992 and Feb. 28, 1992 under 35 U.S.C. .sctn. 119. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 7376184 | 04 nov 2002 | 20 May 2008 | 29 jan 1993 | 31 May 2014 | High-efficiency encoder and video information recording/reproducing apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7376184 file+20: [2022, 11, 4] related_patent+20:[2013, 1, 29] term extension 487 days Case Text: This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/271,458, filed on Mar. 18, 1999 now U.S. Pat. No. 6,870,884, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/113,287, filed Jul. 10, 1998 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,909,252, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/559,488, filed Nov. 15, 1995 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,841,474, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/011,243, filed on Jan. 29, 1993 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,479,264, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference and for which priority is claimed under 35 U.S.C. .sctn. 120; and this application claims priority of application No. 4-013719, 4-037599, 4-037821, and 4-043075 filed in Japan on Jan. 29, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992 and Feb. 28, 1992 under 35 U.S.C. .sctn. 119. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 7756202 | 30 oct 2007 | 13 jul 2010 | 29 jan 1993 | 06 aug 2013 | High-efficiency encoder and video information recording/reproducing apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7756202 file+20: [2027, 10, 30] related_patent+20:[2013, 1, 29] term extension 189 days Case Text: This application is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 11/276,501 filed on Mar. 2, 2006 now U.S. Pat. No. 7,362,805 which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 10/372,212 filed on Feb. 25, 2003 now U.S. Pat. No. 7,336,708, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/271,458, filed on Mar. 18, 1999 now U.S. Pat. No. 6,870,884, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/113,287, filed Jul. 10, 1998 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,909,252, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/559,488, filed Nov. 15, 1995 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,841,474, which is a divisional of application Ser. No. 08/011,243, filed on Jan. 29, 1993 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,479,264, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference and for which priority is claimed under 35 U.S.C. .sctn.120; and this application claims priority of Application No. 4-013719, 4-037599, 4-037821, and 4-043075 filed in Japan on Jan. 29, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992; Feb. 25, 1992 and Feb. 28, 1992 under 35 U.S.C. .sctn.119. | Mitsubishi Mitsubishi The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy... |
| 4958226 | 27 sep 1989 | 18 sep 1990 | 27 sep 1989 | 27 sep 2009 | Conditional motion compensated interpolation of digital motion video | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4958226 file+20: [2009, 9, 27] grant+17:[2007, 9, 18] | Multimedia Patent Trust |
| 5227878 | 15 nov 1991 | 13 jul 1993 | 15 nov 1991 | 15 nov 2011 | Adaptive coding and decoding of frames and fields of video | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5227878 file+20: [2011, 11, 15] grant+17:[2010, 7, 13] | Multimedia Patent Trust |
| 5500678 | 18 mar 1994 | 19 mar 1996 | 18 mar 1994 | 18 mar 2014 | Optimized scanning of transform coefficients in video coding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5500678 file+20: [2014, 3, 18] grant+17:[2013, 3, 19] | Multimedia Patent Trust |
| 5563593 | 18 mar 1994 | 08 oct 1996 | 18 mar 1994 | 18 mar 2014 | Video coding with optimized low complexity variable length codes | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5563593 file+20: [2014, 3, 18] grant+17:[2013, 10, 8] | Multimedia Patent Trust |
| 4849812 | 24 feb 1988 | 18 jul 1989 | 24 feb 1988 | 24 feb 2008 | Television system in which digitized picture signals subjected to a transform coding are transmitted from an encoding station to a decoding station | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4849812 file+20: [2008, 2, 24] grant+17:[2006, 7, 18] | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 4901075 | 11 sep 1987 | 13 feb 1990 | 11 sep 1987 | 11 sep 2007 | Method and apparatus for bit rate reduction | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4901075 file+20: [2007, 9, 11] grant+17:[2007, 2, 13] | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5021879 | 24 sep 1990 | 04 jun 1991 | 25 apr 1988 | 04 jun 2008 | System for transmitting video pictures | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5021879 file+20: [2010, 9, 24] related_patent+20:[2008, 4, 25] grant+17:[2008, 6, 4] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 442,475, filed Nov. 22, 1989 which is a continuation of Ser. No. 185,608 filed Apr. 25, 1988, now abandoned. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5027206 | 13 sep 1989 | 25 jun 1991 | 13 sep 1989 | 13 sep 2009 | High-definition television systems | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5027206 file+20: [2009, 9, 13] grant+17:[2008, 6, 25] | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5128758 | 02 jun 1989 | 07 jul 1992 | 02 jun 1989 | 07 jul 2009 | Method and apparatus for digitally processing a high definition television augmentation signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5128758 file+20: [2009, 6, 2] grant+17:[2009, 7, 7] | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5179442 | 26 nov 1990 | 12 jan 1993 | 02 jun 1989 | 12 jan 2010 | Method and apparatus for digitally processing a high definition television augmentation signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5179442 file+20: [2010, 11, 26] related_patent+20:[2009, 6, 2] grant+17:[2010, 1, 12] Case Text: This application is a continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 361,523 filed Jun. 2, 1989, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,128,758. The contents of this application is specifically incorporated herein by reference. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5333135 | 01 feb 1993 | 26 jul 1994 | 01 feb 1993 | 01 feb 2013 | Identification of a data stream transmitted as a sequence of packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5333135 file+20: [2013, 2, 1] grant+17:[2011, 7, 26] | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5606539 | 31 aug 1994 | 25 feb 1997 | 05 jun 1991 | 25 feb 2014 | Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio and/or video signal, and a record carrier for use with such apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5606539 file+20: [2014, 8, 31] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] grant+17:[2014, 2, 25] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation of Application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of Application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5608697 | 18 mar 1996 | 04 mar 1997 | 05 jun 1991 | 05 jun 2011 | Record carrier containing an audio and/or video signal which has been encoded and includes a decoder delay time parameter indicating a time delay for one or more portions of the signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5608697 file+20: [2016, 3, 18] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a division of application Ser. No. 08/299,027, filed on Aug. 31, 1994, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5740310 | 28 jun 1994 | 14 apr 1998 | 32 May 1991 | 14 apr 2015 | Method of maintaining display continuity from a CD with slow-motion or freeze capability | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5740310 file+20: [2014, 6, 28] related_patent+20:[2011, 5, 32] grant+17:[2015, 4, 14] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/707,527, filed May 30, 1991, now abandoned. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5844867 | 09 sep 1996 | 01 dec 1998 | 05 jun 1991 | 05 jun 2011 | Methods and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio and/or video signal, and a record carrier used therewith or produced therefrom | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5844867 file+20: [2016, 9, 9] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 5] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/299,027, filed on Aug. 31, 1994, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,606,539, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/086,402, filed Jun. 30, 1993 and now abandoned, which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/711,186, filed Jun. 5, 1991 and now abandoned. | Philips Philips Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company.... |
| 5461421 | 29 nov 1993 | 24 oct 1995 | 29 nov 1993 | 29 nov 2013 | Encoding and decoding method and apparatus thereof | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5461421 file+20: [2013, 11, 29] grant+17:[2012, 10, 24] | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 5467086 | 18 jun 1993 | 14 nov 1995 | 18 jun 1993 | 18 jun 2013 | Apparatus and method of coding/decoding video data | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5467086 file+20: [2013, 6, 18] grant+17:[2012, 11, 14] | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 5654706 | 18 dec 1996 | 05 aug 1997 | 15 jul 1993 | 15 jul 2013 | System for variable length decoding digital transmission data which has been compressed by selecting a scanning pattern | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5654706 file+20: [2016, 12, 18] related_patent+20:[2013, 7, 15] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/532,987 filed Sep. 22, 1995, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,602,549 which is a Continuation Application of prior application Ser. No. 08/095,468, Jul. 15, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,497,153. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 6680975 | 02 nov 2000 | 20 jan 2004 | 01 mar 1993 | 12 mar 2014 | Signal encoding and decoding system and method | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6680975 file+20: [2020, 11, 2] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 1] term extension 376 days Case Text: This is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 08/024,305 filed Mar. 1, 1993 now U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7292657 | 03 jul 2003 | 06 nov 2007 | 01 mar 1993 | 01 mar 2013 | Signal compressing signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7292657 file+20: [2023, 7, 3] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 1] Case Text: This is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 09/703,649 filed Nov. 2, 2000; now U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975 which is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 08/024,305 filed Mar. 1, 1993; now U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7609760 | 05 jan 2009 | 27 oct 2009 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7609760 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7616687 | 05 jan 2009 | 10 nov 2009 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7616687 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7684490 | 18 dec 2008 | 23 mar 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7684490 file+20: [2028, 12, 18] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724821 | 24 dec 2008 | 25 May 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724821 file+20: [2028, 12, 24] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue Application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12,338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724822 | 24 dec 2008 | 25 May 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724822 file+20: [2028, 12, 24] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation Application No. 12,338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724823 | 24 dec 2008 | 25 May 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724823 file+20: [2028, 12, 24] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12,338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724824 | 05 jan 2009 | 25 May 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724824 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724828 | 16 nov 2009 | 25 May 2010 | 01 mar 1993 | 01 mar 2013 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724828 file+20: [2029, 11, 16] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 1] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 12/574,255, filed Oct. 6, 2009, which is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 12/348,621, filed Jan. 5, 2009, issued as U.S. Pat. No. 7,616,687 on Nov. 10, 2009, which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008, Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/348,510, 12/348,535, 12/348,539, 12/348,581, 12/348,590, and 12/348,621, all filed on Jan. 5, 2009, and Continuation application Ser. No. 12/497,264, filed on Jul. 2, 2009, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7724829 | 16 nov 2009 | 25 May 2010 | 01 mar 1993 | 01 mar 2013 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7724829 file+20: [2029, 11, 16] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 1] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 12/574,255, filed Oct. 6, 2009, which is a Continuation application of 12/348,621, filed Jan. 5, 2009, issued as U.S. Pat. No. 7,616,687 on Nov. 10, 2009, which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008, Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/348,510, 12/348,535, 12/348,539, 12/348,581, 12/348,590, and 12/348,621, all filed on Jan. 5, 2009, and Continuation application Ser. No. 12/497,264, filed on Jul. 2, 2009, are Continuation applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7742522 | 05 jan 2009 | 22 jun 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7742522 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007, now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation Applications of 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7742527 | 05 jan 2009 | 22 jun 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7742527 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7764735 | 02 jul 2009 | 27 jul 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7764735 file+20: [2029, 7, 2] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 11/873,282 was filed on Oct. 16, 2007; Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647 was filed on Dec. 18, 2008; Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,898, 12/343,797, and 12/343,839 were filed on Dec. 24, 2008; and Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/348,590, 12/348,535, 12/343,539, 12/348,581, 12/348,621, 12/348,510 were filed on Jan. 5, 2009. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7782956 | 16 nov 2009 | 24 aug 2010 | 01 mar 1993 | 01 mar 2013 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7782956 file+20: [2029, 11, 16] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 1] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 12/574,255, filed Oct. 6, 2009, which is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 12/348,621, filed Jan. 5, 2009, issued as U.S. Pat. No. 7,616,687 on Nov. 10, 2009, which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation Application No. Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008, Continuation Application Nos. Ser. No. 12/343,797, Ser. No. 12/343,839, and Ser. No. 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, Continuation Application Nos. Ser. No. 12/348,510, Ser. No. 12/348,535, Ser. No. 12/348,539, Ser. No. 12/348,581, Ser. No. 12/348,590, and Ser. No. 12/348,621, all filed on Jan. 5, 2009, and Continuation Application No. Ser. No. 12/497,264, filed on Jul. 2, 2009, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 7787538 | 05 jan 2009 | 31 aug 2010 | 17 jul 2001 | 17 jul 2021 | Signal compressing system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7787538 file+20: [2029, 1, 5] related_patent+20:[2021, 7, 17] term extension 0 days Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED PATENT APPLICATIONS This is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007 now abandoned; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 10/612,013, filed Jul. 3, 2003, and issued on Nov. 6, 2007, as U.S. Pat. No. 7,292,657; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 09/703,649, filed Nov. 2, 2000, and issued Jan. 20, 2004, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,680,975; which is a Continuation Application of application Ser. No. 08/024,305, filed Mar. 1, 1993, and issued on Jul. 17, 2001, as U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference. One (1) Reissue application Ser. No. 10/609,438, filed on Jul. 1, 2003, of U.S. Pat. No. 6,263,026 has been abandoned. Continuation application Ser. No. 12/338,647, filed Dec. 18, 2008 is a Continuation Application of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. Continuation application Ser. Nos. 12/343,797, 12/343,839, and 12/343,898, all filed on Dec. 24, 2008, are Continuation Applications of Ser. No. 11/873,282, filed Oct. 16, 2007. | Samsung Samsung The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea... |
| 5418782 | 06 jan 1994 | 23 May 1995 | 30 oct 1992 | 30 oct 2012 | Methods and apparatus for providing virtual service selection in a multi-service communications system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5418782 file+20: [2014, 1, 6] related_patent+20:[2012, 10, 30] grant+17:[2012, 5, 23] Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This is a continuation-in-part of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08/027,782, filed Mar. 8, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,359,601 entitled "Apparatus Providing Dynamic Virtual Service Selection in a Multi-Service Communications System" and of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/968,846, filed Oct. 30, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,400,401 entitled "System and Method for Transmitting a Plurality of Digital Services", both of which are hereby incorporated by reference. | Scientific Atlanta |
| 5420866 | 29 mar 1994 | 30 May 1995 | 29 mar 1994 | 29 mar 2014 | Methods for providing conditional access information to decoders in a packet-based multiplexed communications system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5420866 file+20: [2014, 3, 29] grant+17:[2012, 5, 30] | Scientific Atlanta |
| 5457701 | 06 jan 1994 | 10 oct 1995 | 06 jan 1994 | 06 jan 2014 | Method for indicating packet errors in a packet-based multi-hop communications system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5457701 file+20: [2014, 1, 6] grant+17:[2012, 10, 10] | Scientific Atlanta |
| 4864393 | 31 May 1988 | 05 sep 1989 | 31 May 1988 | 31 May 2008 | Motion vector estimation in television images | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4864393 file+20: [2008, 5, 31] grant+17:[2006, 9, 5] Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is related to the following applications for U.S. Letters Patent, each of which was filed concurrently herewith, that is, on May 31, 1988, and has a common assignee herewith: Ser. No. 07/199,680 Ser. No. 07/199,681 Ser. No. 07/199,682 Ser. No. 07/200,421 Ser. No. 07/200,503 Ser. No. 07/200,531 Ser. No. 07/200,562. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| RE37222 | 12 oct 1990 | 21 jul 1992 | 12 oct 1990 | 12 oct 2010 | Video signal transmitting system | Reissue of 05132792 filed 19 jul 1994 granted 12 jun 2001 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE37222 file+20: [2010, 10, 12] related_patent+20:[2010, 10, 32] grant+17:[2009, 7, 21] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5191436 | 30 apr 1991 | 02 mar 1993 | 30 apr 1991 | 30 apr 2011 | Method for recording coded motion picture data | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5191436 file+20: [2011, 4, 30] grant+17:[2010, 3, 2] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5291486 | 07 aug 1992 | 01 mar 1994 | 07 aug 1992 | 07 aug 2012 | Data multiplexing apparatus and multiplexed data demultiplexing apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5291486 file+20: [2012, 8, 7] grant+17:[2011, 3, 1] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5298991 | 24 jul 1992 | 29 mar 1994 | 24 jul 1992 | 24 jul 2012 | Variable length coding apparatus and method for motion vector | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5298991 file+20: [2012, 7, 24] grant+17:[2011, 3, 29] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5343248 | 16 jul 1992 | 30 aug 1994 | 16 jul 1992 | 16 jul 2012 | Moving image compressing and recording medium and moving image data encoder and decoder | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5343248 file+20: [2012, 7, 16] grant+17:[2011, 8, 30] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5428396 | 27 dec 1993 | 27 jun 1995 | 24 jul 1992 | 24 jul 2012 | Variable length coding/decoding method for motion vectors | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5428396 file+20: [2013, 12, 27] related_patent+20:[2012, 7, 24] grant+17:[2012, 6, 27] Case Text: This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/918,010, filed on Jul. 24, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,293,991. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5461420 | 17 sep 1993 | 24 oct 1995 | 17 sep 1993 | 17 sep 2013 | Apparatus for coding and decoding a digital video signal derived from a motion picture film source | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5461420 file+20: [2013, 9, 17] grant+17:[2012, 10, 24] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5481553 | 28 feb 1994 | 02 jan 1996 | 28 feb 1994 | 28 feb 2014 | Methods and apparatus for preventing rounding errors when transform coefficients representing a motion picture signal are inversely transformed | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5481553 file+20: [2014, 2, 28] grant+17:[2013, 1, 2] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5510840 | 15 May 1995 | 23 apr 1996 | 30 aug 1993 | 30 aug 2013 | Methods and devices for encoding and decoding frame signals and recording medium therefor | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5510840 file+20: [2015, 5, 15] related_patent+20:[2013, 8, 30] grant+17:[2013, 4, 23] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/098,280 filed on Aug. 30, 1993 abandoned. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5539466 | 26 sep 1994 | 23 jul 1996 | 32 apr 1993 | 23 jul 2013 | Efficient coding apparatus for picture signal and decoding apparatus therefor | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5539466 file+20: [2014, 9, 26] related_patent+20:[2013, 4, 32] grant+17:[2013, 7, 23] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/030,019, filed as PCT/JP92/00956, Jul. 28, 1992 published as WO93/03578, Feb. 18, 1993, now abandoned. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5543847 | 13 dec 1993 | 06 aug 1996 | 13 dec 1993 | 13 dec 2013 | Picture coding and decoding method for random accessing | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5543847 file+20: [2013, 12, 13] grant+17:[2013, 8, 6] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5559557 | 28 sep 1993 | 24 sep 1996 | 28 sep 1993 | 28 sep 2013 | Motion video coding with adaptive precision for DC component coefficient quantization and variable length coding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5559557 file+20: [2013, 9, 28] grant+17:[2013, 9, 24] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5663763 | 18 oct 1993 | 02 sep 1997 | 18 oct 1993 | 02 sep 2014 | Picture signal encoding method and apparatus and picture signal decoding method and apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5663763 file+20: [2013, 10, 18] grant+17:[2014, 9, 2] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5666461 | 30 May 1995 | 09 sep 1997 | 21 apr 1993 | 09 sep 2014 | High efficiency encoding and decoding of picture signals and recording medium containing same | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5666461 file+20: [2015, 5, 30] related_patent+20:[2013, 4, 21] grant+17:[2014, 9, 9] Case Text: This application is a division of application Ser. No. 08/084,642, filed Jun. 29, 1993 which is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 08/030,019, filed in the United States Patent and Trademark Office on Apr. 21, 1993, and corresponding to International Application No. PCT/JP92/00956, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5701164 | 19 dec 1996 | 23 dec 1997 | 32 dec 1994 | 32 dec 2014 | Macroblock coding including difference between motion vectors | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5701164 file+20: [2016, 12, 19] related_patent+20:[2014, 12, 32] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/290,888, filed as PCT/JP94/00473 Mar. 24, 1994, now abandoned. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5946042 | 02 jul 1997 | 31 aug 1999 | 19 dec 1996 | 19 dec 2016 | Macroblock coding including difference between motion vectors | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5946042 file+20: [2017, 7, 2] related_patent+20:[2016, 12, 19] Case Text: This application is a division of application Ser. No. 08/770,585, filed Dec. 19, 1996, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,701,164, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/290,888, filed Dec. 8, 1994. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 5982437 | 15 oct 1993 | 09 nov 1999 | 15 oct 1993 | 09 nov 2016 | Coding method and system, and decoding method and system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5982437 file+20: [2013, 10, 15] grant+17:[2016, 11, 9] | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 6040863 | 18 dec 1998 | 21 mar 2000 | 19 dec 1996 | 19 dec 2016 | Method of coding and decoding motion vector and apparatus therefor, and method of coding and decoding picture signal and apparatus therefor | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6040863 file+20: [2018, 12, 18] related_patent+20:[2016, 12, 19] Case Text: This is a divisional of prior U.S. application Ser. No. 08/886,804 filed Jul. 2, 1997, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,946,042, which is a divisional of U.S. application Ser. No. 08/770,585 filed Dec. 19, 1996, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,701,164, which is a continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 08/290,888 filed Dec. 8, 1994, now abandoned, which is a 371 of PCT/JP94/00473 filed Mar. 24, 1994. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 6160849 | 30 May 1995 | 12 dec 2000 | 22 mar 1993 | 12 dec 2017 | Selectable field and frame based predictive video coding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6160849 file+20: [2015, 5, 30] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 22] grant+17:[2017, 12, 12] Case Text: This application is a division of application Ser. No. 08/084,642, filed Jun. 29, 1993. This is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 08/030,019, filed in the United States Patent and Trademark Office on Mar. 22, 1993, and corresponding to International Application No. PCT/JP92/00956, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| 7627041 | 30 jun 2005 | 01 dec 2009 | 13 jan 1994 | 16 mar 2015 | Apparatus for encoding and decoding header data in picture signal transmission | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7627041 file+20: [2025, 6, 30] related_patent+20:[2014, 1, 13] term extension 427 days Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/634,122, filed Apr. 19, 1996 now U.S. Pat. No. 7,075,991, the entirety of which is incorporated herein by reference, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/180,613 filed Jan. 13, 1994 now abandoned, the entirety of which is incorporated herein by reference. | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... |
| RE35093 | 03 dec 1990 | 09 mar 1993 | 03 dec 1990 | 03 dec 2010 | Systems and methods for coding even fields of interlaced video sequences | Reissue of 05193004 filed 09 dec 1994 granted 21 nov 1995 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE35093 file+20: [2010, 12, 3] related_patent+20:[2010, 12, 32] grant+17:[2010, 3, 9] Case Text: .Iadd.This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/218,970, filed on Mar. 25, 1994, now abandoned, and is a reissue of U.S. Pat. No. 5,193,004. .Iaddend. | The Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York |
| 4800432 | 24 oct 1986 | 24 jan 1989 | 24 oct 1986 | 24 oct 2006 | Video Difference key generator | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4800432 file+20: [2006, 10, 24] grant+17:[2006, 1, 24] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 4969055 | 25 aug 1988 | 06 nov 1990 | 32 aug 1986 | 06 nov 2007 | Method for recording and/or reproducing digitally coded signals with interframe and interframe coding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4969055 file+20: [2008, 8, 25] related_patent+20:[2006, 8, 32] grant+17:[2007, 11, 6] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 06/901,535, filed Aug. 8th, 1986now abandoned. | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5289276 | 19 jun 1992 | 22 feb 1994 | 19 jun 1992 | 19 jun 2012 | Method and apparatus for conveying compressed video data over a noisy communication channel | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5289276 file+20: [2012, 6, 19] grant+17:[2011, 2, 22] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5365272 | 02 jul 1993 | 15 nov 1994 | 19 jun 1992 | 19 jun 2012 | Method for formatting compressed video data into transport cells | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5365272 file+20: [2013, 7, 2] related_patent+20:[2012, 6, 19] grant+17:[2011, 11, 15] Case Text: This is a division of Ser. No. 07/901,045, filed Jun. 19, 1992. The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for segmenting compressed video data into cells or packets for transmission in a manner to allow a receiver to rapidly recover from occurrences of missing data or corrupted data. | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5381181 | 13 May 1993 | 10 jan 1995 | 13 May 1993 | 13 May 2013 | Clock recovery apparatus as for a compressed video signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5381181 file+20: [2013, 5, 13] grant+17:[2012, 1, 10] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5422676 | 22 oct 1993 | 06 jun 1995 | 22 oct 1993 | 22 oct 2013 | System for coding an image representative signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5422676 file+20: [2013, 10, 22] grant+17:[2012, 6, 6] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5442400 | 29 apr 1993 | 15 aug 1995 | 29 apr 1993 | 29 apr 2013 | Error concealment apparatus for MPEG-like video data | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5442400 file+20: [2013, 4, 29] grant+17:[2012, 8, 15] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5459789 | 22 apr 1994 | 17 oct 1995 | 22 apr 1994 | 22 apr 2014 | Packet TV program component detector | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5459789 file+20: [2014, 4, 22] grant+17:[2012, 10, 17] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5483287 | 03 aug 1994 | 09 jan 1996 | 19 jun 1992 | 09 jan 2013 | Method for forming transport cells for conveying compressed video data | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5483287 file+20: [2014, 8, 3] related_patent+20:[2012, 6, 19] grant+17:[2013, 1, 9] Case Text: This is a continuation of Ser. No. 08/085,364 filed 2 Jul. 1993, now U.S. Pat. No.5,365,272, which is a division of Ser. No. 901,045 filed Jun. 19, 1992, (now U.S. Pat. No. 5,289,276). | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5565923 | 22 aug 1995 | 15 oct 1996 | 32 May 1993 | 32 May 2013 | Apparatus for formatting a digital signal to include multiple time stamps for system synchronization | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5565923 file+20: [2015, 8, 22] related_patent+20:[2013, 5, 32] Case Text: This is a division of Ser. No. 08/060,924 filed May 13, 1993 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,486,864. This invention relates to a method and apparatus for providing a clock signal at a signal decompression apparatus, which clock signal is substantially frequency locked to a clock signal at a encoding apparatus. | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5784110 | 23 May 1996 | 21 jul 1998 | 30 nov 1993 | 21 jul 2015 | Data processor for assembling transport data packets | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5784110 file+20: [2016, 5, 23] pct_file+20:[2013, 11, 30] grant+17:[2015, 7, 21] | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 7020204 | 08 feb 2002 | 28 mar 2006 | 30 dec 1988 | 30 jan 2010 | Adaptive method of encoding and decoding a series of pictures by transformation, and devices for implementing this method | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7020204 file+20: [2022, 2, 8] related_patent+20:[2008, 12, 30] term extension 396 days Case Text: CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is a divisional of application Ser. No. 09/978,376, filed Oct. 17, 2001, now U.S. Pat. No. 6,563,875, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/408,515, filed Nov. 30, 1995 now abandoned claiming the benefit and priority of PCT International Application No. PCT/FR88/00649, filed Dec. 30, 1988, and French Application No. 87 18371, filed Dec. 30, 1987. | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 7334248 | 24 May 2002 | 19 feb 2008 | 24 May 2002 | 18 mar 2026 | Conditional access filter as for a packet video signal inverse transport system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=7334248 file+20: [2022, 5, 24] term extension 1394 days | Thomson Thomson SA Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les... |
| 5317397 | 29 May 1992 | 31 May 1994 | 29 May 1992 | 29 May 2012 | Predictive coding using spatial-temporal filtering and plural motion vectors | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5317397 file+20: [2012, 5, 29] grant+17:[2011, 5, 31] | Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
| 5424779 | 24 nov 1993 | 13 jun 1995 | 32 May 1992 | 13 jun 2012 | Video coding apparatus | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5424779 file+20: [2013, 11, 24] related_patent+20:[2012, 5, 32] grant+17:[2012, 6, 13] Case Text: This is a continuation, of application Ser. No. 07/890,705, filed on May 29, 1992 now U.S. Pat. No. 5,317,397. | Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
| 5467136 | 17 feb 1994 | 14 nov 1995 | 32 May 1992 | 14 nov 2012 | Video decoder for determining a motion vector from a scaled vector and a difference vector | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5467136 file+20: [2014, 2, 17] related_patent+20:[2012, 5, 32] grant+17:[2012, 11, 14] Case Text: CROSS-REFERENCE TO THE RELATED APPLICATION This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/890,705 filed May 29, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,317,397. | Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
| 5742344 | 03 apr 1996 | 21 apr 1998 | 32 May 1992 | 32 May 2012 | Motion compensated video decoding method and system for decoding a coded video signal using spatial and temporal filtering | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5742344 file+20: [2016, 4, 3] related_patent+20:[2012, 5, 32] Case Text: This is a Division of application Ser. No. 08/295,421 filed on Aug. 25, 1994, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,5,41,661, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/156,709 filed on Nov. 24, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,424,779, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/890,705 filed May 29, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,317,397. | Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
| 5986713 | 11 jun 1998 | 16 nov 1999 | 32 May 1992 | 32 May 2012 | Video coding apparatus using inter-field prediction | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5986713 file+20: [2018, 6, 11] related_patent+20:[2012, 5, 32] Case Text: This application is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 09/054,403, filed on Apr. 3, 1998; which is a Division of Ser. No. 08/626,922 filed on Apr. 3, 1996, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,754,231; which is a Division of Ser. No. 08/295,421, filed on Aug. 25, 1994, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,541,661; which is a Continuation of Ser. No. 08/156,709, filed on Nov. 24, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,424,779; which is a Continuation of Ser. No. 07/890,705, filed on May 29, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,317,397. | Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
| RE34965 | 18 jan 1990 | 15 jan 1991 | 18 jan 1990 | 18 jan 2010 | Inter-frame predictive encoding system with encoded and transmitted prediction error | Reissue of 04985768 filed 14 jan 1993 granted 13 jun 1995 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE34965 file+20: [2010, 1, 18] related_patent+20:[2010, 1, 32] grant+17:[2008, 1, 15] | Victor Company JVC , usually referred to as JVC, is a Japanese international consumer and professional electronics corporation based in Yokohama, Japan which was founded in 1927... |
| RE35158 | 26 apr 1990 | 01 jan 1991 | 16 jan 1990 | 16 jan 2010 | Apparatus for adaptive inter-frame predictive encoding of video signal | Reissue of 04982285 filed 28 dec 1992 granted 20 feb 1996 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE35158 file+20: [2010, 4, 26] related_patent+20:[2010, 1, 16] grant+17:[2008, 1, 1] Case Text: The present application is a .Iadd.reissue of application No. 514,015 now U.S. Pat. No. 4,982,285, which is a .Iaddend.continuation-in-part of a U.S. patent application (application number 465,747) with filing date Jan. 16, 1990.Iadd., now U.S. Pat. No. 4,985,768.Iaddend.. | Victor Company JVC , usually referred to as JVC, is a Japanese international consumer and professional electronics corporation based in Yokohama, Japan which was founded in 1927... |
| RE36822 | 17 jun 1996 | 5 May 1998 | 06 nov 1992 | 06 nov 2012 | Moving image signal coding apparatus and coded signal decoding apparatus | Reissue of 05748784 filed 02 oct 1998 granted 15 aug 2000 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE36822 file+20: [2016, 6, 17] related_patent+20:[2012, 11, 6] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/324,481, filed Oct. 18, 1994 which was abandoned upon the filing hereof, and which, in turn, is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/972,564, filed Nov. 6, 1992 now abandoned. | Victor Company JVC , usually referred to as JVC, is a Japanese international consumer and professional electronics corporation based in Yokohama, Japan which was founded in 1927... |
| 5103307 | 18 jan 1991 | 07 apr 1992 | 18 jan 1991 | 18 jan 2011 | Interframe predictive coding/decoding system for varying interval between independent frames | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5103307 file+20: [2011, 1, 18] grant+17:[2009, 4, 7] | Victor Company JVC , usually referred to as JVC, is a Japanese international consumer and professional electronics corporation based in Yokohama, Japan which was founded in 1927... |
| 5175618 | 30 oct 1991 | 29 dec 1992 | 30 oct 1991 | 30 oct 2011 | Compression method for interlace moving image signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5175618 file+20: [2011, 10, 30] grant+17:[2009, 12, 29] | Victor Company JVC , usually referred to as JVC, is a Japanese international consumer and professional electronics corporation based in Yokohama, Japan which was founded in 1927... |
| 5341457 | 20 aug 1993 | 23 aug 1994 | 30 dec 1988 | 23 aug 2011 | Perceptual coding of audio signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5341457 file+20: [2013, 8, 20] related_patent+20:[2008, 12, 30] grant+17:[2011, 8, 23] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/962,151, filed on Oct. 16, 1992 abandoned which is a cont. of Ser. No. 07/844,967 filed Feb. 28, 1992, now abandoned, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/292,598 filed on Dec. 30, 1988, now abandoned, and claims priority thereto. | Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent is a global telecommunications corporation, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It provides telecommunications solutions to service providers, enterprises, and governments around the world, enabling these customers to deliver voice, data, and video services... |
| RE39080 | 22 sep 1994 | 6 May 1997 | 30 dec 1988 | 6 May 2014 | Rate loop processor for perceptual encoder/decoder | Reissue of 05627938 filed 13 aug 2002 granted 25 apr 2006 http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=RE39080 file+20: [2014, 9, 22] related_patent+20:[2008, 12, 30] grant+17:[2014, 5, 6] Case Text: This .Iadd.is a reissue .Iaddend.application .Iadd.of U.S. Pat. No. 5,627,938 filed Sep. 22, 1994 as application Ser. No. 08/310,898 which .Iaddend.is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/844,811, filed on Mar. 2, 1992, now abandoned.Iadd., which is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 07/844,967 filed Feb. 28, 1992, now abandoned, which is a continuation of Ser. No. 07/292,598 filed Dec. 30, 1988 now abandoned.Iaddend.. | Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent Alcatel-Lucent is a global telecommunications corporation, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It provides telecommunications solutions to service providers, enterprises, and governments around the world, enabling these customers to deliver voice, data, and video services... |
| 4972484 | 21 jul 1988 | 20 nov 1990 | 20 nov 1987 | 20 nov 2007 | Method of transmitting or storing masked sub-band coded audio signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4972484 file+20: [2008, 7, 21] pct_file+20:[2007, 11, 20] grant+17:[2007, 11, 20] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5214678 | 31 May 1990 | 25 May 1993 | 31 May 1990 | 31 May 2010 | Digital transmission system using subband coding of a digital signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5214678 file+20: [2010, 5, 31] grant+17:[2010, 5, 25] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5323396 | 21 dec 1992 | 21 jun 1994 | 01 jun 1990 | 21 jun 2011 | Digital transmission system, transmitter and receiver for use in the transmission system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5323396 file+20: [2012, 12, 21] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] grant+17:[2011, 6, 21] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462 filed Jun. 1, 1990 now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5539829 | 07 jun 1995 | 23 jul 1996 | 01 jun 1990 | 23 jul 2013 | Subband coded digital transmission system using some composite signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5539829 file+20: [2015, 6, 7] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] grant+17:[2013, 7, 23] Case Text: This application is a division of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08/173,850 filed Dec. 27, 1993, which is continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/997,158 filed Dec. 21, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,323,396, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462 filed on Jun. 1, 1990 by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff for DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER FOR USE IN THE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, AND RECORD CARRIER OBTAINED BY MEANS OF THE TRANSMITTER IN THE FORM OF A RECORDING DEVICE, now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5606618 | 27 dec 1993 | 25 feb 1997 | 01 jun 1990 | 25 feb 2014 | Subband coded digital transmission system using some composite signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5606618 file+20: [2013, 12, 27] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] grant+17:[2014, 2, 25] Case Text: This application is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/997,158 filed Dec. 21, 1992 now U.S Pat. No. 5,32,396, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462 filed on Jun. 1, 1990 by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff for DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER FOR USE IN THE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, AND RECORD CARRIER OBTAINED BY MEANS OF THE TRANSMITTER IN THE FORM OF A RECORDING DEVICE, now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5530655 | 06 jun 1995 | 25 jun 1996 | 01 jun 1990 | 25 jun 2013 | Digital sub-band transmission system with transmission of an additional signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5530655 file+20: [2015, 6, 6] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] grant+17:[2013, 6, 25] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/190,807, filed Feb. 1, 1994, now abandoned, which is a continuation of co-pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08/173,850 filed Dec. 27, 1993, by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff, Y. F. Dehery, and G. Stoll for SUBBAND CODED DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING SOME COMPOSITE SIGNALS, which is a continuation of co-pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/997,158 filed Dec. 21, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,323,396 issued Jun. 21, 1994, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462, filed on Jun. 1, 1990 by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff for DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER FOR USE IN THE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, AND RECORD CARRIER OBTAINED BY MEANS OF THE TRANSMITTER IN THE FORM OF A RECORDING DEVICE, now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5777992 | 07 jun 1995 | 07 jul 1998 | 01 jun 1990 | 07 jul 2015 | Decoder for decoding and encoded digital signal and a receiver comprising the decoder | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5777992 file+20: [2015, 6, 7] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] grant+17:[2015, 7, 7] Case Text: This application is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08/173,850 filed Dec. 27, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,606,618, which is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 07/997,158 filed Dec. 21, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,323,396, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462 filed on Jun. 1, 1990 by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff for DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER FOR USE IN THE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, AND RECORD CARRIER OBTAINED BY MEANS OF THE TRANSMITTER IN THE FORM OF A RECORDING DEVICE, now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 6289308 | 08 mar 2000 | 11 sep 2001 | 01 jun 1990 | 01 jun 2010 | Encoded wideband digital transmission signal and record carrier recorded with such a signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6289308 file+20: [2020, 3, 8] related_patent+20:[2010, 6, 1] term extension 0 days Case Text: This application is a division of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 08/488,536 filed Jun. 7, 1995 now abandoned, which is a division of application Ser. No. 08/173,850 filed Dec. 27, 1993, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,606,618, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/997,158 filed Dec. 21, 1992, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,323,396, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/532,462 filed on Jun. 1, 1990 now abandoned, by Gerardus C. P. Lokhoff for DIGITAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER FOR USE IN THE TRANSMISSION SYSTEM, AND RECORD CARRIER OBTAINED BY MEANS OF THE TRANSMITTER IN THE FORM OF A RECORDING DEVICE, now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5481643 | 24 apr 1995 | 02 jan 1996 | 18 mar 1993 | 18 mar 2013 | Transmitter, receiver and record carrier for transmitting/receiving at least a first and a second signal component | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5481643 file+20: [2015, 4, 24] related_patent+20:[2013, 3, 18] grant+17:[2013, 1, 2] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/180,004, filed Jan. 11, 1994 which is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 08/032,915, filed Mar. 18, 1993, both now abandoned. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5544247 | 25 oct 1994 | 06 aug 1996 | 25 oct 1994 | 25 oct 2014 | Transmission and reception of a first and a second main signal component | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5544247 file+20: [2014, 10, 25] grant+17:[2013, 8, 6] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5610985 | 21 jan 1994 | 11 mar 1997 | 21 jan 1994 | 11 mar 2014 | Digital 3-channel transmission of left and right stereo signals and a center signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5610985 file+20: [2014, 1, 21] grant+17:[2014, 3, 11] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5740317 | 30 aug 1995 | 14 apr 1998 | 21 jul 1992 | 14 apr 2015 | Process for finding the overall monitoring threshold during a bit-rate-reducing source coding | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5740317 file+20: [2015, 8, 30] related_patent+20:[2013, 9, 17] pct_file+20:[2012, 7, 21] grant+17:[2015, 4, 14] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/119,109, filed Sep. 17, 1993 (now abandoned). | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5878080 | 07 feb 1997 | 02 mar 1999 | 07 feb 1997 | 07 feb 2017 | N-channel transmission, compatible with 2-channel transmission and 1-channel transmission | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5878080 file+20: [2017, 2, 7] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5960037 | 09 apr 1997 | 28 sep 1999 | 09 apr 1997 | 09 apr 2017 | Encoding of a plurality of information signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5960037 file+20: [2017, 4, 9] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 5991715 | 31 aug 1995 | 23 nov 1999 | 31 aug 1995 | 31 aug 2015 | Perceptual audio signal subband coding using value classes for successive scale factor differences | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5991715 file+20: [2015, 8, 31] Case Text: This application is a Continuation of application Ser. No. 08/094,028, filed Jul. 26, 1993 (now abandoned), which is a 371 of PCT/EP91/01211 Jun. 6, 1991. | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 6023490 | 09 apr 1997 | 08 feb 2000 | 09 apr 1997 | 09 apr 2017 | Encoding apparatus for encoding a plurality of information signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6023490 file+20: [2017, 4, 9] | Audio MPEG, Inc |
| 4821260 | 16 dec 1987 | 11 apr 1989 | 16 dec 1987 | 16 dec 2007 | Transmission system | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4821260 file+20: [2007, 12, 16] grant+17:[2006, 4, 11] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 4942607 | 03 feb 1988 | 17 jul 1990 | 03 feb 1988 | 03 feb 2008 | Method of transmitting an audio signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4942607 file+20: [2008, 2, 3] grant+17:[2007, 7, 17] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5214742 | 01 oct 1990 | 25 May 1993 | 26 jan 1990 | 25 May 2010 | Method for transmitting a signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5214742 file+20: [2010, 10, 1] pct_file+20:[2010, 1, 26] grant+17:[2010, 5, 25] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5227990 | 17 jan 1992 | 13 jul 1993 | 17 jan 1992 | 17 jan 2012 | Process for transmitting and receiving a signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5227990 file+20: [2012, 1, 17] grant+17:[2010, 7, 13] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5384811 | 24 aug 1992 | 24 jan 1995 | 08 oct 1990 | 24 jan 2012 | Method for the transmission of a signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5384811 file+20: [2012, 8, 24] pct_file+20:[2010, 10, 8] grant+17:[2012, 1, 24] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5736943 | 31 May 1996 | 07 apr 1998 | 08 jul 1994 | 07 apr 2015 | Method for determining the type of coding to be selected for coding at least two signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5736943 file+20: [2016, 5, 31] pct_file+20:[2014, 7, 8] grant+17:[2015, 4, 7] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5455833 | 26 apr 1993 | 03 oct 1995 | 25 oct 1990 | 03 oct 2012 | Process for the detecting of errors in the transmission of frequency-coded digital signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5455833 file+20: [2013, 4, 26] pct_file+20:[2010, 10, 25] grant+17:[2012, 10, 3] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5559834 | 15 apr 1994 | 24 sep 1996 | 06 oct 1992 | 24 sep 2013 | Method of reducing crosstalk in processing of acoustic or optical signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5559834 file+20: [2014, 4, 15] pct_file+20:[2012, 10, 6] grant+17:[2013, 9, 24] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5321729 | 26 apr 1993 | 14 jun 1994 | 24 jun 1991 | 24 jun 2011 | Method for transmitting a signal | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5321729 file+20: [2013, 4, 26] related_patent+20:[2011, 6, 24] grant+17:[2011, 6, 14] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/718,402, filed Jun. 24, 1991, now abandoned. | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5706309 | 2 May 1995 | 06 jan 1998 | 02 nov 1993 | 06 jan 2015 | Process for transmitting and/or storing digital signals of multiple channels | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5706309 file+20: [2015, 5, 2] pct_file+20:[2013, 11, 2] grant+17:[2015, 1, 6] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5701346 | 12 sep 1996 | 23 dec 1997 | 02 feb 1995 | 02 feb 2015 | Method of coding a plurality of audio signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5701346 file+20: [2016, 9, 12] pct_file+20:[2015, 2, 2] grant+17:[2014, 12, 23] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5742735 | 25 aug 1994 | 21 apr 1998 | 20 apr 1989 | 21 apr 2015 | Digital adaptive transformation coding method | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5742735 file+20: [2014, 8, 25] related_patent+20:[2009, 4, 20] grant+17:[2015, 4, 21] Case Text: This is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/133,273 filed Oct. 7, 1993 now abandoned which is a continuation of Ser. No. 07/982,063 filed Nov. 25, 1992 now abandoned, which is a continuation of Ser. No. 07/716,769 filed Jun. 19, 1991 now abandoned, which is a continuation of Ser. No. 07/347,806, filed as PCT/DE88/00618, Oct. 6, 1988 published as WO89/03574, Apr. 20, 1989 now abandoned. | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5812672 | 15 dec 1994 | 22 sep 1998 | 13 oct 1992 | 22 sep 2015 | Method for reducing data in the transmission and/or storage of digital signals of several dependent channels | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5812672 file+20: [2014, 12, 15] pct_file+20:[2012, 10, 13] grant+17:[2015, 9, 22] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5579430 | 26 jan 1995 | 26 nov 1996 | 32 dec 1991 | 26 nov 2013 | Digital encoding process | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5579430 file+20: [2015, 1, 26] related_patent+20:[2011, 12, 32] grant+17:[2013, 11, 26] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/169,768, filed on Dec. 20, 1993, now abandoned, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/768,239, filed as PCT/DE90/00286 on Apr. 12, 1990, which is now abandoned. | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 6185539 | 26 May 1998 | 06 feb 2001 | 19 feb 1997 | 19 feb 2017 | Process of low sampling rate digital encoding of audio signals | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6185539 file+20: [2018, 5, 26] pct_file+20:[2017, 2, 19] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 6009399 | 16 apr 1997 | 28 dec 1999 | 16 apr 1997 | 16 apr 2017 | Method and apparatus for encoding digital signals employing bit allocation using combinations of different threshold models to achieve desired bit rates | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=6009399 file+20: [2017, 4, 16] | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5924060 | 20 mar 1997 | 13 jul 1999 | 14 jan 1991 | 14 jan 2011 | Digital coding process for transmission or storage of acoustical signals by transforming of scanning values into spectral coefficients | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5924060 file+20: [2017, 3, 20] related_patent+20:[2011, 1, 14] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/650,896, filed on May 17, 1996, (now abandoned) which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/519,620, filed on Sep. 25, 1995, (now abandoned) which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/977,748, filed on Nov. 16, 1992, (now abandoned), which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/816,528, filed on Dec. 30, 1991, (now abandoned), which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/640,550, filed on Jan. 14, 1991, (now abandoned), which was a continuation of application Ser. No. 07/177,550, filed on Apr. 4, 1991, (now abandoned) as international application serial No. PCT/DE87/00384, filed Aug. 29, 1987, claiming priority to foreign appl. No. P3629434.9, filed Aug. 29, 1986. | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
| 5703999 | 18 nov 1996 | 30 dec 1997 | 32 feb 1995 | 32 feb 2015 | Process for reducing data in the transmission and/or storage of digital signals from several interdependent channels | http://patft1.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5703999 file+20: [2016, 11, 18] related_patent+20:[2015, 2, 32] Case Text: This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 08/338,618, filed as PCT/DE93/00448 May 18, 1993. | Thomson Thomson -People:* Thomson , includes a list of people with this name and a description of its origin-Science:*thomson , a unit for mass-to-charge ratio, symbol: Th; named in honor of J. J... |
According to the MPEG-LA Licensing Agreement MPEG-LA, any use of MPEG-2 technology is subject to royalties
Royalties
Royalties are usage-based payments made by one party to another for the right to ongoing use of an asset, sometimes an intellectual property...
.
- Encoders are subject to a royalty of $2.00 per unit.
- Decoders are subject to a royalty of $2.00 per unit.
- Royalty-based sales of encoders and decoders are subject to different rules and $2.50 per unit.
- Also, any packaged medium (DVDs/Data Streams) is subject to licence fees according to length of recording/broadcast.
In the case of free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
such as VLC media player
VLC media player
VLC media player is a free and open source media player and multimedia framework written by the VideoLAN project.VLC is a portable multimedia player, encoder, and streamer supporting many audio and video codecs and file formats as well as DVDs, VCDs, and various streaming protocols. It is able to...
(which uses the ffmpeg
FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a free software project that produces libraries and programs for handling multimedia data. The most notable parts of FFmpeg are libavcodec, an audio/video codec library used by several other projects, libavformat, an audio/video container mux and demux library, and the ffmpeg command line...
library) and in which the software is not sold, the end-user bears the royalty.
See also
- MPEG encodingMPEG encodingMPEG encoding is the process of capturing or converting video and/or audio to one of several MPEG video and/or audio standards for distribution or for archiving to optical disc...
- MPEG-1 Audio Layer II (MP2)MPEG-1 Audio Layer IIMPEG-1 Audio Layer II or MPEG-2 Audio Layer II is a lossy audio compression format defined by ISO/IEC 11172-3 alongside MPEG-1 Audio Layer I and MPEG-1 Audio Layer III...
- MPEG-1 Audio Layer III (MP3)MP3MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
- DVDDVDA DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
- DVB-S2DVB-S2Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the , an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI in March 2005...
External links
- A Beginners Guide for MPEG-2 Standard
- MPEG-2 Overview (figures are lost)
- MPEG-2 video compression
- MIT 6.344 – Slides from lectures on video compression at MIT.
- A Discrete Cosine Transform tutorial
- IPTV MPEG and Quality of Experience Testing
- OpenIPMP: Open Source DRM Project for MPEG-2
- ISO/IEC 13818 – MPEG-2 at the ISO Store.
- MPEG Books - A list of MPEG reference books.

