
Interface conditions for electromagnetic fields
Encyclopedia
Maxwell's equations
describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields; electric field
, electric displacement field, magnetic field
and magnetic field strength. The differential forms of these equations require that there's always an open neighbourhood around the point they're applied to, otherwise the vector fields E, D, B and H are not differentiable. In other words the medium must be continuous. On the interface of two different medium with different values for electrical permittivity
and magnetic permeability
that doesn't apply.
However the interface conditions for the electromagnetic field vectors can be derived from the integral forms of Maxwell's equations.
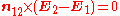
where:
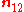 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
Therefore the tangential component of E is continuous across the interface.
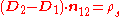
where:
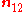 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
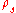 is the surface charge
is the surface charge
between the media.
Therefore the normal component of D has a step of surface charge on the interface surface. If there's no surface charge on the interface, the normal component of D is continuous.
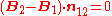
where:
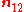 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
Therefore the normal component of B is continuous across the interface.
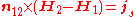
where:
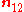 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
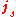 is the surface current density
is the surface current density
between the two media.
Therefore the tangential component of H is continuous across the surface if there's no surface current present.
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields; electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
, electric displacement field, magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
and magnetic field strength. The differential forms of these equations require that there's always an open neighbourhood around the point they're applied to, otherwise the vector fields E, D, B and H are not differentiable. In other words the medium must be continuous. On the interface of two different medium with different values for electrical permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
and magnetic permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
that doesn't apply.
However the interface conditions for the electromagnetic field vectors can be derived from the integral forms of Maxwell's equations.
For electric field
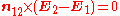
where:
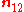 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.Therefore the tangential component of E is continuous across the interface.
For electric displacement field
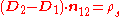
where:
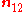 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.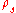 is the surface charge
is the surface chargeSurface charge
Surface charge is the electric charge present at an interface. There are many different processes which can lead to a surface being charged, including adsorption of ions, protonation/deprotonation, and the application of an external electric field...
between the media.
Therefore the normal component of D has a step of surface charge on the interface surface. If there's no surface charge on the interface, the normal component of D is continuous.
For magnetic field
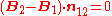
where:
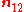 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.Therefore the normal component of B is continuous across the interface.
For magnetic field strength
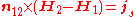
where:
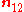 is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.
is normal vector from medium 1 to medium 2.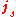 is the surface current density
is the surface current densityCurrent density
Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
between the two media.
Therefore the tangential component of H is continuous across the surface if there's no surface current present.

