Interferometric microscopy
Encyclopedia
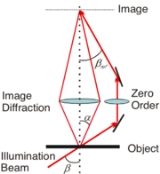
Interferometric microscopy or Imaging interferometric microscopy is the concept of microscopy which
is related to holography
, synthetic-aperture imaging, and off-axis
-dark-field illumination techniques.
Interferometric microscopy allows enhancement of resolution of optical microscopy due to interferometric (holographic
)
registration of several partial images (amplitude and phase) and the numerical combining.
 In interferometric microscopy, the image of a micro-object is synthesized numerically as a coherent combination
In interferometric microscopy, the image of a micro-object is synthesized numerically as a coherent combination
of partial images with registered amplitude and phase
For registration of partial images, the conventional holographic
set-up is used,
with the reference wave, which is usual for the optical holography
.
The multiple exposition allows the numerical emulation of a large Numerical Aperture
objective,
at moderate values of the Numerical Aperture
of the objective used to register partial images
.
Similar techniques allows scanning and precise detection of small particles
.
As the combined image keeps both amplitude and phase information, the interferometric microscopy can be especially efficient for the phase objects
, allowing detection of light variations of index of refraction, which cause the phase shift or the light passing through for a small fraction of a radian.
, or optics of neutral atom beams (see Atomic de Broglie microscope), where the Numerical aperture is usually very limited
.
, Numerical Aperture
, Diffraction limited
is related to holography
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
, synthetic-aperture imaging, and off-axis
Off-axis illumination
In photolithography, off-axis illumination is an optical system setup in which the incoming light strikes the photomask at an oblique angle rather than perpendicularly to it, that is to say, the incident light is not parallel to the axis of the optical system....
-dark-field illumination techniques.
Interferometric microscopy allows enhancement of resolution of optical microscopy due to interferometric (holographic
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
)
registration of several partial images (amplitude and phase) and the numerical combining.
Combining of partial images

of partial images with registered amplitude and phase
For registration of partial images, the conventional holographic
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
set-up is used,
with the reference wave, which is usual for the optical holography
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
.
The multiple exposition allows the numerical emulation of a large Numerical Aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
objective,
at moderate values of the Numerical Aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
of the objective used to register partial images
.
Similar techniques allows scanning and precise detection of small particles
.
As the combined image keeps both amplitude and phase information, the interferometric microscopy can be especially efficient for the phase objects
, allowing detection of light variations of index of refraction, which cause the phase shift or the light passing through for a small fraction of a radian.
Non-optical waves
Although the Interferometric microscopy has been demonstrated only for optical images (visible light), this technics may find application in high resolution atom opticsAtom optics
Atom optics is the area of physics which deals with beams of cold, slowly moving neutral atoms, as a special case of a particle beam....
, or optics of neutral atom beams (see Atomic de Broglie microscope), where the Numerical aperture is usually very limited
.
See also
HolographyHolography
Holography is a technique that allows the light scattered from an object to be recorded and later reconstructed so that when an imaging system is placed in the reconstructed beam, an image of the object will be seen even when the object is no longer present...
, Numerical Aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
, Diffraction limited

