Interferometric visibility
Encyclopedia
The interferometric visibility (also known as "interference visibility" or "fringe visibility" or just "visibility") quantifies the contrast of interference in any system which has wave-like properties, such as optics
, quantum mechanics
, water waves, or electrical signals. Generally, two or more waves are combined and as the phase between them is changed (e.g. in an interferometer) the power
or intensity
(probability or population in quantum mechanics
) of the resulting wave oscillates (forming an interference pattern). The ratio of the size or amplitude
of these oscillations to the sum of the powers of the individual waves is defined as the visibility.
, Michelson interferometer
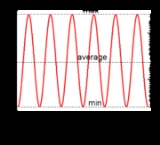
, and Sagnac interferometer interference manifests itself as oscillations in the outgoing intensity, also called "fringes". Under these circumstances, the interferometric visibility is also known as the "Michelson visibility" or the "fringe visibility." For this type of interference, the sum of the intensities (or powers) of the two interfering waves equals the average of the fringes. It follows that the visibility can be written as,

This can also be rewritten as

where max is the maximum of the oscillations and min the minimum of the oscillations. If the two optical fields are ideally monochromatic (consist of only single wavelength) point sources then the predicted visibility will be

where and
and  indicates the intensity of the respective wave. Any dissimilarity between the optical fields will decrease the visibility from the ideal. In this sense, the visibility is a measure of the coherence
indicates the intensity of the respective wave. Any dissimilarity between the optical fields will decrease the visibility from the ideal. In this sense, the visibility is a measure of the coherence
between two optical fields. A more general formula for this is given by the degree of coherence. This definition of interference directly applies to the interference of water waves and electric signals.
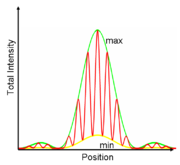
is a wave equation
and all objects can be considered waves in quantum mechanics
, interference is ubiquitous. Some examples: Bose-Einstein condensates can exhibit interference fringes. Atomic populations show interference in a Ramsey interferometer. Photons, atoms, electrons, neutrons, and molecules have exhibited interference in double-slit interferometers.

Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, water waves, or electrical signals. Generally, two or more waves are combined and as the phase between them is changed (e.g. in an interferometer) the power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
or intensity
Intensity (physics)
In physics, intensity is a measure of the energy flux, averaged over the period of the wave. The word "intensity" here is not synonymous with "strength", "amplitude", or "level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech...
(probability or population in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
) of the resulting wave oscillates (forming an interference pattern). The ratio of the size or amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
of these oscillations to the sum of the powers of the individual waves is defined as the visibility.
Visibility in optics
In linear optical interferometers like the Mach-Zehnder interferometerMach-Zehnder interferometer
The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift between two collimated beams from a coherent light source. The interferometer has been used, amongst other things, to measure small phase shifts in one of the two beams caused by a small sample or the change in...
, Michelson interferometer
Michelson interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is the most common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by Albert Abraham Michelson. An interference pattern is produced by splitting a beam of light into two paths, bouncing the beams back and recombining them...
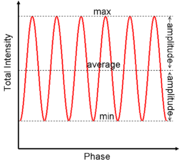
, and Sagnac interferometer interference manifests itself as oscillations in the outgoing intensity, also called "fringes". Under these circumstances, the interferometric visibility is also known as the "Michelson visibility" or the "fringe visibility." For this type of interference, the sum of the intensities (or powers) of the two interfering waves equals the average of the fringes. It follows that the visibility can be written as,

This can also be rewritten as

where max is the maximum of the oscillations and min the minimum of the oscillations. If the two optical fields are ideally monochromatic (consist of only single wavelength) point sources then the predicted visibility will be

where
 and
and  indicates the intensity of the respective wave. Any dissimilarity between the optical fields will decrease the visibility from the ideal. In this sense, the visibility is a measure of the coherence
indicates the intensity of the respective wave. Any dissimilarity between the optical fields will decrease the visibility from the ideal. In this sense, the visibility is a measure of the coherenceCoherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
between two optical fields. A more general formula for this is given by the degree of coherence. This definition of interference directly applies to the interference of water waves and electric signals.


Visibility in quantum mechanics
Since the Schrödinger equationSchrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
is a wave equation
Wave equation
The wave equation is an important second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves – as they occur in physics – such as sound waves, light waves and water waves. It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetics, and fluid dynamics...
and all objects can be considered waves in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, interference is ubiquitous. Some examples: Bose-Einstein condensates can exhibit interference fringes. Atomic populations show interference in a Ramsey interferometer. Photons, atoms, electrons, neutrons, and molecules have exhibited interference in double-slit interferometers.

See also
- degree of coherence
- interferometryInterferometryInterferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
- optical interferometryOptical interferometryOptical interferometry combines two or more light waves in an opticalinstrument in such a way that interference occurs between them.Early interferometers used white light sources and also monochromatic light from atomic sources...
- List of types of interferometers
- Hong–Ou–Mandel effect

