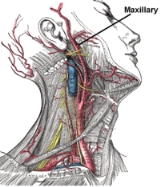
Internal maxillary artery
Encyclopedia
The maxillary artery is an artery that supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery
just deep to the neck of the mandible.
 The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery
The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery
, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland
; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament
, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle
, to the pterygopalatine fossa
.
It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid
, and pterygopalatine
portions.
; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve
, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pterygoid muscle
.
Branches include:
; it then passes between the two heads of origin of this muscle and enters the fossa.
Branches include:
in relation with the pterygopalatine ganglion
. This is considered the terminal branch of the maxillary artery.
Branches include:
Mnemonic to remember branches: D
A
M
I
AM
P
iss D
runk, But S
tupid D
runk I
P
refer, Must Phone Alcoholics Anonymous.
In order: DAM Artery! I Made Dolly Parton's Bra Pop & I Didn't Stop!
External carotid artery
In human anatomy, the external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery.-Course:...
just deep to the neck of the mandible.
Structure

External carotid artery
In human anatomy, the external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery.-Course:...
, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland
Parotid gland
The paired parotid glands are the largest of the salivary glands. They are each found wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secrete saliva through Stensen's ducts into the oral cavity, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches.-Location:The parotid glands...
; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
The sphenomandibular ligament is a flat, thin band which is attached above to the spina angularis of the sphenoid bone, and, becoming broader as it descends, is fixed to the lingula of the mandibular foramen...
, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle
Lateral pterygoid muscle
The lateral pterygoid is a muscle of mastication with two heads. It lies superiorly to the medial pterygoid.-Origin and insertion:...
, to the pterygopalatine fossa
Pterygopalatine fossa
The pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen.-Boundaries:It has the following boundaries:...
.
It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid
Pterygoid
Pterygoid can refer to:* Pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone** The Lateral pterygoid plate by it* a muscle such as Lateral pterygoid muscle or Medial pterygoid muscle* a branch of the Mandibular nerve...
, and pterygopalatine
Pterygopalatine
Pterygopalatine is used to refer to structures of the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid and the palatine bone. Specifically, it can refer to:* Pterygopalatine fossa* Pterygopalatine canal* Pterygopalatine ganglion...
portions.
First portion
The first or mandibular portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerveAuriculotemporal nerve
The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head.-Origin:...
; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve .-Path:...
, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pterygoid muscle
Lateral pterygoid muscle
The lateral pterygoid is a muscle of mastication with two heads. It lies superiorly to the medial pterygoid.-Origin and insertion:...
.
Branches include:
- Deep auricular arteryDeep auricular arteryThe deep auricular artery often arises in common with the anterior tympanic artery.It ascends in the substance of the parotid gland, behind the temporomandibular articulation, pierces the cartilaginous or bony wall of the external acoustic meatus, and supplies its cuticular lining and the outer...
- Anterior tympanic arteryAnterior tympanic arteryThe anterior tympanic artery usually arises as a branch of the mandibular part of the maxillary artery. It passes upward behind the temporomandibular articulation, enters the tympanic cavity through the petrotympanic fissure, and ramifies upon the tympanic membrane, forming a vascular circle...
- Middle meningeal arteryMiddle meningeal arteryThe middle meningeal artery is typically the third branch of the first part of the maxillary artery, one of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery...
- Inferior alveolar arteryInferior alveolar artery- Course :It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible.It runs along the mandibular canal in the substance of the bone, accompanied by the nerve, and opposite the first premolar tooth divides into two branches, incisor and...
which gives off its mylohyoid branch just prior to entering the mandibular foramenMandibular foramenThe Mandibular foramen is an opening on the internal surface of the ramus for divisions of the mandibular vessels and nerve to pass.-Contents:... - Accessory meningeal artery
Second portion
The second or pterygoid portion runs obliquely forward and upward under cover of the ramus of the mandible and insertion of the temporalis, on the superficial (very frequently on the deep) surface of the lateral pterygoid muscleLateral pterygoid muscle
The lateral pterygoid is a muscle of mastication with two heads. It lies superiorly to the medial pterygoid.-Origin and insertion:...
; it then passes between the two heads of origin of this muscle and enters the fossa.
Branches include:
- Masseteric arteryMasseteric arteryThe masseteric artery is small and passes laterally through the mandibular notch to the deep surface of the masseter muscle, which it supplies.It anastomoses with the masseteric branches of the external maxillary artery and with the transverse facial artery....
- Pterygoid branchesPterygoid branches of maxillary arteryThe pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, irregular in their number and origin, supply the lateral pterygoid muscle and medial pterygoid muscle.-External links:*...
- Deep temporal arteriesDeep temporal arteriesThe deep temporal arteries, two in number, anterior and posterior, ascend between the Temporalis and the pericranium.They supply the muscle, and anastomose with the middle temporal artery....
(anterior and posterior) - Buccal artery
Third portion
The third or pterygopalatine portion lies in the pterygopalatine fossaPterygopalatine fossa
The pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen.-Boundaries:It has the following boundaries:...
in relation with the pterygopalatine ganglion
Pterygopalatine ganglion
The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion found in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck....
. This is considered the terminal branch of the maxillary artery.
Branches include:
- Sphenopalatine arterySphenopalatine arteryThe sphenopalatine artery is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis.-Course:The sphenopalatine artery is a branch of the maxillary artery which passes through the sphenopalatine foramen into the cavity of the nose, at the back part of the superior meatus...
(Nasopalatine artery is the terminal branch of the Maxillary artery) - Descending palatine arteryDescending palatine artery-Course:It descends through the pterygopalatine canal with the anterior palatine branch of the sphenopalatine ganglion, and, emerging from the greater palatine foramen, runs forward in a groove on the medial side of the alveolar border of the hard palate to the incisive canal; the terminal branch...
- Infraorbital arteryInfraorbital arteryThe infraorbital artery is an artery in the head that runs in the maxilla, emerging through the infraorbital foramen, just under the orbit of the eye.-Course:...
- Posterior superior alveolar arteryPosterior superior alveolar arteryThe posterior superior alveolar artery is given off from the maxillary, frequently in conjunction with the infraorbital artery just as the trunk of the vessel is passing into the pterygopalatine fossa.-Branches:...
- Artery of pterygoid canal
- Pharyngeal artery
- Middle superior alveolar
- Anterior Superior Alveolar
Nomenclature
- Formerly, the term "external maxillary artery" was used to describe what is now known as the facial arteryFacial arteryThe facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.-Structure:...
(per Terminologia anatomicaTerminologia AnatomicaTerminologia Anatomica is the international standard on human anatomic terminology. It was developed by the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology and the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists and was released in 1998. It supersedes the previous standard, Nomina...
.) Currently, the term "external maxillary artery" is less commonly used, and the terms "internal maxillary artery" and "maxillary artery" are equivalent.
Mnemonic to remember branches: D
Deep auricular artery
The deep auricular artery often arises in common with the anterior tympanic artery.It ascends in the substance of the parotid gland, behind the temporomandibular articulation, pierces the cartilaginous or bony wall of the external acoustic meatus, and supplies its cuticular lining and the outer...
A
Anterior tympanic artery
The anterior tympanic artery usually arises as a branch of the mandibular part of the maxillary artery. It passes upward behind the temporomandibular articulation, enters the tympanic cavity through the petrotympanic fissure, and ramifies upon the tympanic membrane, forming a vascular circle...
M
Middle meningeal artery
The middle meningeal artery is typically the third branch of the first part of the maxillary artery, one of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery...
I
Inferior alveolar artery
- Course :It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible.It runs along the mandibular canal in the substance of the bone, accompanied by the nerve, and opposite the first premolar tooth divides into two branches, incisor and...
AM
Masseteric artery
The masseteric artery is small and passes laterally through the mandibular notch to the deep surface of the masseter muscle, which it supplies.It anastomoses with the masseteric branches of the external maxillary artery and with the transverse facial artery....
P
Pterygoid branches of maxillary artery
The pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, irregular in their number and origin, supply the lateral pterygoid muscle and medial pterygoid muscle.-External links:*...
iss D
Deep temporal arteries
The deep temporal arteries, two in number, anterior and posterior, ascend between the Temporalis and the pericranium.They supply the muscle, and anastomose with the middle temporal artery....
runk, But S
Sphenopalatine artery
The sphenopalatine artery is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis.-Course:The sphenopalatine artery is a branch of the maxillary artery which passes through the sphenopalatine foramen into the cavity of the nose, at the back part of the superior meatus...
tupid D
Descending palatine artery
-Course:It descends through the pterygopalatine canal with the anterior palatine branch of the sphenopalatine ganglion, and, emerging from the greater palatine foramen, runs forward in a groove on the medial side of the alveolar border of the hard palate to the incisive canal; the terminal branch...
runk I
Infraorbital artery
The infraorbital artery is an artery in the head that runs in the maxilla, emerging through the infraorbital foramen, just under the orbit of the eye.-Course:...
P
Posterior superior alveolar artery
The posterior superior alveolar artery is given off from the maxillary, frequently in conjunction with the infraorbital artery just as the trunk of the vessel is passing into the pterygopalatine fossa.-Branches:...
refer, Must Phone Alcoholics Anonymous.
In order: DAM Artery! I Made Dolly Parton's Bra Pop & I Didn't Stop!

