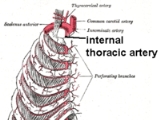
Internal thoracic artery
Encyclopedia
In human anatomy
, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously known as the internal mammary artery (a name still common among surgeon
s), is an artery
that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.
 The internal thoracic artery arises from the subclavian artery
The internal thoracic artery arises from the subclavian artery
near its origin.
It travels downward on the inside of the ribcage, approximately a centimeter from the sides of the sternum, and thus medial to the nipple
.
It runs deep to the internal intercostal muscles, but superficial to the transverse thoracic muscles.
It continues downward until it divides into the musculophrenic artery
and the superior epigastric artery
around the sixth intercostal space
.
After passing the sixth intercostal space, the internal thoracic artery splits into the following two terminal branches:
blood vessel
of choice for coronary artery bypass grafting. The left ITA has a superior long-term patency to saphenous vein
grafts and other arterial grafts (e.g. radial artery
, gastroepiploic artery
) when grafted to the left anterior descending coronary artery, generally the most important vessel, clinically, to revascularize.
Plastic surgeons may use either the left or right internal thoracic arteries for autologous free flap reconstruction of the breast after mastectomy. Usually a micro-vascular anastomosis is performed at the second intercostal space to the artery on which the free flap is based.
Human anatomy
Human anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously known as the internal mammary artery (a name still common among surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
s), is an artery
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.
Course

Subclavian artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are two major arteries of the upper thorax , below the clavicle . They receive blood from the top of the aorta...
near its origin.
It travels downward on the inside of the ribcage, approximately a centimeter from the sides of the sternum, and thus medial to the nipple
Nipple
In its most general form, a nipple is a structure from which a fluid emanates. More specifically, it is the projection on the breasts or udder of a mammal by which breast milk is delivered to a mother's young. In this sense, it is often called a teat, especially when referring to non-humans, and...
.
It runs deep to the internal intercostal muscles, but superficial to the transverse thoracic muscles.
It continues downward until it divides into the musculophrenic artery
Musculophrenic artery
The musculophrenic artery arises from the internal thoracic artery, directed obliquely downward and laterally, behind the cartilages of the false ribs; it perforates the diaphragm at the eighth or ninth costal cartilage, and ends, considerably reduced in size, opposite the last intercostal space.It...
and the superior epigastric artery
Superior epigastric artery
In human anatomy, superior epigastric artery refers to a blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood and arises from the internal thoracic artery...
around the sixth intercostal space
Intercostal space
The intercostal space is the space between two ribs . Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.-Structures in intercostal space:* several kinds of intercostal muscle...
.
Branches
- Mediastinal branches
- Thymic branches
- Pericardiacophrenic arteryPericardiacophrenic arteryThe pericardiacophrenic artery is a long slender branch of the internal thoracic artery. It accompanies the phrenic nerve, between the pleura and pericardium, to the diaphragm, to which it is distributed. It anastomoses with the musculophrenic and inferior phrenic arteries.-External links: -...
- travels with the phrenic nervePhrenic nerveThe phrenic nerve originates mainly from the 4th cervical nerve, but also receives contributions from the 5th and 3rd cervical nerves in humans.... - Sternal branches
- Perforating branchesPerforating branches of internal thoracic arteryThe perforating branches of the internal thoracic artery pierce through the internal intercostal muscles of the superior six intercostal spaces. These small arteries run with the anterior cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves....
- Twelve anterior intercostal branches, two to each of the top six intercostal spaceIntercostal spaceThe intercostal space is the space between two ribs . Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.-Structures in intercostal space:* several kinds of intercostal muscle...
s. In a given space, the upper branch travelling laterally along the bottom of the rib until it anastomoses with its corresponding posterior intercostal artery. The lower branch of the space anastomoses with a collateral branch of the posterior intercostal artery.
After passing the sixth intercostal space, the internal thoracic artery splits into the following two terminal branches:
- Musculophrenic arteryMusculophrenic arteryThe musculophrenic artery arises from the internal thoracic artery, directed obliquely downward and laterally, behind the cartilages of the false ribs; it perforates the diaphragm at the eighth or ninth costal cartilage, and ends, considerably reduced in size, opposite the last intercostal space.It...
- roughly follows the costal margin - Superior epigastric arterySuperior epigastric arteryIn human anatomy, superior epigastric artery refers to a blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood and arises from the internal thoracic artery...
- continues the course of the internal thoracic artery, travelling downward into the abdominal wall
Revascularization with the ITA
The internal thoracic artery is the cardiac surgeon'sCardiac surgery
Cardiovascular surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease , correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart...
blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
of choice for coronary artery bypass grafting. The left ITA has a superior long-term patency to saphenous vein
Great saphenous vein
The great saphenous vein , also long saphenous vein, is the large superficial vein of the leg and thigh.The terms "safaina" and "el safin" have both been claimed as the origin for the word "saphenous."-Path:The GSV originates from where the dorsal vein of the first digit...
grafts and other arterial grafts (e.g. radial artery
Radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the lateral aspect of the forearm.-Course:The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the forearm...
, gastroepiploic artery
Gastroepiploic artery
Gastroepiploic artery is the name of two different arteries serving the stomach and greater omentum:* Left gastro-omental artery, a branch of the splenic artery* Right gastro-omental artery, a branch of the gastroduodenal artery...
) when grafted to the left anterior descending coronary artery, generally the most important vessel, clinically, to revascularize.
Plastic surgeons may use either the left or right internal thoracic arteries for autologous free flap reconstruction of the breast after mastectomy. Usually a micro-vascular anastomosis is performed at the second intercostal space to the artery on which the free flap is based.
Figures of ITA grafts
- Figure of heart with two saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) and a LITA graft - texheartsurgeons.com
- Drawing of the heart with a SVG to the right coronary artery (RCA) and a LITA graft to the LAD - darcystudios.com
- Drawing of the heart with a SVG to the RCA and a LITA graft to the LAD - mayoclinic.org

