
International Chemical Identifier
Encyclopedia
The IUPAC International Chemical Identifier (InChI, pronounced ˈɪntʃiː or ˈɪŋkiː ) is a textual identifier
for chemical substance
s, designed to provide a standard and human-readable way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by IUPAC
and NIST
during 2000–2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary and the software is freely available under the open source
LGPL license.
The continuing development of the standard has been supported since 2010 by the not-for-profit InChI Trust
, of which IUPAC is a member. The current version is 1.04 and was released in September 2011.
ic information, isotope
information, stereochemistry
, and electronic charge information.
Not all layers have to be provided; for instance, the tautomer layer can be omitted if that type of information is not relevant to the particular application.
InChIs differ from the widely used CAS registry number
s in three respects:
InChIs can thus be seen as akin to a general and extremely formalized version of IUPAC names. They can express more information than the simpler SMILES
notation and differ in that every structure has a unique InChI string which is important in database applications. Information about the 3-dimensional coordinates of atoms is not represented in InChI; for this purpose a format such as PDB
can be used.
The InChI algorithm converts input structural information into a unique InChI identifier in a three-step process: normalization (to remove redundant information), canonicalization (to generate a unique number label for each atom), and serialization (to give a string of characters).
The InChIKey, sometimes referred to as a hashed InChI, is a fixed length (25 character) condensed digital representation of the InChI that is not human-understandable. The InChIKey specification was released in September 2007 in order to facilitate web searches for chemical compounds, since these were problematic with the full-length InChI.
In January 2009 the final 1.02 version of the InChI software was released. This provided a means to generate so called standard InChI, which does not allow for user selectable options in dealing with the stereochemistry and tautomeric layers of the InChI string. The standard InChIKey is then the hashed version of the standard InChI string. The standard InChI will simplify comparison of InChI strings and keys generated by different groups, and subsequently accessed via diverse sources such as databases and web resources.
The delimiter-prefix format has the advantage that a user can easily use a wildcard
search to find identifiers that match only in certain layers.
version of the full standard InChI (using the SHA-256 algorithm), designed to allow for easy web searches of chemical compounds. Most chemical structures on the Web up to 2007 have been represented as GIF files, which are not searchable for chemical content. The full InChI turned out to be too lengthy for easy searching, and therefore the InChIKey was developed. There is a very small, but finite chance of two different molecules having the same InChIKey, but the probability for duplication of only the first 14 characters has been estimated as only one duplication in 75 databases each containing one billion unique structures. With all databases currently having below 50 million structures, such duplication appears unlikely at present.
InChIKeys consist of 14 characters resulting from a hash of the connectivity information of the InChI, followed by a hyphen, followed by 9 characters resulting from a hash of the remaining layers of the InChI, followed by a single character indication the version of InChI used, another hyphen, followed by single checksum
character.
Example: Morphine
has the structure shown on right. The standard InChI for morphine is InChI=1S/C17H19NO3/c1-18-7-6-17-10-3-5-13(20)16(17)21-15-12(19)4-2-9(14(15)17)8-11(10)18/h2-5,10-11,13,16,19-20H,6-8H2,1H3/t10-,11+,13-,16-,17-/m0/s1
and the standard InChIKey for morphine is BQJCRHHNABKAKU-KBQPJGBKSA-N.
and ChemSpider
. The InChI Trust funds the development, testing and documentation of the InChI. Current extensions are being defined to handle polymer
s and mixture
s, Markush structures, reactions and organometallics, and once accepted by the Division VIII Subcommittee will be added to the algorithm.
Identifier
An identifier is a name that identifies either a unique object or a unique class of objects, where the "object" or class may be an idea, physical [countable] object , or physical [noncountable] substance...
for chemical substance
Chemical substance
In chemistry, a chemical substance is a form of matter that has constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. It cannot be separated into components by physical separation methods, i.e. without breaking chemical bonds. They can be solids, liquids or gases.Chemical substances are...
s, designed to provide a standard and human-readable way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by IUPAC
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. It is a member of the International Council for Science . The international headquarters of IUPAC is located in Zürich,...
and NIST
National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology , known between 1901 and 1988 as the National Bureau of Standards , is a measurement standards laboratory, otherwise known as a National Metrological Institute , which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce...
during 2000–2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary and the software is freely available under the open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
LGPL license.
The continuing development of the standard has been supported since 2010 by the not-for-profit InChI Trust
InChI Trust
The InChI Trust is a not-for-profit organisation which promotes and improves the International Chemical Identifier standard for describing chemical substances.-History and current status:...
, of which IUPAC is a member. The current version is 1.04 and was released in September 2011.
Overview
The identifiers describe chemical substances in terms of layers of information — the atoms and their bond connectivity, tautomerTautomer
Tautomers are isomers of organic compounds that readily interconvert by a chemical reaction called tautomerization. This reaction commonly results in the formal migration of a hydrogen atom or proton, accompanied by a switch of a single bond and adjacent double bond...
ic information, isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
information, stereochemistry
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms within molecules. An important branch of stereochemistry is the study of chiral molecules....
, and electronic charge information.
Not all layers have to be provided; for instance, the tautomer layer can be omitted if that type of information is not relevant to the particular application.
InChIs differ from the widely used CAS registry number
CAS registry number
CAS Registry Numbersare unique numerical identifiers assigned by the "Chemical Abstracts Service" toevery chemical described in the...
s in three respects:
- they are freely usable and non-proprietary;
- they can be computed from structural information and do not have to be assigned by some organization;
- most of the information in an InChI is human readable (with practice).
InChIs can thus be seen as akin to a general and extremely formalized version of IUPAC names. They can express more information than the simpler SMILES
Simplified molecular input line entry specification
The simplified molecular-input line-entry specification or SMILES is a specification in form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical molecules using short ASCII strings...
notation and differ in that every structure has a unique InChI string which is important in database applications. Information about the 3-dimensional coordinates of atoms is not represented in InChI; for this purpose a format such as PDB
Protein Data Bank (file format)
The Protein Data Bank file format is a textual file format describing the three dimensional structures of molecules held in the Protein Data Bank. The pdb format accordingly provides for description and annotation of protein and nucleic acid structures including atomic coordinates, observed...
can be used.
The InChI algorithm converts input structural information into a unique InChI identifier in a three-step process: normalization (to remove redundant information), canonicalization (to generate a unique number label for each atom), and serialization (to give a string of characters).
The InChIKey, sometimes referred to as a hashed InChI, is a fixed length (25 character) condensed digital representation of the InChI that is not human-understandable. The InChIKey specification was released in September 2007 in order to facilitate web searches for chemical compounds, since these were problematic with the full-length InChI.
In January 2009 the final 1.02 version of the InChI software was released. This provided a means to generate so called standard InChI, which does not allow for user selectable options in dealing with the stereochemistry and tautomeric layers of the InChI string. The standard InChIKey is then the hashed version of the standard InChI string. The standard InChI will simplify comparison of InChI strings and keys generated by different groups, and subsequently accessed via diverse sources such as databases and web resources.
Format and layers
Every InChI starts with the string "InChI=" followed by the version number, currently 1. This is followed by the letter S for standard InChIs. The remaining information is structured as a sequence of layers and sub-layers, with each layer providing one specific type of information. The layers and sub-layers are separated by the delimiter "/" and start with a characteristic prefix letter (except for the chemical formula sub-layer of the main layer). The six layers with important sublayers are:- Main layer
- Chemical formulaChemical formulaA chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
(no prefix). This is the only sublayer that must occur in every InChI. - Atom connections (prefix: "c"). The atoms in the chemical formula (except for hydrogens) are numbered in sequence; this sublayer describes which atoms are connected by bonds to which other ones.
- HydrogenHydrogenHydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms (prefix: "h"). Describes how many hydrogen atoms are connected to each of the other atoms.
- Chemical formula
- Charge layer
- positive charge sublayer (prefix: "p" for "protons")
- negative charge sublayer (prefix: "q")
- Stereochemical layer
- double bonds (prefix: "b")
- tetrahedral stereochemistry (prefixes: "t", "m")
- type of stereochemistry information (prefix: "s")
- IsotopicIsotopeIsotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
layer (prefixes: "i", "h", as well as "b", "t", "m", "s" for isotopic stereochemistry) - Fixed-H layer
- Reconnected layer
The delimiter-prefix format has the advantage that a user can easily use a wildcard
Wildcard character
-Telecommunication:In telecommunications, a wildcard character is a character that may be substituted for any of a defined subset of all possible characters....
search to find identifiers that match only in certain layers.
Examples
| CH3CH2OH ethanol Ethanol Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a... |
InChI=1/C2H6O/c1-2-3/h3H,2H2,1H3 InChI=1S/C2H6O/c1-2-3/h3H,2H2,1H3 (standard InChI) |
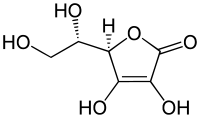 L-ascorbic acid Ascorbic acid Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound with antioxidant properties. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves well in water to give mildly acidic solutions. Ascorbic acid is one form of vitamin C. The name is derived from a- and scorbutus , the... |
InChI=1/C6H8O6/c7-1-2(8)5-3(9)4(10)6(11)12-5/h2,5,7-10H,1H2/t2-,5+/m0/s1 InChI=1S/C6H8O6/c7-1-2(8)5-3(9)4(10)6(11)12-5/h2,5,7-8,10-11H,1H2/t2-,5+/m0/s1 (standard InChI) |
InChIKey
The condensed, 27 character standard InChIKey is a hashedHash function
A hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
version of the full standard InChI (using the SHA-256 algorithm), designed to allow for easy web searches of chemical compounds. Most chemical structures on the Web up to 2007 have been represented as GIF files, which are not searchable for chemical content. The full InChI turned out to be too lengthy for easy searching, and therefore the InChIKey was developed. There is a very small, but finite chance of two different molecules having the same InChIKey, but the probability for duplication of only the first 14 characters has been estimated as only one duplication in 75 databases each containing one billion unique structures. With all databases currently having below 50 million structures, such duplication appears unlikely at present.
InChIKeys consist of 14 characters resulting from a hash of the connectivity information of the InChI, followed by a hyphen, followed by 9 characters resulting from a hash of the remaining layers of the InChI, followed by a single character indication the version of InChI used, another hyphen, followed by single checksum
Checksum
A checksum or hash sum is a fixed-size datum computed from an arbitrary block of digital data for the purpose of detecting accidental errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. The integrity of the data can be checked at any later time by recomputing the checksum and...
character.
Example: Morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
has the structure shown on right. The standard InChI for morphine is InChI=1S/C17H19NO3/c1-18-7-6-17-10-3-5-13(20)16(17)21-15-12(19)4-2-9(14(15)17)8-11(10)18/h2-5,10-11,13,16,19-20H,6-8H2,1H3/t10-,11+,13-,16-,17-/m0/s1
and the standard InChIKey for morphine is BQJCRHHNABKAKU-KBQPJGBKSA-N.
InChI Resolvers
As the InChI cannot be reconstructed from the InChIKey, an InChIKey always needs to be linked to the original InChI to get back to the original structure. InChI Resolvers act as a lookup service to make these links, and prototype services are available from NCINCI
NCI can stand for:*National Cancer Institute*National Captioning Institute*Nordic Centre in India*National College of Ireland*Native Communications Inc - Aboriginal Public Broadcaster in Manitoba, Canada....
and ChemSpider
ChemSpider
ChemsSpider is a free chemical database, owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry.-Database:The database contains more than 26 million unique molecules from over 400 data sources including those listed below.* A-L: EPA DSSTox, U.S...
Name
The format was originally called IChI (IUPAC Chemical Identifier), then renamed in July 2004 to INChI (IUPAC-NIST Chemical Identifier), and renamed again in November 2004 to InChI (IUPAC International Chemical Identifier), a trademark of IUPAC.Continuing development
Scientific direction of the InChI standard is carried out by the IUPAC Division VIII Subcommittee, and funding of subgroups investigating and defining the expansion of the standard is carried out by both IUPAC and the InChI TrustInChI Trust
The InChI Trust is a not-for-profit organisation which promotes and improves the International Chemical Identifier standard for describing chemical substances.-History and current status:...
. The InChI Trust funds the development, testing and documentation of the InChI. Current extensions are being defined to handle polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
s and mixture
Mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material system made up by two or more different substances which are mixed together but are not combined chemically...
s, Markush structures, reactions and organometallics, and once accepted by the Division VIII Subcommittee will be added to the algorithm.
See also
- Molecular Query LanguageMolecular Query LanguageThe Molecular Query Language was designed to allow more complex, problem-specific search methods in chemoinformatics....
- SMILES
- Molecule editorMolecule editorA molecule editor is a computer program for creating and modifying representations of chemical structures.Molecule editors can manipulate chemical structure representations in either two- or three-dimensions. Two-Dimensional editors generate output used as illustrations or for querying chemical...
- SYBYL Line NotationSYBYL Line NotationThe SYBYL line notation or SLN is a specification for unambiguously describing the structure of chemical molecules using short ASCII strings....
Documentation and presentations
- InChI Trust site
- IUPAC InChI site
- Unofficial InChI FAQ
- Description of the canonicalization algorithm
- Googling for InChIs a presentation to the W3C.
- The Semantic Chemical Web: GoogleInChI and other Mashups, Google Tech Talk by Peter Murray-Rust, 13 Sept 2006
- IUPAC InChI, Google Tech Talk by Steve Heller and Steve Stein, 2 November 2006
- InChI Release 1.02 InChI final version 1.02 and explanation of Standard InChI, January 2009
Software and services
- ChemSpider InChI resolver
- NCI InChI resolver
- NCI/CADD Chemical Identifier Resolver Generates and resolves InChI/InChIKeys and many other chemical identifiers
- Generate InChI (interactive service at University of Cambridge, either interactive or WSDL)
- Search Google for molecules (generates InChI from interactive chemical and searches Google for any pages with embedded InChIs). Requires Javascript enabled on browser
- ChemSketch, free chemical structure drawing package that includes input and output in InCHI format
- PubChem online molecule editor that supports SMILES/SMARTS and InChI
- ChemSpider Services that allows generation of InChI and conversion of InChI to structure (also SMILES and generation of other properties)
- MarvinSketch from ChemAxonChemaxonChemAxon is a software company specializing in application programming interfaces and end user applications for cheminformatics and life science research...
, implementation to draw structures (or open other file formats) and output to InChI file format - BKchem implements its own InChI parser and uses the IUPAC implementation to generate InChI strings

