
Isoenthalpic–isobaric ensemble
Encyclopedia
The isoenthalpic-isobaric ensemble (constant enthalpy
and constant pressure
ensemble) is a statistical mechanical
ensemble that maintains constant enthalpy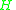 and constant pressure
and constant pressure 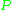 applied. It is also called the
applied. It is also called the 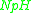 -ensemble, where the number of particles
-ensemble, where the number of particles 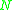 is also kept as a constant. It was developed by physicist H. C. Andersen in 1980. The ensemble adds another degree of freedom
is also kept as a constant. It was developed by physicist H. C. Andersen in 1980. The ensemble adds another degree of freedom
, which represents the variable volume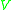 of a system to which the coordinates of all particles are relative. The volume
of a system to which the coordinates of all particles are relative. The volume 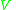 becomes a dynamical variable
becomes a dynamical variable
with potential energy
and kinetic energy
given by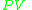 . The enthalpy
. The enthalpy 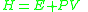 is a conserved quantity
is a conserved quantity
.
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
and constant pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
ensemble) is a statistical mechanical
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
ensemble that maintains constant enthalpy
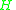 and constant pressure
and constant pressure 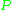 applied. It is also called the
applied. It is also called the 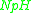 -ensemble, where the number of particles
-ensemble, where the number of particles 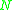 is also kept as a constant. It was developed by physicist H. C. Andersen in 1980. The ensemble adds another degree of freedom
is also kept as a constant. It was developed by physicist H. C. Andersen in 1980. The ensemble adds another degree of freedomDegrees of freedom (physics and chemistry)
A degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter, often called a dimension, in the formal description of the state of a physical system...
, which represents the variable volume
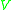 of a system to which the coordinates of all particles are relative. The volume
of a system to which the coordinates of all particles are relative. The volume 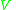 becomes a dynamical variable
becomes a dynamical variableVariable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
with potential energy
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
and kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
given by
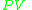 . The enthalpy
. The enthalpy 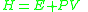 is a conserved quantity
is a conserved quantityConserved quantity
In mathematics, a conserved quantity of a dynamical system is a function H of the dependent variables that is a constant along each trajectory of the system. A conserved quantity can be a useful tool for qualitative analysis...
.

