
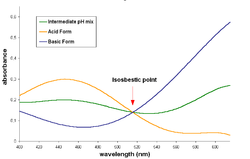
Isosbestic point
Encyclopedia
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
, an isosbestic point is a specific wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
at which two chemical species have the same molar absorptivity
Molar absorptivity
The molar absorption coefficient, molar extinction coefficient, or molar absorptivity, is a measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a given wavelength...
(ε) or -more generally- are linearly related. The word derives from two Greek words: isos: equal, and sbestos: extinguishable.
Isosbestic plot
When an isosbestic plot is constructed by the superposition of the absorption spectraSpectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
of two species (whether by using molar absorptivity
Molar absorptivity
The molar absorption coefficient, molar extinction coefficient, or molar absorptivity, is a measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a given wavelength...
for the representation, or by using absorbance and keeping the same molar concentration for both species), the isosbestic point corresponds to a wavelength at which these spectra cross each other.
A pair of substances can have several isosbestic points in their spectra.
When a 1-to-1 (one mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of reactant gives one mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
) chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
(including equilibria
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
) involves a pair of substances with an isosbestic point, the absorbance of the reaction mixture at this wavelength remains invariant, regardless of the extent of reaction (or the position of the chemical equilibrium). This occurs because the two substances absorb light of that specific wavelength to the same extent, and the analytical concentration remains constant.
For the reaction:

the analytical concentration is the same at any point in the reaction:
 .
.The absorbance of the reaction mixture (assuming it depends only on X and Y) is:
 .
.But at the isosbestic point both molar absorptivities are the same:
 .
.Hence, the absorbance

does not depend on the extent of reaction (i.e. in the particular concentrations of X and Y)
The requirement for an isosbestic point to occur is that the two species involved are related linearly by stoichiometry, such that the absorbance is invariant for one particular wavelength. Thus other ratios than one to one are possible. The presence of an isosbestic point typically does indicate that only two species that vary in concentration contribute to the absorption around the isosbestic point. If a third one is partaking in the process the spectra typically intersect at varying wavelengths as concentrations change, creating the impression that the isosbestic point is 'out of focus', or that it will shift as conditions change. The reason for this is that it would be very unlikely for three compounds to have extinction coefficients linked in a linear relationship by chance for one particular wavelength.
Applications
In chemical kineticsChemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
, isosbestic points are used as reference points in the study of reaction rates, as the absorbance at those wavelengths remains constant throughout the whole reaction.
Isosbestic points are used in medicine in a laboratory technique called oximetry to determine hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
concentration, regardless of its saturation. Oxyhaemoglobin and deoxyhaemoglobin have isosbestic points at 590 nm and near 800 nm.
Isosbestic points are also used in clinical chemistry, as a quality assurance
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance, or QA for short, is the systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of a project, service or facility to maximize the probability that minimum standards of quality are being attained by the production process...
method, to verify the accuracy in the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of a spectrophotometer. This is done by measuring the spectra
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
of a standard substance at two different pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
conditions (above and below the pKa
PKA
PKA, pKa, or other similar variations may stand for:* pKa, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American social fraternity...
of the substance). The standards used include potassium dichromate (isosbestic points at 339 and 445 nm), bromothymol blue
Bromothymol blue
Bromothymol blue is a chemical indicator for weak acids and bases. The chemical is also used for observing photosynthetic activities or respiratory indicators .Bromothymol blue acts as a weak acid in solution...
(325 and 498 nm) and congo red
Congo red
Congo red is the sodium salt of 3,3'-bis. It is a secondary diazo dye...
(541 nm). The wavelength of the isosbestic point determined does not depend on the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of the substance used, and so, it becomes a very reliable reference.

