
Jeu de taquin
Encyclopedia
In the mathematical
field of combinatorics
, jeu de taquin is a construction due to which defines an equivalence relation
on the set of skew standard Young tableaux. A jeu de taquin slide is a transformation where the numbers in a tableau are moved around in a way similar to how the pieces in the fifteen puzzle move. Two tableaux are jeu de taquin equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a sequence of such slides.
"Jeu de taquin" (literally "teasing game") is the French name for the fifteen puzzle.
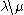 , pick an adjacent empty cell c that can be added to
, pick an adjacent empty cell c that can be added to 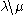 ; what this means is that c must share at least one edge with some cell in T, and
; what this means is that c must share at least one edge with some cell in T, and 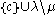 must also be a skew shape. There are two kinds of slide, depending on whether c lies to the upper left of T or to the lower right. Suppose to begin with that c lies to the upper left. Slide the number from its neighbouring cell into c; if c has neighbours both to its right and below, then pick the smallest of these two numbers. (This rule is designed so that the tableau property of having increasing rows and columns will be preserved.) If the cell that just has been emptied has no neighbour to its right or below, then the slide is completed. Otherwise, slide a number into that cell according to the same rule as before, and continue in this way until the slide is completed. After this transformation, the resulting tableau is still a skew (or possibly straight) standard Young tableux.
must also be a skew shape. There are two kinds of slide, depending on whether c lies to the upper left of T or to the lower right. Suppose to begin with that c lies to the upper left. Slide the number from its neighbouring cell into c; if c has neighbours both to its right and below, then pick the smallest of these two numbers. (This rule is designed so that the tableau property of having increasing rows and columns will be preserved.) If the cell that just has been emptied has no neighbour to its right or below, then the slide is completed. Otherwise, slide a number into that cell according to the same rule as before, and continue in this way until the slide is completed. After this transformation, the resulting tableau is still a skew (or possibly straight) standard Young tableux.
The other kind of slide, when c lies to the lower right of T, just goes in the opposite direction. In this case, one slides numbers into an empty cell from the neighbour to its left or above, picking the larger number whenever there is a choice. The two types of slides are mutual inverses – a slide of one kind can be undone using a slide of the other kind.
, the Littlewood–Richardson rule
, and Knuth equivalence.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
field of combinatorics
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
, jeu de taquin is a construction due to which defines an equivalence relation
Equivalence relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a relation that, loosely speaking, partitions a set so that every element of the set is a member of one and only one cell of the partition. Two elements of the set are considered equivalent if and only if they are elements of the same cell...
on the set of skew standard Young tableaux. A jeu de taquin slide is a transformation where the numbers in a tableau are moved around in a way similar to how the pieces in the fifteen puzzle move. Two tableaux are jeu de taquin equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a sequence of such slides.
"Jeu de taquin" (literally "teasing game") is the French name for the fifteen puzzle.
Definition of a jeu de taquin slide
Given a skew standard Young tableau T of skew shape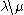 , pick an adjacent empty cell c that can be added to
, pick an adjacent empty cell c that can be added to 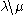 ; what this means is that c must share at least one edge with some cell in T, and
; what this means is that c must share at least one edge with some cell in T, and 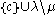 must also be a skew shape. There are two kinds of slide, depending on whether c lies to the upper left of T or to the lower right. Suppose to begin with that c lies to the upper left. Slide the number from its neighbouring cell into c; if c has neighbours both to its right and below, then pick the smallest of these two numbers. (This rule is designed so that the tableau property of having increasing rows and columns will be preserved.) If the cell that just has been emptied has no neighbour to its right or below, then the slide is completed. Otherwise, slide a number into that cell according to the same rule as before, and continue in this way until the slide is completed. After this transformation, the resulting tableau is still a skew (or possibly straight) standard Young tableux.
must also be a skew shape. There are two kinds of slide, depending on whether c lies to the upper left of T or to the lower right. Suppose to begin with that c lies to the upper left. Slide the number from its neighbouring cell into c; if c has neighbours both to its right and below, then pick the smallest of these two numbers. (This rule is designed so that the tableau property of having increasing rows and columns will be preserved.) If the cell that just has been emptied has no neighbour to its right or below, then the slide is completed. Otherwise, slide a number into that cell according to the same rule as before, and continue in this way until the slide is completed. After this transformation, the resulting tableau is still a skew (or possibly straight) standard Young tableux.The other kind of slide, when c lies to the lower right of T, just goes in the opposite direction. In this case, one slides numbers into an empty cell from the neighbour to its left or above, picking the larger number whenever there is a choice. The two types of slides are mutual inverses – a slide of one kind can be undone using a slide of the other kind.
Applications
Jeu de taquin is closely connected to such topics as the Robinson–Schensted–Knuth correspondenceRobinson–Schensted–Knuth correspondence
In mathematics, the Robinson–Schensted–Knuth correspondence, also referred to as the RSK correspondence or RSK algorithm, is a combinatorial bijection between matrices with non-negative integer entries and pairs of semistandard Young tableaux of equal shape, whose size equals the sum of the...
, the Littlewood–Richardson rule
Littlewood–Richardson rule
In mathematics, the Littlewood–Richardson rule is a combinatorial description of the coefficients that arise when decomposing a product of two Schur functions as a linear combination of other Schur functions. These coefficients are natural numbers, which the Littlewood–Richardson rule describes as...
, and Knuth equivalence.

