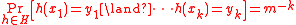K-independent hashing
Encyclopedia
A family of hash functions is said to be  -independent or
-independent or  -universal if selecting a hash function
-universal if selecting a hash function
at random from the family guarantees that the hash codes of any designated keys are independent random variables (see precise mathematical definitions below). Such families allow good average case performance in randomized algorithms or data structures, even if the input data is chosen by an adversary. The trade-offs between the degree of independence and the efficiency of evaluating the hash function are well studied, and many
keys are independent random variables (see precise mathematical definitions below). Such families allow good average case performance in randomized algorithms or data structures, even if the input data is chosen by an adversary. The trade-offs between the degree of independence and the efficiency of evaluating the hash function are well studied, and many  -independent families have been proposed.
-independent families have been proposed.
 into a smaller range, such as
into a smaller range, such as  bins (labelled
bins (labelled 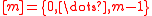 ). In the analysis of randomized algorithms and data structures, it is often desirable for the hash codes of various keys to "behave randomly". For instance, if the hash code of each key were an independent random choice in
). In the analysis of randomized algorithms and data structures, it is often desirable for the hash codes of various keys to "behave randomly". For instance, if the hash code of each key were an independent random choice in  , the number of keys per bin could be analyzed using the Chernoff bound
, the number of keys per bin could be analyzed using the Chernoff bound
. A deterministic hash function cannot offer any such guarantee in an adversarial setting, as the adversary may choose the keys to be the precisely the preimage
of a bin. Furthermore, a deterministic hash function does not allow for rehashing: sometimes the input data turns out to be bad for the hash function (e.g. there are too many collisions), so one would like to change the hash function.
The solution to these problems is to pick a function randomly from a large family of hash functions. The randomness in choosing the hash function can be used to guarantee some desired random behavior of the hash codes of any keys of interest. The first definition along these lines was universal hashing
, which guarantees a low collision probability for any two designated keys. The concept of -independent hashing, introduced by Wegman and Carter in 1981, strengthens the guarantees of random behavior to families of
-independent hashing, introduced by Wegman and Carter in 1981, strengthens the guarantees of random behavior to families of  designated keys, and adds a guarantee on the uniform distribution of hash codes.
designated keys, and adds a guarantee on the uniform distribution of hash codes.
 hash family", is the following. A family of hash functions
hash family", is the following. A family of hash functions 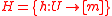 is
is  -independent iff for any
-independent iff for any  distinct keys
distinct keys 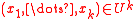 and any
and any  hash codes (not necessarily distinct)
hash codes (not necessarily distinct) 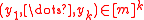 , we have:
, we have:
This definition is equivalent to the following two conditions:
Often it is inconvenient to achieve the perfect joint probability of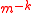 due to rounding issues. Following, one may define a
due to rounding issues. Following, one may define a 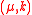 -independent family to satisfy:
-independent family to satisfy:
Observe that, even if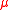 is close to 1,
is close to 1, 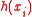 are no longer independent random variables, which is often a problem in the analysis of randomized algorithms. Therefore, a more common alternative to dealing with rounding issues is to prove that the hash family is close in statistical distance
are no longer independent random variables, which is often a problem in the analysis of randomized algorithms. Therefore, a more common alternative to dealing with rounding issues is to prove that the hash family is close in statistical distance
to a -independent family, which allows black-box use of the independence properties.
-independent family, which allows black-box use of the independence properties.
 -independent or
-independent or  -universal if selecting a hash function
-universal if selecting a hash functionHash function
A hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
at random from the family guarantees that the hash codes of any designated
 keys are independent random variables (see precise mathematical definitions below). Such families allow good average case performance in randomized algorithms or data structures, even if the input data is chosen by an adversary. The trade-offs between the degree of independence and the efficiency of evaluating the hash function are well studied, and many
keys are independent random variables (see precise mathematical definitions below). Such families allow good average case performance in randomized algorithms or data structures, even if the input data is chosen by an adversary. The trade-offs between the degree of independence and the efficiency of evaluating the hash function are well studied, and many  -independent families have been proposed.
-independent families have been proposed.Introduction
The goal of hashing is usually to map keys from some large domain (universe) into a smaller range, such as
into a smaller range, such as  bins (labelled
bins (labelled 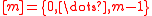 ). In the analysis of randomized algorithms and data structures, it is often desirable for the hash codes of various keys to "behave randomly". For instance, if the hash code of each key were an independent random choice in
). In the analysis of randomized algorithms and data structures, it is often desirable for the hash codes of various keys to "behave randomly". For instance, if the hash code of each key were an independent random choice in  , the number of keys per bin could be analyzed using the Chernoff bound
, the number of keys per bin could be analyzed using the Chernoff boundChernoff bound
In probability theory, the Chernoff bound, named after Herman Chernoff, gives exponentially decreasing bounds on tail distributions of sums of independent random variables...
. A deterministic hash function cannot offer any such guarantee in an adversarial setting, as the adversary may choose the keys to be the precisely the preimage
Image (mathematics)
In mathematics, an image is the subset of a function's codomain which is the output of the function on a subset of its domain. Precisely, evaluating the function at each element of a subset X of the domain produces a set called the image of X under or through the function...
of a bin. Furthermore, a deterministic hash function does not allow for rehashing: sometimes the input data turns out to be bad for the hash function (e.g. there are too many collisions), so one would like to change the hash function.
The solution to these problems is to pick a function randomly from a large family of hash functions. The randomness in choosing the hash function can be used to guarantee some desired random behavior of the hash codes of any keys of interest. The first definition along these lines was universal hashing
Universal hashing
Using universal hashing refers to selecting a hash function at random from a family of hash functions with a certain mathematical property . This guarantees a low number of collisions in expectation, even if the data is chosen by an adversary...
, which guarantees a low collision probability for any two designated keys. The concept of
 -independent hashing, introduced by Wegman and Carter in 1981, strengthens the guarantees of random behavior to families of
-independent hashing, introduced by Wegman and Carter in 1981, strengthens the guarantees of random behavior to families of  designated keys, and adds a guarantee on the uniform distribution of hash codes.
designated keys, and adds a guarantee on the uniform distribution of hash codes.Mathematical Definitions
The strictest definition, introduced by Wegman and Carter under the name "strongly universal hash family", is the following. A family of hash functions
hash family", is the following. A family of hash functions 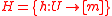 is
is  -independent iff for any
-independent iff for any  distinct keys
distinct keys 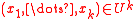 and any
and any  hash codes (not necessarily distinct)
hash codes (not necessarily distinct) 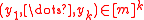 , we have:
, we have:
This definition is equivalent to the following two conditions:
- for any fixed
 , as
, as 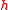 is drawn randomly from
is drawn randomly from 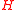 ,
, 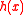 is uniformly distributed in
is uniformly distributed in  .
. - for any fixed, distinct keys
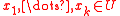 , as
, as 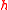 is drawn randomly from
is drawn randomly from 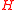 ,
,  are independent random variables.
are independent random variables.
Often it is inconvenient to achieve the perfect joint probability of
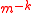 due to rounding issues. Following, one may define a
due to rounding issues. Following, one may define a 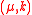 -independent family to satisfy:
-independent family to satisfy:-
 distinct
distinct 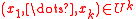 and
and 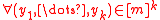 ,
, 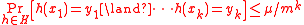
Observe that, even if
 is close to 1,
is close to 1, 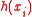 are no longer independent random variables, which is often a problem in the analysis of randomized algorithms. Therefore, a more common alternative to dealing with rounding issues is to prove that the hash family is close in statistical distance
are no longer independent random variables, which is often a problem in the analysis of randomized algorithms. Therefore, a more common alternative to dealing with rounding issues is to prove that the hash family is close in statistical distanceStatistical distance
In statistics, probability theory, and information theory, a statistical distance quantifies the distance between two statistical objects, which can be two samples, two random variables, or two probability distributions, for example.-Metrics:...
to a
 -independent family, which allows black-box use of the independence properties.
-independent family, which allows black-box use of the independence properties.See also
- Universal hashingUniversal hashingUsing universal hashing refers to selecting a hash function at random from a family of hash functions with a certain mathematical property . This guarantees a low number of collisions in expectation, even if the data is chosen by an adversary...
- Tabulation hashingTabulation hashingIn computer science, tabulation hashing is a method for constructing universal families of hash functions by combining table lookup with exclusive or operations...
, a technique for generating 3-independent hash functions