Kana
Encyclopedia
Kana are the syllabic
Japanese scripts
, as opposed to the logographic
Chinese character
s known in Japan as kanji
and the Roman alphabet
known as rōmaji. There are three kana scripts: modern cursive hiragana
(ひらがな), modern angular katakana
(カタカナ), and the old syllabic use of kanji known as man’yōgana(万葉仮名) that was ancestral to both.
Katakana with a few additions is also used to write Ainu
. Kana was used in Taiwanese as a gloss (furigana
) for Chinese character
s during the Japanese administration of Taiwan. See Taiwanese kana
.
Kana syllabograms are always CV (consonant onset with vowel nucleus) or V (only vowel) with the sole exception of the C grapheme for nasal
coda
s. This structure had some scholars label the system mora
ic instead of syllabic, because it requires the combination of two syllabograms to represent a CVC syllable with coda (i.e. CVn, CVm, CVng), a CVV syllable with complex nucleus (i.e. multiple or expressively long vowels), or a CCV syllable with complex onset (i.e. including a glide
, CyV, CwV).
readings of kanji.
. Syllables beginning with [p] are spelled with kana from the h column and the half-voicing mark, handakuten.
consonants are spelled with kana from the i row followed by small Ya, Yu or Yo. These digraph
s are called yōon
.
, and grammatical word endings (okurigana
). It is also used to represent entire words (usually of Japanese, rather than Chinese, origin) in place of kanji
. See the article hiragana
for details.
Today katakana is most commonly used to write words of foreign origin that do not have kanji representations. Katakana is also used to represent onomatopoeia, technical and scientific terms, and some corporate branding. See the article katakana
for details.
Kana can be written in small form above or next to lesser-known kanji in order to show pronunciation; this is called furigana
. Furigana is used most widely in children's books. Literature for young children who do not yet know kanji may dispense with it altogether and instead use hiragana combined with spaces.
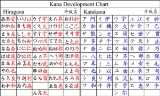
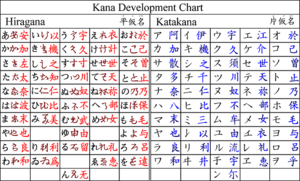 The first kana was a system called man'yōgana, a set of kanji used for their phonetic values, much as Chinese uses characters for their phonetic values in foreign loanwords today. Man'yōshū(万葉集), a poetry anthology assembled in 759, is written in this early script. Hiragana
The first kana was a system called man'yōgana, a set of kanji used for their phonetic values, much as Chinese uses characters for their phonetic values in foreign loanwords today. Man'yōshū(万葉集), a poetry anthology assembled in 759, is written in this early script. Hiragana
developed as a distinct script from cursive
man'yōgana, whereas katakana
developed from abbreviated parts of regular script
man'yōgana as a gloss
ing system to add readings or explanations to Buddhist sutras. Hiragana was developed for speed, whereas katakana developed to be small.
Kana is traditionally said to have been invented by the Buddhist
priest
Kūkai
in the 9th century. Kūkai certainly brought the Siddham script home on his return from China
in 806; his interest in the sacred aspects of speech and writing
led him to the conclusion that Japanese would be better represented by a phonetic alphabet than by the kanji which had been used up to that point. The modern arrangement of kana reflects that of Siddham, but the traditional iroha
arrangement follows a poem which uses each kana once.
The present set of kana was codified in 1900, and rules for their usage in 1946.
in Japanese. They are taken in the order given by the gojūon
(あ い う え お … わ を ん), though iroha
(い ろ は に ほ へ と … せ す (ん)) ordering is used for enumeration in some circumstances. Dictionaries differ in the sequence order for long/short vowel distinction, small tsu and diacritics. As the Japanese do not use word spaces (except for children), there can be no word-by-word collation; all collation is kana-by-kana.
is U+3040 ... U+309F, and the Katakana range is U+30A0 ... U+30FF. The obsolete and rare characters (WI and WE) also have their proper codepoints, except for hentaigana
, as hentaigana are considered glyph
variants of more common kana.
Code points U+3040, U+3097, and U+3098 are unassigned as of Unicode 4.1. Characters U+3095 and U+3096 are hiragana small ka and small ke, respectively. U+30F5 and U+30F6 are their katakana equivalents. Characters U+3099 and U+309A are combining dakuten
and handakuten, which correspond to the spacing characters U+309B and U+309C. U+309D is the hiragana iteration mark
, used to repeat a previous hiragana. U+309E is the voiced hiragana iteration mark, which stands in for the previous hiragana but with the consonant voiced (k becomes g, h becomes b, etc.). U+30FD and U+30FE are the katakana iteration marks. U+309F is a ligature of "yori" (より
) sometimes used in vertical writing. U+30FF is a ligature of "koto" (コト
), also found in vertical writing.
Additionally, there are halfwidth equivalents to the standard fullwidth katakana. These are encoded within the Halfwidth and Fullwidth Forms block (U+FF00–U+FFEF), starting at U+FF65 and ending at U+FF9F (characters U+FF61–U+FF64 are halfwidth punctuation marks):
There is also a small "Katakana Phonetic Extensions" range (U+31F0 ... U+31FF), which includes some extra characters for writing the Ainu language
.
Unicode version 6.0 also includes "Katakana letter archaic E" (U+1B000) and "Hiragana letter archaic YE" (U+1B001) in the Kana Supplement block.
Syllabary
A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel...
Japanese scripts
Japanese writing system
The modern Japanese writing system uses three main scripts:*Kanji, adopted Chinese characters*Kana, a pair of syllabaries , consisting of:...
, as opposed to the logographic
Logogram
A logogram, or logograph, is a grapheme which represents a word or a morpheme . This stands in contrast to phonograms, which represent phonemes or combinations of phonemes, and determinatives, which mark semantic categories.Logograms are often commonly known also as "ideograms"...
Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s known in Japan as kanji
Kanji
Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
and the Roman alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
known as rōmaji. There are three kana scripts: modern cursive hiragana
Hiragana
is a Japanese syllabary, one basic component of the Japanese writing system, along with katakana, kanji, and the Latin alphabet . Hiragana and katakana are both kana systems, in which each character represents one mora...
(ひらがな), modern angular katakana
Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji, and in some cases the Latin alphabet . The word katakana means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana scripts are derived from components of more complex kanji. Each kana represents one mora...
(カタカナ), and the old syllabic use of kanji known as man’yōgana(万葉仮名) that was ancestral to both.
Katakana with a few additions is also used to write Ainu
Ainu language
Ainu is one of the Ainu languages, spoken by members of the Ainu ethnic group on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō....
. Kana was used in Taiwanese as a gloss (furigana
Furigana
is a Japanese reading aid, consisting of smaller kana, or syllabic characters, printed next to a kanji or other character to indicate its pronunciation. In horizontal text, yokogaki, they are placed above the line of text, while in vertical text, tategaki, they are placed to the right of the line...
) for Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s during the Japanese administration of Taiwan. See Taiwanese kana
Taiwanese kana
Taiwanese kana is a katakana-based writing system once used to write Holo Taiwanese, when Taiwan was ruled by Japan. It functioned as a phonetic guide to hanzi, much like furigana in Japanese or Zhuyin fuhao in Chinese...
.
Kana syllabograms are always CV (consonant onset with vowel nucleus) or V (only vowel) with the sole exception of the C grapheme for nasal
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
coda
Syllable coda
In phonology, a syllable coda comprises the consonant sounds of a syllable that follow the nucleus, which is usually a vowel. The combination of a nucleus and a coda is called a rime. Some syllables consist only of a nucleus with no coda...
s. This structure had some scholars label the system mora
Mora (linguistics)
Mora is a unit in phonology that determines syllable weight, which in some languages determines stress or timing. As with many technical linguistic terms, the definition of a mora varies. Perhaps the most succinct working definition was provided by the American linguist James D...
ic instead of syllabic, because it requires the combination of two syllabograms to represent a CVC syllable with coda (i.e. CVn, CVm, CVng), a CVV syllable with complex nucleus (i.e. multiple or expressively long vowels), or a CCV syllable with complex onset (i.e. including a glide
Semivowel
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:...
, CyV, CwV).
Hiragana and katakana
The difference in usage between hiragana and katakana is stylistic. Usually, hiragana is the default syllabary, and katakana is used for foreign borrowings, onomatopoeia and interjections, and transcriptions of the Sino-JapaneseSino-Japanese
Sino-Japanese, or Kango in Japanese, refers to that portion of the Japanese vocabulary that originated in the Chinese language or has been created from elements borrowed from Chinese. Some grammatical or sentence patterns can also be identified with Sino-Japanese. Sino-Japanese vocabulary is...
readings of kanji.
| – | k | s | t | n | h | m | y | r | w | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | あア | かカ | さサ | たタ | なナ | はハ | まマ | やヤ | らラ | わワ |
| i | いイ | きキ | しシ | ちチ | にニ | ひヒ | みミ | * | りリ | ゐヰ |
| u | うウ | くク | すス | つツ | ぬヌ | ふフ | むム | ゆユ | るル | * |
| e | えエ | けケ | せセ | てテ | ねネ | へヘ | めメ | * | れレ | ゑヱ |
| o | おオ | こコ | そソ | とト | のノ | ほホ | もモ | よヨ | ろロ | をヲ |
| – | * | * | * | * | んン | * | * | * | * | * |
- There are no kana for Ye, Yi or Wu, as corresponding syllables do not occur in Japanese natively. The [je] sound is believed to have existed in pre-Classical Japanese, mostly prior to the advent of kana, and is generally represented for purposes of reconstruction by the kanji 江, although an archaic hiragana ye, 𛀁, does exist. In later periods, the syllabogram We came to be realized as [jɛ], as demonstrated by 17th century-era European sources, but it later merged with the vowel E and was eliminated from official orthography in 1946. In modern orthography, [je] may be written いぇ, イェ.
- Si, Ti, Tu, Hu, Wi and We are often transcribed into English with shi, chi, tsu, fu, i and e instead, according to contemporary pronunciation.
- While no longer part of standard Japanese orthography, Wi and We are sometimes used stylistically, as in ウヰスキー for whisky and ヱビス for Yebisu, a brand of beer. Hiragana Wi and We are still used in certain Okinawan writing systemOkinawan writing systemOkinawan language, spoken in Okinawa Island, was once the official language of the Ryukyuan Kingdom. At the time, documents were written in kanji and hiragana, derived from Japan. However, after Japan annexed the kingdom, the language was labeled as the "dialect" of mainland Japanese...
s, while katakana Wi and We are still used in Ainu.
Diacritics
Syllables beginning with the voiced consonants [g], [z], [d] and [b] are spelled with kana from the corresponding unvoiced columns (k, s, t and h) and the voicing mark, dakutenDakuten
, colloquially ten-ten , is a diacritic sign most often used in the Japanese kana syllabaries to indicate that the consonant of a syllable should be pronounced voiced. Handakuten , colloquially maru , is a diacritic used with the kana for syllables starting with h to indicate that they should...
. Syllables beginning with [p] are spelled with kana from the h column and the half-voicing mark, handakuten.
| g | z | d | b | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | が ガ | ざ ザ | だ ダ | ば バ | ぱ パ |
| i | ぎ ギ | じ ジ | ぢ ヂ | び ビ | ぴ ピ |
| u | ぐ グ | ず ズ | づ ヅ | ぶ ブ | ぷ プ |
| e | げ ゲ | ぜ ゼ | で デ | べ ベ | ぺ ペ |
| o | ご ゴ | ぞ ゾ | ど ド | ぼ ボ | ぽ ポ |
- Zi, Di and Du are often transcribed into English as ji, ji and zu instead, according to contemporary pronunciation.
Digraphs
Syllables beginning with palatalizedPalatalization
In linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate....
consonants are spelled with kana from the i row followed by small Ya, Yu or Yo. These digraph
Digraph
Digraph may refer to:* Digraph , a pair of characters used together to represent a single sound, such as "sh" in English* Typographical ligature, the joining of two letters as a single glyph, such as "æ"...
s are called yōon
Yoon
is a feature of the Japanese language in which a mora is formed with an added sound.Yōon are represented in hiragana using a kana ending in i, such as き , plus a smaller-than-usual version of one of the three y kana, ya, yu or yo. For example kyō, "today", is written きょう, using a small version of...
.
| k | s | t | n | h | m | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ya | きゃ | しゃ | ちゃ | にゃ | ひゃ | みゃ | りゃ |
| yu | きゅ | しゅ | ちゅ | にゅ | ひゅ | みゅ | りゅ |
| yo | きょ | しょ | ちょ | にょ | ひょ | みょ | りょ |
- There are no digraphs for the semivowelSemivowelIn phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:...
y and w columns. - The digraphs are usually transcribed with three letters, leaving out the i: CyV.
- Si+Y* and Ti+Y* are often transcribed sh* and ch* instead of sy* and ty*.
- In earlier Japanese, digraphs could also be formed with w-kana. Although obsolete in modern Japanese, the digraphs くゎ (/kwa/) and くゐ/くうぃ(/kwi/), are still used in certain Okinawan orthographies. In addition, the kana え can be used in Okinawan to form the digraph くぇ, which represents the /kwe/ sound.
Modern usage
Hiragana is mostly used to indicate prefixes, particlesJapanese particles
Japanese particles, or , are suffixes or short words in Japanese grammar that immediately follow the modified noun, verb, adjective, or sentence. Their grammatical range can indicate various meanings and functions, such as speaker affect and assertiveness....
, and grammatical word endings (okurigana
Okurigana
are kana suffixes following kanji stems in Japanese written words. They serve two purposes: to inflect adjectives and verbs, and to disambiguate kanji with multiple readings...
). It is also used to represent entire words (usually of Japanese, rather than Chinese, origin) in place of kanji
Kanji
Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
. See the article hiragana
Hiragana
is a Japanese syllabary, one basic component of the Japanese writing system, along with katakana, kanji, and the Latin alphabet . Hiragana and katakana are both kana systems, in which each character represents one mora...
for details.
Today katakana is most commonly used to write words of foreign origin that do not have kanji representations. Katakana is also used to represent onomatopoeia, technical and scientific terms, and some corporate branding. See the article katakana
Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji, and in some cases the Latin alphabet . The word katakana means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana scripts are derived from components of more complex kanji. Each kana represents one mora...
for details.
Kana can be written in small form above or next to lesser-known kanji in order to show pronunciation; this is called furigana
Furigana
is a Japanese reading aid, consisting of smaller kana, or syllabic characters, printed next to a kanji or other character to indicate its pronunciation. In horizontal text, yokogaki, they are placed above the line of text, while in vertical text, tategaki, they are placed to the right of the line...
. Furigana is used most widely in children's books. Literature for young children who do not yet know kanji may dispense with it altogether and instead use hiragana combined with spaces.
History

Hiragana
is a Japanese syllabary, one basic component of the Japanese writing system, along with katakana, kanji, and the Latin alphabet . Hiragana and katakana are both kana systems, in which each character represents one mora...
developed as a distinct script from cursive
Cursive script (East Asia)
Cursive script , sometimes translated as Grass script is a style of Chinese calligraphy. Cursive script is faster to write than other styles, but difficult to read for those unfamiliar with it. It functions primarily as a kind of shorthand script or calligraphic style...
man'yōgana, whereas katakana
Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji, and in some cases the Latin alphabet . The word katakana means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana scripts are derived from components of more complex kanji. Each kana represents one mora...
developed from abbreviated parts of regular script
Regular script
Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 , 楷体 and 正書 , is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is the newest of the Chinese script styles Regular script , also called 正楷 , 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷体 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is...
man'yōgana as a gloss
Gloss
A gloss is a brief notation of the meaning of a word or wording in a text. It may be in the language of the text, or in the reader's language if that is different....
ing system to add readings or explanations to Buddhist sutras. Hiragana was developed for speed, whereas katakana developed to be small.
Kana is traditionally said to have been invented by the Buddhist
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
priest
Priest
A priest is a person authorized to perform the sacred rites of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities...
Kūkai
Kukai
Kūkai , also known posthumously as , 774–835, was a Japanese monk, civil servant, scholar, poet, and artist, founder of the Shingon or "True Word" school of Buddhism. Shingon followers usually refer to him by the honorific titles of and ....
in the 9th century. Kūkai certainly brought the Siddham script home on his return from China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
in 806; his interest in the sacred aspects of speech and writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
led him to the conclusion that Japanese would be better represented by a phonetic alphabet than by the kanji which had been used up to that point. The modern arrangement of kana reflects that of Siddham, but the traditional iroha
Iroha
The is a Japanese poem, probably written in the Heian era . Originally the poem was attributed to the founder of the Shingon Esoteric sect of Buddhism in Japan, Kūkai, but more modern research has found the date of composition to be later in the Heian Period. The first record of its existence...
arrangement follows a poem which uses each kana once.
The present set of kana was codified in 1900, and rules for their usage in 1946.
| a | i | u | e | o | =:≠ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | ≠ | ≠ | = | ≠ | = | 2:3 |
| k | = | = | = | ≠ | = | 4:1 |
| s | ≠ | = | ≠ | = | = | 3:2 |
| t | ≠ | ≠ | = | = | = | 3:2 |
| n | = | = | = | = | = | 5:0 |
| h | ≠ | = | = | = | = | 4:1 |
| m | = | ≠ | ≠ | = | = | 3:2 |
| y | = | = | = | 3:0 | ||
| r | = | = | ≠ | = | = | 4:1 |
| w | = | ≠ | = | ≠ | 2:2 | |
| n | ≠ | 0:1 | ||||
| =:≠ | 6:4 | 5:4 | 6:4 | 7:2 | 9:1 | 33:15 |
Collation
Kana are the basis for collationCollation
Collation is the assembly of written information into a standard order. One common type of collation is called alphabetization, though collation is not limited to ordering letters of the alphabet...
in Japanese. They are taken in the order given by the gojūon
Gojuon
The is a Japanese ordering of kana.It is named for the 5×10 grid in which the characters are displayed, but the grid is not completely filled, and, further, there is an extra character added outside the grid at the end: with 5 gaps and 1 extra character, the current number of distinct kana in a...
(あ い う え お … わ を ん), though iroha
Iroha
The is a Japanese poem, probably written in the Heian era . Originally the poem was attributed to the founder of the Shingon Esoteric sect of Buddhism in Japan, Kūkai, but more modern research has found the date of composition to be later in the Heian Period. The first record of its existence...
(い ろ は に ほ へ と … せ す (ん)) ordering is used for enumeration in some circumstances. Dictionaries differ in the sequence order for long/short vowel distinction, small tsu and diacritics. As the Japanese do not use word spaces (except for children), there can be no word-by-word collation; all collation is kana-by-kana.
Kana in Unicode
The Hiragana range in UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
is U+3040 ... U+309F, and the Katakana range is U+30A0 ... U+30FF. The obsolete and rare characters (WI and WE) also have their proper codepoints, except for hentaigana
Hentaigana
are historical variants of modern standard hiragana. They are a legacy of man'yōgana, where many different kanji could be used to represent the same sound value. As the man'yōgana became simplified into cursive forms, multiple hiragana, including the hentaigana, was the result...
, as hentaigana are considered glyph
Glyph
A glyph is an element of writing: an individual mark on a written medium that contributes to the meaning of what is written. A glyph is made up of one or more graphemes....
variants of more common kana.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| 304x | ぁ | あ | ぃ | い | ぅ | う | ぇ | え | ぉ | お | か | が | き | ぎ | く | ||
| 305x | ぐ | け | げ | こ | ご | さ | ざ | し | じ | す | ず | せ | ぜ | そ | ぞ | た | |
| 306x | だ | ち | ぢ | っ | つ | づ | て | で | と | ど | な | に | ぬ | ね | の | は | |
| 307x | ば | ぱ | ひ | び | ぴ | ふ | ぶ | ぷ | へ | べ | ぺ | ほ | ぼ | ぽ | ま | み | |
| 308x | む | め | も | ゃ | や | ゅ | ゆ | ょ | よ | ら | り | る | れ | ろ | ゎ | わ | |
| 309x | ゐ | ゑ | を | ん | ゔ | ゕ | ゖ | |゙ |゚ |゛ |゜ |
ゝ | ゞ | ゟ | ||||||
| 30Ax | ゠ | ァ | ア | ィ | イ | ゥ | ウ | ェ | エ | ォ | オ | カ | ガ | キ | ギ | ク | |
| 30Bx | グ | ケ | ゲ | コ | ゴ | サ | ザ | シ | ジ | ス | ズ | セ | ゼ | ソ | ゾ | タ | |
| 30Cx | ダ | チ | ヂ | ッ | ツ | ヅ | テ | デ | ト | ド | ナ | ニ | ヌ | ネ | ノ | ハ | |
| 30Dx | バ | パ | ヒ | ビ | ピ | フ | ブ | プ | ヘ | ベ | ペ | ホ | ボ | ポ | マ | ミ | |
| 30Ex | ム | メ | モ | ャ | ヤ | ュ | ユ | ョ | ヨ | ラ | リ | ル | レ | ロ | ヮ | ワ | |
| 30Fx | ヰ | ヱ | ヲ | ン | ヴ | ヵ | ヶ | ヷ | ヸ | ヹ | ヺ | ・ | ー | ヽ | ヾ | ヿ |
Code points U+3040, U+3097, and U+3098 are unassigned as of Unicode 4.1. Characters U+3095 and U+3096 are hiragana small ka and small ke, respectively. U+30F5 and U+30F6 are their katakana equivalents. Characters U+3099 and U+309A are combining dakuten
Dakuten
, colloquially ten-ten , is a diacritic sign most often used in the Japanese kana syllabaries to indicate that the consonant of a syllable should be pronounced voiced. Handakuten , colloquially maru , is a diacritic used with the kana for syllables starting with h to indicate that they should...
and handakuten, which correspond to the spacing characters U+309B and U+309C. U+309D is the hiragana iteration mark
Iteration mark
Iteration marks are characters or punctuation marks that represent a duplicated character or word.-Chinese:In Chinese, 二 or 々 is used in casual writing to represent a doubled character, but it is never used in formal writing or printed matter...
, used to repeat a previous hiragana. U+309E is the voiced hiragana iteration mark, which stands in for the previous hiragana but with the consonant voiced (k becomes g, h becomes b, etc.). U+30FD and U+30FE are the katakana iteration marks. U+309F is a ligature of "yori" (より
Yori (kana)
, read as yori, is a typographic ligature in the Japanese language, consisting of a combination of the hiragana graphs of and , and thus represents their combined sound, より . It is drawn with two strokes. It is uncommon and found almost exclusively in vertical writing.-In Unicode:...
) sometimes used in vertical writing. U+30FF is a ligature of "koto" (コト
Koto (kana)
, read as koto, is a typographic ligature in the Japanese language, consisting of a combination of the katakana graphs of and , and thus represents their combined sound, コト . It is drawn with one stroke. It is uncommon and used only in vertical writing....
), also found in vertical writing.
Additionally, there are halfwidth equivalents to the standard fullwidth katakana. These are encoded within the Halfwidth and Fullwidth Forms block (U+FF00–U+FFEF), starting at U+FF65 and ending at U+FF9F (characters U+FF61–U+FF64 are halfwidth punctuation marks):
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| FF6x | 。 | 「 | 」 | 、 | ・ | ヲ | ァ | ィ | ゥ | ェ | ォ | ャ | ュ | ョ | ッ | ||
| FF7x | ー | ア | イ | ウ | エ | オ | カ | キ | ク | ケ | コ | サ | シ | ス | セ | ソ | |
| FF8x | タ | チ | ツ | テ | ト | ナ | ニ | ヌ | ネ | ノ | ハ | ヒ | フ | ヘ | ホ | マ | |
| FF9x | ミ | ム | メ | モ | ヤ | ユ | ヨ | ラ | リ | ル | レ | ロ | ワ | ン |゙ |゚ |
There is also a small "Katakana Phonetic Extensions" range (U+31F0 ... U+31FF), which includes some extra characters for writing the Ainu language
Ainu language
Ainu is one of the Ainu languages, spoken by members of the Ainu ethnic group on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō....
.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| 31Fx | ㇰ | ㇱ | ㇲ | ㇳ | ㇴ | ㇵ | ㇶ | ㇷ | ㇸ | ㇹ | ㇺ | ㇻ | ㇼ | ㇽ | ㇾ | ㇿ |
Unicode version 6.0 also includes "Katakana letter archaic E" (U+1B000) and "Hiragana letter archaic YE" (U+1B001) in the Kana Supplement block.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| 1B00x | 𛀀 | 𛀁 |
See also
- GojūonGojuonThe is a Japanese ordering of kana.It is named for the 5×10 grid in which the characters are displayed, but the grid is not completely filled, and, further, there is an extra character added outside the grid at the end: with 5 gaps and 1 extra character, the current number of distinct kana in a...
- Romaji
- TransliterationTransliterationTransliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
and TranscriptionTranscription (linguistics)Transcription in the linguistic sense is the systematic representation of language in written form. The source can either be utterances or preexisting text in another writing system, although some linguists only consider the former as transcription.Transcription should not be confused with...
- Historical kana usageHistorical kana usageThe , or , refers to the in general use until orthographic reforms after World War II; the current orthography was adopted by Cabinet order in 1946. By that point the historical orthography was no longer in accord with Japanese pronunciation...
- Man'yōgana
- HentaiganaHentaiganaare historical variants of modern standard hiragana. They are a legacy of man'yōgana, where many different kanji could be used to represent the same sound value. As the man'yōgana became simplified into cursive forms, multiple hiragana, including the hentaigana, was the result...
External links
- KanaQ Kana flashcard tool that runs on mobile phones.
- Real Kana Practice hiragana and katakana using different typefaces.
- Origin of Hiragana
- Origin of Katakana
- Change Kanji into Romaji and Hiragana
- Kana web translator - Transliterate Kana to Rōmaji
- Kana Copybook (PDF)
- Kana no quiz Free/libre and cross-platform educational software to memorize Japanese kana pronouncing & transcription.
- KanaQuest Memorize Japanese words and kana with multiple quizzes.

