
Taiwanese kana
Encyclopedia

Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji, and in some cases the Latin alphabet . The word katakana means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana scripts are derived from components of more complex kanji. Each kana represents one mora...
-based writing system
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
once used to write Holo Taiwanese, when Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
was ruled
Taiwan under Japanese rule
Between 1895 and 1945, Taiwan was a dependency of the Empire of Japan. The expansion into Taiwan was a part of Imperial Japan's general policy of southward expansion during the late 19th century....
by Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. It functioned as a phonetic guide to hanzi, much like furigana
Furigana
is a Japanese reading aid, consisting of smaller kana, or syllabic characters, printed next to a kanji or other character to indicate its pronunciation. In horizontal text, yokogaki, they are placed above the line of text, while in vertical text, tategaki, they are placed to the right of the line...
in Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
or Zhuyin fuhao in Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
. There were similar systems for other languages in Taiwan as well, including Hakka and Formosan languages
Formosan languages
The Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
.
The system was imposed by Japan at the time, and used in a few dictionaries, as well as textbooks. The Japanese-Taiwanese Dictionary (日臺大辭典), published in 1931-1932, is an example. It uses various signs and diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s to denote sounds that do not exist in Japanese. The system is chiefly based on the Amoy (Xiamen
Xiamen
Xiamen , also known as Amoy , is a major city on the southeast coast of the People's Republic of China. It is administered as a sub-provincial city of Fujian province with an area of and population of 3.53 million...
) dialect of Min Nan
Min Nan
The Southern Min languages, or Min Nan , are a family of Chinese languages spoken in southern Fujian, eastern Guangdong, Hainan, Taiwan, and southern Zhejiang provinces of China, and by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora....
.
Through the system, the Office of the Governor-General of Taiwan
Governor-General of Taiwan
The position of Governor-General of Taiwan existed when Taiwan and the Pescadores were part of the Empire of Japan, from 1895 to 1945.The Japanese Governors-General were members of the Diet, civilian officials, Japanese nobles or generals...
aimed to help Taiwanese people
Taiwanese people
Taiwanese people may refer to individuals who either claim or are imputed cultural identity focused on the island of Taiwan and/or Taiwan Area which have been governed by the Republic of China since 1945...
learn the Japanese language, as well as help Japanese people
Japanese people
The are an ethnic group originating in the Japanese archipelago and are the predominant ethnic group of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 130 million people are of Japanese descent; of these, approximately 127 million are residents of Japan. People of Japanese ancestry who live in other countries...
learn the Taiwanese language. Linguistically speaking, however, the syllabary
Syllabary
A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel...
system was cumbersome for a language that has phonology far more complicated than Japanese. After Japanese administration ended, the system soon became obsolete. Now, only a few scholars, such as those who would study the aforementioned dictionary, learn Taiwanese kana.
Currently, Mojikyo
Mojikyo
is a set of computer software and fonts for enhanced logogram word-processing. , it collected 126,560/142,228 characters . Among them, 101,936/128,573 characters belong to the extended CJKV family...
is the only piece of software
Computer software
Computer software, or just software, is a collection of computer programs and related data that provide the instructions for telling a computer what to do and how to do it....
/encoding
Character encoding
A character encoding system consists of a code that pairs each character from a given repertoire with something else, such as a sequence of natural numbers, octets or electrical pulses, in order to facilitate the transmission of data through telecommunication networks or storage of text in...
that fully supports the system. Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
lacks small katakana wo
Wo (kana)
を, in hiragana, or ヲ in katakana, is one of the Japanese kana, each of which represent one mora.-Modern usage:In Japanese, this kana is used almost exclusively for a particle; therefore, the katakana form is fairly uncommon in everyday language — mostly used as a stand-in for its hiragana...
and tone signs; although it also lacks precomposed overlined and underdotted kana, combining character sequences containing the combining overline
Overline
An overline or overbar or overscore , refers to the typographical feature of a line drawn immediately above the text, for example used to indicate medieval sigla. Specifically, a line drawn over one symbol is a macron, and a line over a collection of symbols is a vinculum...
and combining dot below are sufficient for representing overlined and underdotted kana.
The system has undergone some modification over time. This article is mainly about the last edition, used from roughly 1931.
Basic rules
Mapped sounds are mostly similar to katakanaKatakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji, and in some cases the Latin alphabet . The word katakana means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana scripts are derived from components of more complex kanji. Each kana represents one mora...
in Japanese. Notable differences include:
- All the syllables (with a few exceptions) are written with 2 or 3 kana. When a vowelVowelIn phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
is not followed by another vowelDiphthongA diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
or a consonantConsonantIn articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
, kana for the vowel is repeated. (for example カア for POJ ka, キイ for ki.) - When a syllable contains 3 vowels, or 2 vowels followed by a consonant, a vowel in middle is written with a small vowel kana. (for example キアウ for kiau, キエク for kiek.)
- The sound /ɔ/ is spelt オ, while /o/ is ヲ. Therefore, POJ o· is always オ, while o may be spelt オ or ヲ, depending on the pronunciation. (for example o /o/ is ヲヲ, o· /ɔ/ is オオ. oak /uak/ is ヲアク, but iok /iɔk/ is イオク. kió /kio˥˧/ is キヲ
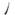 , but kióⁿ /kiɔ̃˥˧/ is キオ
, but kióⁿ /kiɔ̃˥˧/ is キオ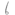 .) Unlike in Japanese, ヲ is never */wo/.
.) Unlike in Japanese, ヲ is never */wo/. - A consonant is written with a vowel "o", when it precedes ヲ. (for example コヲ for ko.)
- Final nasalsNasal consonantA nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
n/m/ng are ヌ/ム/ン respectively. ヌ/ム can also be used for nu/mu in initials. (for example カヌ for kan, ヌヌ for nun.) - Syllabic ng /ŋ̍/ is spelt (u+)ン. (for example クン for kng.) The syllable "ng" (without a preceding vowel) is ン, not ウン or ンン.
- Syllabic m /m̩/ is spelt (u+)ム. (for example フム for hm.) The syllable "m" (without a preceding vowel) is ム, not ウム or ムム.
- Initial ng is spelt as g with a nasal tone sign. (for example ガア
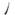 for gá, ガア
for gá, ガア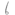 for ngá.)
for ngá.) - Final consonants k/t/p are small ク/ツ/プ respectively, similar to the kana used in AinuAinu languageAinu is one of the Ainu languages, spoken by members of the Ainu ethnic group on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō....
. - Final consonant h /ʔ/ is written as a small kana after the preceding vowel. (for example カア for kah, カウ for kauh.)
- Aspirated consonantsAspiration (phonetics)In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of air that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. To feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say pin ...
are written as kana with a dot under it. (for example ト̣ for tho.) - There are five (ten if one counts aspirates) overlined kana to deal with t and ch. チ sounds similar to ティ in modern Japanese katakana. ツ is similar to トゥ, サ to ツァ, セ to ツェ, and ソ to ツォ.
a i u e o·/o t タ チ ツ テ ト th チ̣ ツ̣ テ̣ ト̣ ch サ チ ツ セ ソ chh サ̣ チ̣ ツ̣ セ̣ ソ̣ - フ is not */ɸu/ as in Japanese, but /hu/.
- ヤ, ユ, ヨ, ワ, ヰ, and ヱ are not used.
- There are two optional vowel kana for Choâⁿ-chiu (QuánzhōuQuanzhouQuanzhou is a prefecture-level city in Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It borders all other prefecture-level cities in Fujian but two and faces the Taiwan Strait...
) dialect. ウ for /ɨ/, オ for /ə/. (for example クウ for /kɨ/, コオ for /kə/, クウヌ for /kɨn/.)
Tone signs
There are different toneTone (linguistics)
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information, and to convey emphasis, contrast, and other such features in what is called...
signs for normal vowels and nasal vowel
Nasal vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the velum so that air escapes both through nose as well as the mouth. By contrast, oral vowels are ordinary vowels without this nasalisation...
s.
| POJ | a | á | à | ah | â | ā | a̍h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal vowels | None | 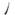 |
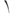 |
 |
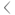 |
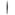 |
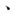 |
| Nasal vowels | 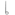 |
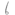 |
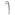 |
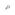 |
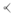 |
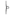 |
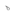 |
- When a text is written verticallyHorizontal and vertical writing in East Asian scriptsMany East Asian scripts can be written horizontally or vertically. The Chinese, Japanese and Korean scripts can be oriented in either direction, as they consist mainly of disconnected syllabic units, each occupying a square block of space...
, those signs are written on the right side of letters. Taiwanese kana is only attested in vertical orientation, so it is unknown where the signs would be placed if it were written horizontally. - Initial consonants m/n/ng are always written with nasal vowel tone signs.
Comparison chart with POJ
| - | p | ph | b | m | t | th | l | n | k | kh | g/ng1 | ch | chh | j | s | h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | アア2 | パア | パ̣ア | バア | マア | タア | タ̣ア | ラア | ナア | カア | カ̣ア | ガア | サア | サ̣ア | ザア | サア | ハア |
| e | エエ2 | ペエ | ペ̣エ | ベエ | メエ | テエ | テ̣エ | レエ | ネエ | ケエ | ケ̣エ | ゲエ | セエ | セ̣エ | ゼエ | セエ | ヘエ |
| i | イイ | ピイ | ピ̣イ | ビイ | ミイ | チイ | チ̣イ | リイ | ニイ | キイ | キ̣イ | ギイ | チイ | チ̣イ | ジイ | シイ | ヒイ |
| o· | オオ | ポオ | ポ̣オ | ボオ | モオ | トオ | ト̣オ | ロオ | ノオ | コオ | コ̣オ | ゴオ | ソオ | ソ̣オ | ゾオ | ソオ | ホオ |
| o3 | ヲヲ | ポヲ | ポ̣ヲ | ボヲ | モヲ | トヲ | ト̣ヲ | ロヲ | ノヲ | コヲ | コ̣ヲ | ゴヲ | ソヲ | ソ̣ヲ | ゾヲ | ソヲ | ホヲ |
| u | ウウ | プウ | プ̣ウ | ブウ | ムウ | ツウ | ツ̣ウ | ルウ | ヌウ | クウ | ク̣ウ | グウ | ツウ | ツ̣ウ | ズウ | スウ | フウ |
| ng | ン | プン | プ̣ン | ブン | ムン | ツン | ツ̣ン | ルン | ヌン | クン | ク̣ン | グン | ツン | ツ̣ン | ズン | スン | フン |
| m | ム | プム | プ̣ム | ブム | ムム | ツム | ツ̣ム | ルム | ヌム | クム | ク̣ム | グム | ツム | ツ̣ム | ズム | スム | フム |
| ai | アイ | パイ | パ̣イ | バイ | マイ | タイ | タ̣イ | ライ | ナイ | カイ | カ̣イ | ガイ | サイ | サ̣イ | ザイ | サイ | ハイ |
| au | アウ | パウ | パ̣ウ | バウ | マウ | タウ | タ̣ウ | ラウ | ナウ | カウ | カ̣ウ | ガウ | サウ | サ̣ウ | ザウ | サウ | ハウ |
| ia | イア | ピア | ピ̣ア | ビア | ミア | チア | チ̣ア | リア | ニア | キア | キ̣ア | ギア | チア | チ̣ア | ジア | シア | ヒア |
| iau | イアウ | ピアウ | ピ̣アウ | ビアウ | ミアウ | チアウ | チ̣アウ | リアウ | ニアウ | キアウ | キ̣アウ | ギアウ | チアウ | チ̣アウ | ジアウ | シアウ | ヒアウ |
| io3 | イヲ | ピヲ | ピ̣ヲ | ビヲ | ミヲ | チヲ | チ̣ヲ | リヲ | ニヲ | キヲ | キ̣ヲ | ギヲ | チヲ | チ̣ヲ | ジヲ | シヲ | ヒヲ |
| iu | イウ | ピウ | ピ̣ウ | ビウ | ミウ | チウ | チ̣ウ | リウ | ニウ | キウ | キ̣ウ | ギウ | チウ | チ̣ウ | ジウ | シウ | ヒウ |
| oa | ヲア | ポア | ポ̣ア | ボア | モア | トア | ト̣ア | ロア | ノア | コア | コ̣ア | ゴア | ソア | ソ̣ア | ゾア | ソア | ホア |
| oai | ヲアイ | ポアイ | ポ̣アイ | ボアイ | モアイ | トアイ | ト̣アイ | ロアイ | ノアイ | コアイ | コ̣アイ | ゴアイ | ソアイ | ソ̣アイ | ゾアイ | ソアイ | ホアイ |
| oe | ヲエ | ポエ | ポ̣エ | ボエ | モエ | トエ | ト̣エ | ロエ | ノエ | コエ | コ̣エ | ゴエ | ソエ | ソ̣エ | ゾエ | ソエ | ホエ |
| ui | ウイ | プイ | プ̣イ | ブイ | ムイ | ツイ | ツ̣イ | ルイ | ヌイ | クイ | ク̣イ | グイ | ツイ | ツ̣イ | ズイ | スイ | フイ |
| am | アム | パム | パ̣ム | バム | マム | タム | タ̣ム | ラム | ナム | カム | カ̣ム | ガム | サム | サ̣ム | ザム | サム | ハム |
| im | イム | ピム | ピ̣ム | ビム | ミム | チム | チ̣ム | リム | ニム | キム | キ̣ム | ギム | チム | チ̣ム | ジム | シム | ヒム |
| iam | イアム | ピアム | ピ̣アム | ビアム | ミアム | チアム | チ̣アム | リアム | ニアム | キアム | キ̣アム | ギアム | チアム | チ̣アム | ジアム | シアム | ヒアム |
| om | オム | ポム | ポ̣ム | ボム | モム | トム | ト̣ム | ロム | ノム | コム | コ̣ム | ゴム | ソム | ソ̣ム | ゾム | ソム | ホム |
| an | アヌ | パヌ | パ̣ヌ | バヌ | マヌ | タヌ | タ̣ヌ | ラヌ | ナヌ | カヌ | カ̣ヌ | ガヌ | サヌ | サ̣ヌ | ザヌ | サヌ | ハヌ |
| in | イヌ | ピヌ | ピ̣ヌ | ビヌ | ミヌ | チヌ | チ̣ヌ | リヌ | ニヌ | キヌ | キ̣ヌ | ギヌ | チヌ | チ̣ヌ | ジヌ | シヌ | ヒヌ |
| ian | イエヌ | ピエヌ | ピ̣エヌ | ビエヌ | ミエヌ | チエヌ | チ̣エヌ | リエヌ | ニエヌ | キエヌ | キ̣エヌ | ギエヌ | チエヌ | チ̣エヌ | ジエヌ | シエヌ | ヒエヌ |
| oan | ヲアヌ | ポアヌ | ポ̣アヌ | ボアヌ | モアヌ | トアヌ | ト̣アヌ | ロアヌ | ノアヌ | コアヌ | コ̣アヌ | ゴアヌ | ソアヌ | ソ̣アヌ | ゾアヌ | ソアヌ | ホアヌ |
| un | ウヌ | プヌ | プ̣ヌ | ブヌ | ムヌ | ツヌ | ツ̣ヌ | ルヌ | ヌヌ | クヌ | ク̣ヌ | グヌ | ツヌ | ツ̣ヌ | ズヌ | スヌ | フヌ |
| ang | アン | パン | パ̣ン | バン | マン | タン | タ̣ン | ラン | ナン | カン | カ̣ン | ガン | サン | サ̣ン | ザン | サン | ハン |
| eng | イエン | ピエン | ピ̣エン | ビエン | ミエン | チエン | チ̣エン | リエン | ニエン | キエン | キ̣エン | ギエン | チエン | チ̣エン | ジエン | シエン | ヒエン |
| iang | イアン | ピアン | ピ̣アン | ビアン | ミアン | チアン | チ̣アン | リアン | ニアン | キアン | キ̣アン | ギアン | チアン | チ̣アン | ジアン | シアン | ヒアン |
| iong | イオン | ピオン | ピ̣オン | ビオン | ミオン | チオン | チ̣オン | リオン | ニオン | キオン | キ̣オン | ギオン | チオン | チ̣オン | ジオン | シオン | ヒオン |
| ong | オン | ポン | ポ̣ン | ボン | モン | トン | ト̣ン | ロン | ノン | コン | コ̣ン | ゴン | ソン | ソ̣ン | ゾン | ソン | ホン |
| oang | ヲアン | ポアン | ポ̣アン | ボアン | モアン | トアン | ト̣アン | ロアン | ノアン | コアン | コ̣アン | ゴアン | ソアン | ソ̣アン | ゾアン | ソアン | ホアン |
| ah | アア | パア | パ̣ア | バア | マア | タア | タ̣ア | ラア | ナア | カア | カ̣ア | ガア | サア | サ̣ア | ザア | サア | ハア |
| eh | エエ | ペエ | ペ̣エ | ベエ | メエ | テエ | テ̣エ | レエ | ネエ | ケエ | ケ̣エ | ゲエ | セエ | セ̣エ | ゼエ | セエ | ヘエ |
| ih | イイ | ピイ | ピ̣イ | ビイ | ミイ | チイ | チ̣イ | リイ | ニイ | キイ | キ̣イ | ギイ | チイ | チ̣イ | ジイ | シイ | ヒイ |
| o·h | オオ | ポオ | ポ̣オ | ボオ | モオ | トオ | ト̣オ | ロオ | ノオ | コオ | コ̣オ | ゴオ | ソオ | ソ̣オ | ゾオ | ソオ | ホオ |
| oh | ヲヲ | ポヲ | ポ̣ヲ | ボヲ | モヲ | トヲ | ト̣ヲ | ロヲ | ノヲ | コヲ | コ̣ヲ | ゴヲ | ソヲ | ソ̣ヲ | ゾヲ | ソヲ | ホヲ |
| uh | ウウ | プウ | プ̣ウ | ブウ | ムウ | ツウ | ツ̣ウ | ルウ | ヌウ | クウ | ク̣ウ | グウ | ツウ | ツ̣ウ | ズウ | スウ | フウ |
| auh | アウ | パウ | パ̣ウ | バウ | マウ | タウ | タ̣ウ | ラウ | ナウ | カウ | カ̣ウ | ガウ | サウ | サ̣ウ | ザウ | サウ | ハウ |
| iah | イア | ピア | ピ̣ア | ビア | ミア | チア | チ̣ア | リア | ニア | キア | キ̣ア | ギア | チア | チ̣ア | ジア | シア | ヒア |
| iauh | イアウ | ピアウ | ピ̣アウ | ビアウ | ミアウ | チアウ | チ̣アウ | リアウ | ニアウ | キアウ | キ̣アウ | ギアウ | チアウ | チ̣アウ | ジアウ | シアウ | ヒアウ |
| ioh | イヲ | ピヲ | ピ̣ヲ | ビヲ | ミヲ | チヲ | チ̣ヲ | リヲ | ニヲ | キヲ | キ̣ヲ | ギヲ | チヲ | チ̣ヲ | ジヲ | シヲ | ヒヲ |
| oah | ヲア | ポア | ポ̣ア | ボア | モア | トア | ト̣ア | ロア | ノア | コア | コ̣ア | ゴア | ソア | ソ̣ア | ゾア | ソア | ホア |
| oeh | ヲエ | ポエ | ポ̣エ | ボエ | モエ | トエ | ト̣エ | ロエ | ノエ | コエ | コ̣エ | ゴエ | ソエ | ソ̣エ | ゾエ | ソエ | ホエ |
| ap | アプ | パプ | パ̣プ | バプ | マプ | タプ | タ̣プ | ラプ | ナプ | カプ | カ̣プ | ガプ | サプ | サ̣プ | ザプ | サプ | ハプ |
| iap | イアプ | ピアプ | ピ̣アプ | ビアプ | ミアプ | チアプ | チ̣アプ | リアプ | ニアプ | キアプ | キ̣アプ | ギアプ | チアプ | チ̣アプ | ジアプ | シアプ | ヒアプ |
| ip | イプ | ピプ | ピ̣プ | ビプ | ミプ | チプ | チ̣プ | リプ | ニプ | キプ | キ̣プ | ギプ | チプ | チ̣プ | ジプ | シプ | ヒプ |
| op | オプ | ポプ | ポ̣プ | ボプ | モプ | トプ | ト̣プ | ロプ | ノプ | コプ | コ̣プ | ゴプ | ソプ | ソ̣プ | ゾプ | ソプ | ホプ |
| at | アツ | パツ | パ̣ツ | バツ | マツ | タツ | タ̣ツ | ラツ | ナツ | カツ | カ̣ツ | ガツ | サツ | サ̣ツ | ザツ | サツ | ハツ |
| it | イツ | ピツ | ピ̣ツ | ビツ | ミツ | チツ | チ̣ツ | リツ | ニツ | キツ | キ̣ツ | ギツ | チツ | チ̣ツ | ジツ | シツ | ヒツ |
| iat | イエツ | ピエツ | ピ̣エツ | ビエツ | ミエツ | チエツ | チ̣エツ | リエツ | ニエツ | キエツ | キ̣エツ | ギエツ | チエツ | チ̣エツ | ジエツ | シエツ | ヒエツ |
| oat | ヲアツ | ポアツ | ポ̣アツ | ボアツ | モアツ | トアツ | ト̣アツ | ロアツ | ノアツ | コアツ | コ̣アツ | ゴアツ | ソアツ | ソ̣アツ | ゾアツ | ソアツ | ホアツ |
| ut | ウツ | プツ | プ̣ツ | ブツ | ムツ | ツツ | ツ̣ツ | ルツ | ヌツ | クツ | ク̣ツ | グツ | ツツ | ツ̣ツ | ズツ | スツ | フツ |
| ak | アク | パク | パ̣ク | バク | マク | タク | タ̣ク | ラク | ナク | カク | カ̣ク | ガク | サク | サ̣ク | ザク | サク | ハク |
| ek | イエク | ピエク | ピ̣エク | ビエク | ミエク | チエク | チ̣エク | リエク | ニエク | キエク | キ̣エク | ギエク | チエク | チ̣エク | ジエク | シエク | ヒエク |
| iak | イアク | ピアク | ピ̣アク | ビアク | ミアク | チアク | チ̣アク | リアク | ニアク | キアク | キ̣アク | ギアク | チアク | チ̣アク | ジアク | シアク | ヒアク |
| iok | イオク | ピオク | ピ̣オク | ビオク | ミオク | チオク | チ̣オク | リオク | ニオク | キオク | キ̣オク | ギオク | チオク | チ̣オク | ジオク | シオク | ヒオク |
| ok | オク | ポク | ポ̣ク | ボク | モク | トク | ト̣ク | ロク | ノク | コク | コ̣ク | ゴク | ソク | ソ̣ク | ゾク | ソク | ホク |
| oak | ヲアク | ポアク | ポ̣アク | ボアク | モアク | トアク | ト̣アク | ロアク | ノアク | コアク | コ̣アク | ゴアク | ソアク | ソ̣アク | ゾアク | ソアク | ホアク |
- Some combinations don't exist in reality.
- You always have to put tone signs.
- 1: g always takes normal vowel tone signs, ng always takes nasal vowel tone signs.
- 2: Some spellings are not clear. 仔(á) was sometimes written as ア rather than アア. 的(ê) was sometimes written as エ rather than エエ.
- 3: Nasal vowels (oⁿ, ioⁿ) are spelt with オ, such as オオ, ポオ, イオ, ピオ, and so on.
Example
()Taiwanese kana: :シェヌ シイ
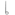 コン
コン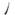 、ハク
、ハク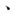 シェン チァム
シェン チァム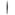 チァム
チァム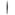 チ̣ア
チ̣ア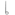 。
。Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Sian-siⁿ kóng, ha̍k-seng tiām-tiām thiaⁿ.
Traditional Chinese
Traditional Chinese character
Traditional Chinese characters refers to Chinese characters in any character set which does not contain newly created characters or character substitutions performed after 1946. It most commonly refers to characters in the standardized character sets of Taiwan, of Hong Kong, or in the Kangxi...
: 先生講、學生恬恬聽。
Translation: A teacher is speaking. Students are quietly listening.
External links
- National Taichung Library , including the scan of The Taiwanese-Japanese Dictionary. http://jdlib.ntl.gov.tw/cgi-bin/browse.cgi?bookid=bjn00172v01 bookid=bjn00172v02
- 台灣總督府ê日本國民讀本 (Japanese textbook by the Governor-General of Taiwan)

