
Kinetic inductance
Encyclopedia
Kinetic inductance is the manifestation of the inertial mass of mobile charge carriers in alternating electric fields as an equivalent series inductance
. Kinetic inductance is observed in high carrier mobility conductors (e.g. superconductors) and at very high frequencies.
(emf) will be opposed by the inertia
of the charge carriers since, like all objects with mass, they prefer to be traveling at constant velocity and therefore it takes a finite time to accelerate the particle. This is similar to how a change in emf is opposed by the finite rate of change of magnetic flux in an inductor. The resulting phase lag in voltage is identical for both energy storage mechanisms, making them indistinguishable in a normal circuit.
Kinetic inductance ( ) arises naturally in the Drude model
) arises naturally in the Drude model
of electrical conduction when the relaxation time (collision time) is taken to be non-zero. This model defines a complex
is taken to be non-zero. This model defines a complex
conductivity in a time-varying electric field of frequency given by
given by 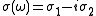 . The imaginary part arises from kinetic inductance, with
. The imaginary part arises from kinetic inductance, with  . The Drude complex conductivity can be expanded into its real and imaginary components:
. The Drude complex conductivity can be expanded into its real and imaginary components:

where is the mass of the charge carrier (i.e. the effective electron
is the mass of the charge carrier (i.e. the effective electron
mass in metallic conductors
) and is the carrier number density. In normal metals the collision time is typically
is the carrier number density. In normal metals the collision time is typically  s, so for frequencies < 100 GHz the term
s, so for frequencies < 100 GHz the term  is very small and can be ignored. Kinetic inductance is therefore only significant at optical frequencies and in superconductors, where
is very small and can be ignored. Kinetic inductance is therefore only significant at optical frequencies and in superconductors, where  .
.
For a superconducting wire, the kinetic inductance can be calculated by equating the total kinetic energy of the Cooper pairs with an equivalent inductive energy:

where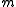 is the electron mass (
is the electron mass ( is the mass of a Cooper pair),
is the mass of a Cooper pair),  is the average Cooper pair velocity,
is the average Cooper pair velocity,  is the density of Cooper pairs,
is the density of Cooper pairs, 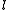 is the length of the wire,
is the length of the wire, 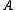 is the wire cross-sectional area, and
is the wire cross-sectional area, and  is the current. Using the fact that the current
is the current. Using the fact that the current 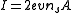 , where
, where  is the electron charge, this yields:
is the electron charge, this yields:

The same procedure can be used to calculate the kinetic inductance of a normal (i.e. non-superconducting) wire, except with replaced by
replaced by  ,
,  replaced by
replaced by  , and
, and 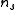 replaced by the normal carrier density
replaced by the normal carrier density  . This yields:
. This yields:
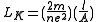
The kinetic inductance increases as the carrier density decreases. Physically, this is because a smaller number of carriers must have a greater velocity than a larger number of carriers in order to achieve the same current. In a normal metal wire, the resistivity
also increases as the carrier density decreases. As a result, in normal metals the resistive contribution to the impedance
decreases. As a result, in normal metals the resistive contribution to the impedance
dominates the contribution from kinetic inductance up to frequencies ~ THz.
delay lines as it increases the inductance per unit length of superconducting transmission lines.
Kinetic inductance can be used to make sensitive photon
detectors, known as kinetic inductance detectors (KIDs), as the change in the Cooper pair
density brought about by the absorption of a photon in a strip of superconducting material produces a measurable change in kinetic inductance.
Kinetic inductance is also used in a design parameter for superconducting flux qubit
s: is the ratio of the kinetic inductance of the Josephson junctions in the qubit to the geometrical inductance of the flux qubit. A design with a low beta behaves more like a simple inductive loop, while a design with a high beta is dominated by the Josephson junctions and has more hysteretic behavior.
is the ratio of the kinetic inductance of the Josephson junctions in the qubit to the geometrical inductance of the flux qubit. A design with a low beta behaves more like a simple inductive loop, while a design with a high beta is dominated by the Josephson junctions and has more hysteretic behavior.
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
. Kinetic inductance is observed in high carrier mobility conductors (e.g. superconductors) and at very high frequencies.
Explanation
A change in electromotive forceElectromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
(emf) will be opposed by the inertia
Inertia
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest, or the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. It is proportional to an object's mass. The principle of inertia is one of the fundamental principles of classical physics which are used to...
of the charge carriers since, like all objects with mass, they prefer to be traveling at constant velocity and therefore it takes a finite time to accelerate the particle. This is similar to how a change in emf is opposed by the finite rate of change of magnetic flux in an inductor. The resulting phase lag in voltage is identical for both energy storage mechanisms, making them indistinguishable in a normal circuit.
Kinetic inductance (
 ) arises naturally in the Drude model
) arises naturally in the Drude modelDrude model
The Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials...
of electrical conduction when the relaxation time (collision time)
 is taken to be non-zero. This model defines a complex
is taken to be non-zero. This model defines a complexComplex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
conductivity in a time-varying electric field of frequency
 given by
given by 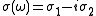 . The imaginary part arises from kinetic inductance, with
. The imaginary part arises from kinetic inductance, with  . The Drude complex conductivity can be expanded into its real and imaginary components:
. The Drude complex conductivity can be expanded into its real and imaginary components:
where
 is the mass of the charge carrier (i.e. the effective electron
is the mass of the charge carrier (i.e. the effective electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
mass in metallic conductors
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
) and
 is the carrier number density. In normal metals the collision time is typically
is the carrier number density. In normal metals the collision time is typically  s, so for frequencies < 100 GHz the term
s, so for frequencies < 100 GHz the term  is very small and can be ignored. Kinetic inductance is therefore only significant at optical frequencies and in superconductors, where
is very small and can be ignored. Kinetic inductance is therefore only significant at optical frequencies and in superconductors, where  .
.For a superconducting wire, the kinetic inductance can be calculated by equating the total kinetic energy of the Cooper pairs with an equivalent inductive energy:

where
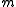 is the electron mass (
is the electron mass ( is the mass of a Cooper pair),
is the mass of a Cooper pair),  is the average Cooper pair velocity,
is the average Cooper pair velocity,  is the density of Cooper pairs,
is the density of Cooper pairs, 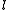 is the length of the wire,
is the length of the wire, 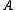 is the wire cross-sectional area, and
is the wire cross-sectional area, and  is the current. Using the fact that the current
is the current. Using the fact that the current 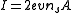 , where
, where  is the electron charge, this yields:
is the electron charge, this yields:
The same procedure can be used to calculate the kinetic inductance of a normal (i.e. non-superconducting) wire, except with
 replaced by
replaced by  ,
,  replaced by
replaced by  , and
, and 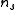 replaced by the normal carrier density
replaced by the normal carrier density  . This yields:
. This yields: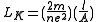
The kinetic inductance increases as the carrier density decreases. Physically, this is because a smaller number of carriers must have a greater velocity than a larger number of carriers in order to achieve the same current. In a normal metal wire, the resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
also increases as the carrier density
 decreases. As a result, in normal metals the resistive contribution to the impedance
decreases. As a result, in normal metals the resistive contribution to the impedanceElectrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
dominates the contribution from kinetic inductance up to frequencies ~ THz.
Applications
Kinetic inductance in superconductors is exploited to make efficient microwaveMicrowave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
delay lines as it increases the inductance per unit length of superconducting transmission lines.
Kinetic inductance can be used to make sensitive photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
detectors, known as kinetic inductance detectors (KIDs), as the change in the Cooper pair
Cooper pair
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair is two electrons that are bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper...
density brought about by the absorption of a photon in a strip of superconducting material produces a measurable change in kinetic inductance.
Kinetic inductance is also used in a design parameter for superconducting flux qubit
Flux qubit
In quantum computing, flux qubits are micrometer sized loops of superconducting metal interrupted by a number of Josephson junctions. The junction parameters are engineered during fabrication so that a persistent current will flow continuously when an external flux is applied...
s:
 is the ratio of the kinetic inductance of the Josephson junctions in the qubit to the geometrical inductance of the flux qubit. A design with a low beta behaves more like a simple inductive loop, while a design with a high beta is dominated by the Josephson junctions and has more hysteretic behavior.
is the ratio of the kinetic inductance of the Josephson junctions in the qubit to the geometrical inductance of the flux qubit. A design with a low beta behaves more like a simple inductive loop, while a design with a high beta is dominated by the Josephson junctions and has more hysteretic behavior.See also
- Drude modelDrude modelThe Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials...
- Electrical conduction
- Electron mobilityElectron mobilityIn solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterizes how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor, when pulled by an electric field. In semiconductors, there is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility...
- InductanceInductanceIn electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
- SuperconductivitySuperconductivitySuperconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance occurring in certain materials below a characteristic temperature. It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum...

