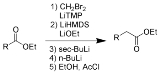
Kowalski ester homologation
Encyclopedia
The Kowalski ester homologation is a chemical reaction
for the homologation
of ester
s.
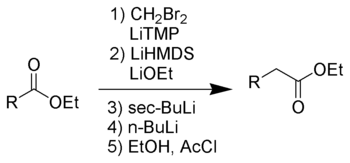 This reaction was designed as a safer alternative to the Arndt-Eistert synthesis
This reaction was designed as a safer alternative to the Arndt-Eistert synthesis
. The Kowalski reaction is named after its inventor, Conrad J. Kowalski.
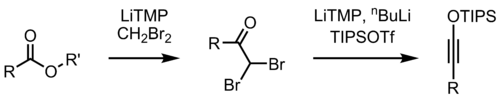 The mechanism is disputed.
The mechanism is disputed.
By changing the reagent
in the second step of the reaction, the Kowalski ester homologation can also be used for the preparation of silyl ynol
ether
s.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
for the homologation
Homologation reaction
A homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A Homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the...
of ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s.

Arndt-Eistert synthesis
The Arndt-Eistert synthesis is a series of chemical reactions designed to convert a carboxylic acid to a higher carboxylic acid homologue and is considered a homologation process...
. The Kowalski reaction is named after its inventor, Conrad J. Kowalski.
Reaction mechanism
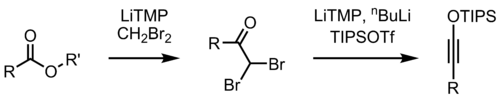
Variations
A modification of the procedure has been described that results in higher yields.By changing the reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
in the second step of the reaction, the Kowalski ester homologation can also be used for the preparation of silyl ynol
Ynol
In chemistry, an ynol is an alkyne with a hydroxyl group affixed to one of the two carbons composing the triple bond. The deprotonated anions of ynols are known as ynolates...
ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
s.

