Kyoto shogi
Encyclopedia
Kyoto shogi is a modern variant
of shogi
(Japanese chess). It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976.
Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board. However, the pieces alternately promote and demote with every move, and the promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi.
Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are:
The names of the pieces combine their promoted and unpromoted values, and are puns in Japanese for words with the same pronunciations but different kanji. For example, the lance/tokin is homonymous with the name of the city 京都 Kyoto
, and provides the name of the game.
style="background:#ffdead" border="1" cellspacing="0">
5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
P
G
K
S
T
a
b
c
d
T
S
K
G
P
e
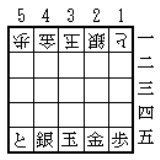
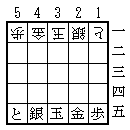
Each side places his pieces in the positions shown below, pointing toward the opponent.
That is, the first rank is |T|S|K|G|P|.
The promotion rules and values are reminiscent of microshogi
and entirely different from standard shogi:
Shogi variant
Many variants of shogi have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest...
of shogi
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a two-player board game in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, and Chinese Xiangqi, and is the most popular of a family of chess variants native to Japan...
(Japanese chess). It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976.
Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board. However, the pieces alternately promote and demote with every move, and the promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi.
Game equipment
Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of 5 ranks (rows) by 5 files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color.Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are:
- 1 king
- 1 gold general
- 1 silver general
- 1 tokin
- 1 pawn
| Piece | Kanji Kanji Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet... |
Rōmaji |
|---|---|---|
| White king | 王将 | ōshō |
| Black king | 玉将 | gyokushō |
| Rook/pawn | 飛歩 | hifu |
| Silver-general/bishop | 銀角 | ginkaku |
| Gold-general/knight | 金桂 | kinkei |
| Lance/tokin | 香と | kyōto |
The names of the pieces combine their promoted and unpromoted values, and are puns in Japanese for words with the same pronunciations but different kanji. For example, the lance/tokin is homonymous with the name of the city 京都 Kyoto
Kyoto
is a city in the central part of the island of Honshū, Japan. It has a population close to 1.5 million. Formerly the imperial capital of Japan, it is now the capital of Kyoto Prefecture, as well as a major part of the Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto metropolitan area.-History:...
, and provides the name of the game.
Setup

| style="background:#ffdead" border="1" cellspacing="0"> | |||||
| 5 | | 4 | | 3 | | 2 | | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 歩 | 金 | 王 | 銀 | と | 一 |
| 二 | |||||
| 三 | |||||
| 四 | |||||
| と | 銀 | 玉 | 金 | 歩 | 五 |
Each side places his pieces in the positions shown below, pointing toward the opponent.
- In the rank nearest the player:
- The king (K) is placed in the center file.
- The gold general (G) is placed in the adjacent files to the right of the king.
- The silver general (S) is placed in the adjacent files to the left of the king.
- The tokin (T) is placed in the left corner.
- The pawn (P) is placed in the right corner.
That is, the first rank is |T|S|K|G|P|.
Promotion
There is no promotion zone in Kyoto shogi. Every time a piece makes a move it alternately promotes and reverts to its unpromoted state. Promotion is effected by turning the piece over after it moves, revealing the name of its promoted rank; demotion is effected by turning the piece back.The promotion rules and values are reminiscent of microshogi
Microshogi
Microshogi is a modern variant of shogi , with very different rules for promotion, and depromotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOST gave it this English name. Although not confirmed, he credits its invention to the late Oyama Yasuharu, a top level shogi player...
and entirely different from standard shogi:
- A king cannot promote: K
- A tokin (T) promotes to a lance and vice versa: T ↔ L
- A silver general promotes to a bishop and vice versa: S ↔ B
- A gold general promotes to a knight and vice versa: G ↔ N
- A pawn promotes to a rook and vice versa: P ↔ R
Movement and capture
A piece is allowed to move, capture or be dropped in a manner that will prevent it from moving on a subsequent turn, which is illegal in standard shogi. For example, a rook can move onto the farthest rank, becoming a pawn and unable to move further. Such pieces may be captured as any other.See also
- Shogi variantShogi variantMany variants of shogi have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest...
- Whale shogiWhale shogiWhale Shogi is a modern variant of shogi . It is not, however, Japanese: it was invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger of the United States in 1981...
- MinishogiMinishogi|right|Minishogi board setupMinishogi is a modern variant of shogi . Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka, Japan, invented or rediscovered the game c. 1970...
- Judkins shogiJudkins shogiJudkins shogi is a modern variant of shogi , however it is not Japanese. Credit for its invention has been given to Paul Judkins of Norwich, UK, prior to April 1998.- Game equipment :...
- MicroshogiMicroshogiMicroshogi is a modern variant of shogi , with very different rules for promotion, and depromotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOST gave it this English name. Although not confirmed, he credits its invention to the late Oyama Yasuharu, a top level shogi player...
- Cannon shogiCannon shogiCannon shogi is a modern variant of shogi . It was invented by Peter Michaelsen in February 1998.- Game equipment :Two players, Black and White , play on a board ruled into a grid of 9 ranks by 9 files...
- Yari shogiYari shogiYari shogi is a modern variant of shogi , however it is not Japanese. It was invented in 1981 by Christian Freeling of the Netherlands...

