Microshogi
Encyclopedia
Microshogi is a modern variant
of shogi
(Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and depromotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOST (knights Of the Square Table) gave it this English name. Although not confirmed, he credits its invention to the late Oyama Yasuharu, a top level shogi player. The game was invented before 1982.

Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces. The pieces are of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (or most to least powerful) they are:
style="background:#ffdead" border="1" cellspacing="0">
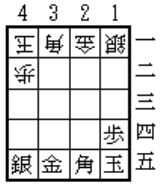
4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
K
B
G
S
a
P
b
c
P
d
S
G
B
K
e
Each side places his pieces in the following positions, pointing toward the opponent. For more information click here.
That is, the first rank is |S|G|B|K|.
Promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi:
Thus when a lance, tokin, rook, or knight makes a capture, it reverts back to its former state.
A knight which reaches one of the two far ranks is trapped, as is a pawn which captures and thus promotes there. Likewise, a pawn that reaches the far rank is trapped, as is a knight which captures there. A lance is also trapped at the far rank, but can escape if it captures there and thus demotes to a silver. A silver which captures in the far rank and therefore promotes to a lance is trapped.
Any trapped piece may be captured and returned to play as part of the opposing army.
A tokin moves the same way as a golden general.
Shogi variant
Many variants of shogi have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest...
of shogi
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a two-player board game in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, and Chinese Xiangqi, and is the most popular of a family of chess variants native to Japan...
(Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and depromotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOST (knights Of the Square Table) gave it this English name. Although not confirmed, he credits its invention to the late Oyama Yasuharu, a top level shogi player. The game was invented before 1982.

Game equipment
Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of 5 ranks (rows) by 4 files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color.Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces. The pieces are of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (or most to least powerful) they are:
- 1 king
- 1 bishop
- 1 gold general
- 1 silver general
- 1 pawn
Setup
| style="background:#ffdead" border="1" cellspacing="0"> | ||||
| 4 | | 3 | | 2 | | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 王 将 |
角 行 |
金 将 |
銀 将 |
一 |
| 歩 兵 |
二 | |||
| |
三 | |||
| 歩 兵 |
四 | |||
| 銀 将 |
金 将 |
角 行 |
玉 将 |
五 |
Each side places his pieces in the following positions, pointing toward the opponent. For more information click here.
- In the rank nearest the player:
- The king is placed in the right corner
- The bishop is placed in the adjacent file to the king.
- The gold general is placed adjacent to the bishop.
- The silver general is placed adjacent to the gold general in the left corner.
That is, the first rank is |S|G|B|K|.
- In the second rank, each player places the pawn in the same file as the king.
Promotion
Unlike standard shogi, microshogi has no promotion zone. Instead, a piece promotes when it captures, and promotion is mandatory. When a promoted piece captures, it demotes—that is, it is flipped back over to show its original unpromoted value.Promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi:
- A king does not promote: K
- A silver general becomes a lance and vice versa: S ↔ L
- A bishop becomes a tokin (T) and vice versa: B ↔ T
- A gold general becomes a rook and vice versa: G ↔ R
- A pawn becomes a knight and vice versa: P ↔ N
Thus when a lance, tokin, rook, or knight makes a capture, it reverts back to its former state.
A knight which reaches one of the two far ranks is trapped, as is a pawn which captures and thus promotes there. Likewise, a pawn that reaches the far rank is trapped, as is a knight which captures there. A lance is also trapped at the far rank, but can escape if it captures there and thus demotes to a silver. A silver which captures in the far rank and therefore promotes to a lance is trapped.
Any trapped piece may be captured and returned to play as part of the opposing army.
A tokin moves the same way as a golden general.
Drops
Drops are similar to standard shogi, except that:- A player may drop a piece with either side facing up.
- Except for dropping in the far rank, there are no other restrictions when dropping pawns. That is, a player may have two unpromoted pawns on the same file, and a pawn can be dropped to give immediate checkmate.
See also
- Shogi variantShogi variantMany variants of shogi have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest...
- Tori shogiTori shogiTori shōgi is a variant of shogi attributed to Ōhashi Sōei in the late 18th century. The game is played on a 7×7 board and uses the drop rule; it's the only Japanese variant to do so...
- MinishogiMinishogi|right|Minishogi board setupMinishogi is a modern variant of shogi . Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka, Japan, invented or rediscovered the game c. 1970...
- Judkins shogiJudkins shogiJudkins shogi is a modern variant of shogi , however it is not Japanese. Credit for its invention has been given to Paul Judkins of Norwich, UK, prior to April 1998.- Game equipment :...
- Kyoto shogiKyoto shogiKyoto shogi is a modern variant of shogi . It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976.Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board...
- Cannon shogiCannon shogiCannon shogi is a modern variant of shogi . It was invented by Peter Michaelsen in February 1998.- Game equipment :Two players, Black and White , play on a board ruled into a grid of 9 ranks by 9 files...
- Yari shogiYari shogiYari shogi is a modern variant of shogi , however it is not Japanese. It was invented in 1981 by Christian Freeling of the Netherlands...

