
L
Encyclopedia

English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
as L with stroke, is a letter of the Polish
Polish alphabet
The Polish alphabet is the script of the Polish language, the basis for the Polish system of orthography . It is based on the Latin alphabet, but includes certain letters with diacritics: the line or kreska, which is graphically similar to an acute accent ; the overdot or kropka ; the tail or...
, Kashubian
Kashubian alphabet
The Kashubian alphabet is the script of the Kashubian language, based on the Latin alphabet. The Kashubian alphabet consists of 34 letters:...
, Sorbian
Sorbian alphabet
The Sorbian alphabet is based on the basic Latin alphabet but uses diacritics such as the acute accent and the caron, making it similar to the Czech and Polish alphabets...
, Łacinka (Latin Belarusian
Belarusian language
The Belarusian language , sometimes referred to as White Russian or White Ruthenian, is the language of the Belarusian people...
), Łatynka
Ukrainian Latin alphabet
A Latin alphabet for the Ukrainian language has been proposed or imposed several times in the history in Ukraine, but has never challenged the conventional Cyrillic Ukrainian alphabet. Actually it is promoted as a way of facilitating the Ukrainian integration within the European Union.In or...
(Latin Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
), Wilamowicean, Navajo
Navajo language
Navajo or Navaho is an Athabaskan language spoken in the southwestern United States. It is geographically and linguistically one of the Southern Athabaskan languages .Navajo has more speakers than any other Native American language north of the...
, Dene Suline
Dene Suline language
Dene Suline or Chipewyan is the language spoken by the Chipewyan people of central Canada. It is a part of the Athabaskan family...
, Inupiaq
Inupiaq language
The Inupiat language, also known as Inupiatun, Inupiaq, Iñupiaq, Inyupiaq, Inyupiat, Inyupeat, Inyupik, and Inupik, is a group of dialects of the Inuit language, spoken in northern and northwestern Alaska. The Iñupiaq language is a member of the Eskimo languages group. There are roughly 2,100...
, Zuni
Zuni language
Zuni is a language of the Zuni people, indigenous to western New Mexico and eastern Arizona in the United States. It is spoken by around 9,500 people worldwide, especially in the vicinity of Zuni Pueblo, New Mexico, and much smaller numbers in parts of Arizona.Unlike most indigenous languages in...
, Hupa
Hupa language
-External links :* * overview at the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages*...
, and Dogrib
Dogrib language
Dogrib, the English translation of the indigenous name ' , is a Northern Athabaskan language spoken by the First Nations Tłı̨chǫ people of the Canadian territory Northwest Territories...
alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
s, several proposed alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
s for the Venetian language
Venetian language
Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
, and the ISO 11940
ISO 11940
ISO 11940 is an ISO standard for the romanization of the Thai alphabet, published in 1998 and updated in September 2003.-Consonants:The transliteration of the pure consonants is derived from their usual pronunciation as an initial consonant. An unmarked h is used to form digraphs denoting...
romanization of the Thai alphabet
Thai alphabet
Thai script , is used to write the Thai language and other, minority, languages in Thailand. It has forty-four consonants , fifteen vowel symbols that combine into at least twenty-eight vowel forms, and four tone marks ....
. In Slavic languages, it represents the Lechitic
Lechitic languages
The Lechitic languages include three languages spoken in Central Europe, mainly in Poland, and historically also in the eastern and northern parts of modern Germany. This language group is a branch of the larger West Slavic language family...
–West Slavic
West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group that includes Czech, Polish, Slovak, Kashubian and Sorbian.Classification:* Indo-European** Balto-Slavic*** Slavic**** West Slavic***** Czech-Slovak languages****** Czech...
continuation of Proto-Slavic non-palatal
Palatal consonant
Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate...
l (see dark L). In most non-European languages, it represents a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
or similar sound.
Polish
In Polish, Ł is used to distinguish historical dark (velarizedVelarization
Velarization is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant.In the International Phonetic Alphabet, velarization is transcribed by one of three diacritics:...
) L from clear L.
In 1440 Jakub Parkoszowic proposed a letter resembling
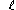 to represent clear L. For dark L he suggested l with a stroke running in the opposite direction as the modern version. The latter was introduced in 1514–1515 by Stanisław Zaborowski in his Orthographia seu modus recte scribendi et legendi Polonicum idioma quam ultissimus. L with stroke originally represented a velarized alveolar lateral approximant
to represent clear L. For dark L he suggested l with a stroke running in the opposite direction as the modern version. The latter was introduced in 1514–1515 by Stanisław Zaborowski in his Orthographia seu modus recte scribendi et legendi Polonicum idioma quam ultissimus. L with stroke originally represented a velarized alveolar lateral approximantVelarized alveolar lateral approximant
-See also:* Lateral consonant* Velarization* l-vocalization* Ł...
[ɫ], a pronunciation which is preserved in the eastern part of Poland and among the Polish minority in Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
. This pronunciation is similar to Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
unpalatalised <Л
El (Cyrillic)
El is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.El commonly represents the alveolar lateral approximant , like the pronunciation of ⟨l⟩ in "lip".-Form:...
> in native words and grammar forms.
In modern Polish, Ł is normally pronounced /w/ (almost exactly as w in English as a consonant, as in were, will, firewall but not as in new or straw). This pronunciation first appeared among Polish lower classes in the 16th century. It was considered an uncultured accent by the upper class
Upper class
In social science, the "upper class" is the group of people at the top of a social hierarchy. Members of an upper class may have great power over the allocation of resources and governmental policy in their area.- Historical meaning :...
es (who pronounced Ł almost exactly as: л in East Slavic languages
East Slavic languages
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken in Eastern Europe. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. Current East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian,...
or L in English pull) until the mid-20th century when this distinction gradually began to fade. Polish final Ł also often corresponds to Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
final/pre-consonant <В
Ve (Cyrillic)
Ve is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiced labiodental fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨v⟩ in "very"....
> (Cyrillic) and Belarusian
Belarusian language
The Belarusian language , sometimes referred to as White Russian or White Ruthenian, is the language of the Belarusian people...
<Ў> (Cyrillic). Thus, "he gave" is "dał" in Polish, "дав" in Ukrainian, "даў" in Belarusian, but "дал" in Russian. The old pronunciation [ɫ] of Ł is still fully understandable but is considered theatrical in most regions.
The shift from [ɫ] to [w] in Polish has affected all instances of dark L, even word-initially or intervocalically, e.g.
ładny ("pretty, nice") is pronounced [ˈwadnɨ], słowo ("word") is [ˈswɔvɔ], and ciało ("body") is [ˈtɕawɔ].
In Polish Ł often alternates with clear L, such as the plural forms
Grammatical number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, and adjective and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions ....
of adjective
Adjective
In grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
s and verbs in the past tense that are associated with masculine personal nouns, e.g. mały → mali ([ˈmawɨ] → [ˈmali]). Alternation is also common in declension
Declension
In linguistics, declension is the inflection of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and articles to indicate number , case , and gender...
of nouns, e.g. from nominative
Nominative case
The nominative case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments...
to locative
Locative case
Locative is a grammatical case which indicates a location. It corresponds vaguely to the English prepositions "in", "on", "at", and "by"...
, tło → na tle ([twɔ] → [naˈtlɛ]).
Some examples of words with 'ł':
- WisłaVistulaThe Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
(Vistula) - Łódź
- Michał (Michael)
- złoty (zloty)
In countries where Ł is not available, basic L is used instead. Thus, the surname Małecki would be spelled Malecki in a foreign country. Similarly, the stroke is sometimes omitted on the internet, as may happen with all diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
-enhanced letters. Although this is regarded as lazy, leaving out the diacritic does not impede communication for native speakers. However, it may be confusing for those learning Polish.
Other languages
In Belarusian Łacinka, Ł corresponds to CyrillicCyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
л
El (Cyrillic)
El is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.El commonly represents the alveolar lateral approximant , like the pronunciation of ⟨l⟩ in "lip".-Form:...
, and is normally pronounced /ɫ/ (almost exactly as l in English pull), both in the 1929 and 1962 versions.
The letter Ł is also used for non-Slavic languages.
In Navajo
Navajo language
Navajo or Navaho is an Athabaskan language spoken in the southwestern United States. It is geographically and linguistically one of the Southern Athabaskan languages .Navajo has more speakers than any other Native American language north of the...
, Ł is used for a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
(ɬ), like the Welsh Ll
Ll
Ll/ll is a digraph which occurs in several natural languages.-In English:In English, ll represents the same sound as single l:...
.
In Venetian
Venetian language
Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
Ł is used in substitution for L in many words in which the pronunciation of L has become different for several varieties of the language, such as becoming mute or becoming the sound of English a and the Venetian e. For example: "la gondoła " can be pronounced as (in Venetian) "la góndola", or "la góndoa", or "la góndoea".
When writing Scandinavian
North Germanic languages
The North Germanic languages or Scandinavian languages, the languages of Scandinavians, make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages, a sub-family of the Indo-European languages, along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages...
dialects having the pronunciation of a retroflex flap for the standard languages' L, many authors employ Ł.
Ł is used in orthographic transcription of Ahtna
Ahtna language
Ahtna or Ahtena is the Na-Dené language of the Ahtna ethnic group of the Copper River area of Alaska. The language is also known as Copper River or Mednovskiy...
, an Athabaskan language
Athabaskan languages
Athabaskan or Athabascan is a large group of indigenous peoples of North America, located in two main Southern and Northern groups in western North America, and of their language family...
spoken in Alaska; it represents a breathy
Breathy voice
Breathy voice is a phonation in which the vocal cords vibrate, as they do in normal voicing, but are held further apart, so that a larger volume of air escapes between them. This produces an audible noise...
lateral fricative. It is also used in Tanacross
Tanacross language
Tanacross is an endangered Athabaskan language spoken by fewer than 60 persons in eastern Interior Alaska.- Overview :The word Tanacross Tanacross (also Transitional Tanana) is an endangered Athabaskan language spoken by fewer than 60 persons in eastern Interior Alaska.- Overview :The word...
, a related Athabaskan language.
Computer usage
The UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
codepoints for the letter are U+0142 for the lower case, and U+0141 for the capital.
In the LaTeX
LaTeX
LaTeX is a document markup language and document preparation system for the TeX typesetting program. Within the typesetting system, its name is styled as . The term LaTeX refers only to the language in which documents are written, not to the editor used to write those documents. In order to...
typesetting system Ł and ł may be typeset with the commands \L and \l, respectively. The HTML-codes are Ł and ł for Ł and ł, respectively.
See also
- Ў, ў - Short U (Belarusian Cyrillic)Short UShort U is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.The only Slavic language using this letter is the Belarusian Cyrillic alphabet....
- Л, л - El (Cyrillic)El (Cyrillic)El is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.El commonly represents the alveolar lateral approximant , like the pronunciation of ⟨l⟩ in "lip".-Form:...
External links
- Kreska ukośna in Polish Diacritics: How to?, by Adam Twardoch, PolishPolandPoland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
country delegate at ATypIATypIThe ATypI or the Association Typographique Internationale is an international non-profit organisation dedicated to typography.-The organisation:...

