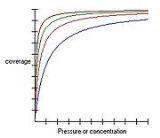
Langmuir equation
Overview
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
of molecules on a solid surface to gas pressure or concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of a medium above the solid surface at a fixed temperature. The equation was developed by Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir was an American chemist and physicist. His most noted publication was the famous 1919 article "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules" in which, building on Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom theory and Walther Kossel's chemical bonding theory, he outlined his...
in 1916. The equation is stated as:
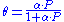
θ or theta is the fractional coverage of the surface, P is the gas pressure or concentration, α alpha
Alpha
Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. Alpha or ALPHA may also refer to:-Science:*Alpha , the highest ranking individuals in a community of social animals...
is a constant.
The constant α is the Langmuir adsorption constant and increases with an increase in the binding energy of adsorption and with a decrease in temperature.
The Langmuir equation is derived starting from the equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
between empty surface sites (
 ), particles (
), particles (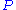 ) and filled particle sites (
) and filled particle sites (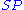 )
)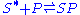
The equilibrium constant
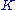 is thus given by the equation:
is thus given by the equation: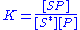
Because the number of filled surface sites (
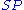 ) is proportional to θ, the number of unfilled sites (
) is proportional to θ, the number of unfilled sites (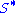 ) is proportional to 1-θ, and the number of particles is proportional to the gas pressure or concentration (p), the equation can be rewritten as:
) is proportional to 1-θ, and the number of particles is proportional to the gas pressure or concentration (p), the equation can be rewritten as: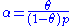
where
 is a constant.
is a constant.Rearranging this as follows:
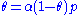
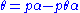
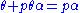
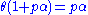
leads to Langmuir equation:
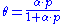
Other equations relating to adsorption exist, such as the Temkin equation or the Freundlich equation
Freundlich equation
The Freundlich equation or Freundlich adsorption isotherm is an adsorption isotherm, which is a curve relating the concentration of a solute on the surface of an adsorbent, to the concentration of the solute in the liquid with which it is in contact...
.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

