
Laser linewidth
Encyclopedia
←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth
of a laser
beam.
Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence
and spectral coherence
. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence
of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser linewidth of the radiation. Although the concept of laser linewidth can have varied theoretical descriptions here this article provides a simple experimental description. One of the first methods used to measure the coherence of a laser was interferometry
. An alternative approach is the use of spectrometry.
He-Ne laser (at a wavelength
of 632.8 nm), in the absence of intracavity line narrowing optics, can be of the order of 1 GHz. On the other hand, the laser linewidth from stabilized low-power continuous-wave lasers can be very narrow and reach down to less than 1 kHz. Often this type of linewidth is limited by fundamental quantum processes. This limit is known as the Schawlow–Townes linewidth which can be lower than Hz for some kind of CW lasers. Nevertheless observed linewidths are larger due to a technical noise (from noise in current, vibrations etc.).
s it can range from a few nm wide to as broad as 10 nm.
Laser linewidth from high-power high-gain pulsed laser oscillators, comprising line narrowing optics, is a function of the geometrical and dispersive features of the laser cavity. To a first approximation the laser linewidth, in an optimized cavity, is directly proportional to the beam divergence
of the emission multiplied by the inverse of the overall intracavity dispersion
. That is,
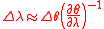
This is known as the cavity linewidth equation where is the beam divergence
is the beam divergence
and the term in parenthesis (elevated to –1) is the overall intracavity dispersion. This equation was originally derived from classical optics. However, in 1992 Duarte
derived this equation from quantum interferometric
principles, thus linking a quantum expression with the overall intracavity angular dispersion.
An optimized multiple-prism grating laser oscillator
can deliver pulse emission in the kW regime at single-longitudinal-mode linewidths of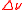 ≈ 350 MHz (equivalent to
≈ 350 MHz (equivalent to 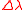 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm).
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm).
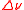 and is given in units of GHz, MHz, or kHz. In the spectral domain the laser linewidth is denoted as
and is given in units of GHz, MHz, or kHz. In the spectral domain the laser linewidth is denoted as 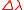 and is often given in units of nm. In the field of spectroscopy
and is often given in units of nm. In the field of spectroscopy
the use of the reciprocal cm, or cm-1, is widespread.
In more detail, the laser linewidth in frequency units can be written as

where c is the speed of light (in units of meters per second) and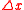 is the coherence length (in meters) so that the linewidth
is the coherence length (in meters) so that the linewidth 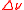 is in units of Hz. The equivalent definition in the wavelength domain is
is in units of Hz. The equivalent definition in the wavelength domain is
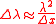
Thus the quantity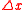 is the common factor between the equivalent linewidths in Hz and meter units. With these definitions it can shown, for example, that
is the common factor between the equivalent linewidths in Hz and meter units. With these definitions it can shown, for example, that 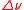 ≈ 350 MHz is equivalent to
≈ 350 MHz is equivalent to 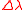 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm.
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm.
Spectral linewidth
The spectral linewidth characterizes the width of a spectral line, such as in the electromagnetic emission spectrum of an atom, or the frequency spectrum of an acoustic or electronic system...
of a laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
beam.
Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
and spectral coherence
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence
Beam divergence
The beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam...
of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser linewidth of the radiation. Although the concept of laser linewidth can have varied theoretical descriptions here this article provides a simple experimental description. One of the first methods used to measure the coherence of a laser was interferometry
Optical interferometry
Optical interferometry combines two or more light waves in an opticalinstrument in such a way that interference occurs between them.Early interferometers used white light sources and also monochromatic light from atomic sources...
. An alternative approach is the use of spectrometry.
CW lasers
Laser linewidth in a typical single-transverse-modeTransverse mode
A transverse mode of a beam of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of radiation measured in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction of the beam...
He-Ne laser (at a wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of 632.8 nm), in the absence of intracavity line narrowing optics, can be of the order of 1 GHz. On the other hand, the laser linewidth from stabilized low-power continuous-wave lasers can be very narrow and reach down to less than 1 kHz. Often this type of linewidth is limited by fundamental quantum processes. This limit is known as the Schawlow–Townes linewidth which can be lower than Hz for some kind of CW lasers. Nevertheless observed linewidths are larger due to a technical noise (from noise in current, vibrations etc.).
Pulsed lasers
Laser linewidth from high-power high-gain pulsed lasers, in the absence of intracavity line narrowing optics, can be quite broad and in the case of powerful broadband dye laserDye laser
A dye laser is a laser which uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and...
s it can range from a few nm wide to as broad as 10 nm.
Laser linewidth from high-power high-gain pulsed laser oscillators, comprising line narrowing optics, is a function of the geometrical and dispersive features of the laser cavity. To a first approximation the laser linewidth, in an optimized cavity, is directly proportional to the beam divergence
Beam divergence
The beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam...
of the emission multiplied by the inverse of the overall intracavity dispersion
Multiple-prism dispersion theory
The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959...
. That is,
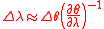
This is known as the cavity linewidth equation where
 is the beam divergence
is the beam divergenceBeam divergence
The beam divergence of an electromagnetic beam is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the electromagnetic beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam...
and the term in parenthesis (elevated to –1) is the overall intracavity dispersion. This equation was originally derived from classical optics. However, in 1992 Duarte
F. J. Duarte
F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory and has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations...
derived this equation from quantum interferometric
N-slit interferometric equation
Quantum mechanics was first applied to optics, and interference in particular, by Paul Dirac. Feynman, in his lectures, uses Dirac’s notation to describe thought experiments on double-slit interference of electrons...
principles, thus linking a quantum expression with the overall intracavity angular dispersion.
An optimized multiple-prism grating laser oscillator
Multiple-prism grating laser oscillator
Multiple-prism grating laser oscillators, or MPG laser oscillators, use multiple-prism beam expansion to illuminate a diffraction grating mounted either in Littrow configuration or grazing-incidence configuration...
can deliver pulse emission in the kW regime at single-longitudinal-mode linewidths of
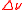 ≈ 350 MHz (equivalent to
≈ 350 MHz (equivalent to 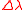 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm).
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm).Linewidth equivalence
In the frequency domain the laser linewidth is denoted as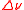 and is given in units of GHz, MHz, or kHz. In the spectral domain the laser linewidth is denoted as
and is given in units of GHz, MHz, or kHz. In the spectral domain the laser linewidth is denoted as 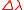 and is often given in units of nm. In the field of spectroscopy
and is often given in units of nm. In the field of spectroscopySpectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
the use of the reciprocal cm, or cm-1, is widespread.
In more detail, the laser linewidth in frequency units can be written as

where c is the speed of light (in units of meters per second) and
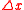 is the coherence length (in meters) so that the linewidth
is the coherence length (in meters) so that the linewidth 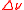 is in units of Hz. The equivalent definition in the wavelength domain is
is in units of Hz. The equivalent definition in the wavelength domain is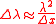
Thus the quantity
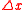 is the common factor between the equivalent linewidths in Hz and meter units. With these definitions it can shown, for example, that
is the common factor between the equivalent linewidths in Hz and meter units. With these definitions it can shown, for example, that 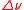 ≈ 350 MHz is equivalent to
≈ 350 MHz is equivalent to 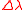 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm.
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm.See also
- Multiple-prism dispersion theoryMultiple-prism dispersion theoryThe first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959...
- Multiple-prism grating laser oscillatorMultiple-prism grating laser oscillatorMultiple-prism grating laser oscillators, or MPG laser oscillators, use multiple-prism beam expansion to illuminate a diffraction grating mounted either in Littrow configuration or grazing-incidence configuration...
- N-slit interferometric equationN-slit interferometric equationQuantum mechanics was first applied to optics, and interference in particular, by Paul Dirac. Feynman, in his lectures, uses Dirac’s notation to describe thought experiments on double-slit interference of electrons...
- Oscillator linewidthOscillator linewidthThe concept of a linewidth is borrowed from laser spectroscopy. The linewidth of a laser is a measure of its phase noise. The spectrogram of a laser is produced by passing its light through a prism. The spectrogram of the output of a pure noise-free laser will consist of a single infinitely thin...
- Solid state dye lasersSolid state dye lasersSolid state dye lasers were introduced in 1967 by Soffer and McFarland. In these solid state lasers, the gain medium is a laser dye-doped organic matrix such as poly , rather than a liquid solution of the dye...

