
Multiple-prism dispersion theory
Encyclopedia
The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton
in his book Opticks
. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster
in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born
and Wolf
in 1959. The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory was introduced by Duarte
and Piper in 1982.
and Piper, and is given by
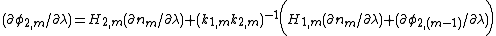
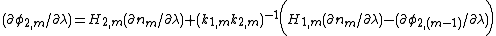
 where
where
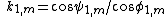
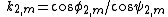
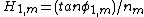
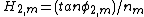
Here,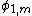 is the angle of incidence, at the mth prism, and
is the angle of incidence, at the mth prism, and 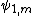 its corresponding angle of refraction. Similarly,
its corresponding angle of refraction. Similarly, 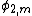 is the exit angle and
is the exit angle and 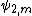 its corresponding angle of refraction. The two main equations give the first order dispersion for an array of m prisms at the exit surface of the mth prism. The plus sign in the second term in parenthesis refers to a positive dispersive configuration while the minus sign refers to a compensating configuration. The k factors are the corresponding beam expansions, and the H factors are additional geometrical quantities. It can also be seen that the dispersion of the mth prism depends on the dispersion of the previous prism (m - 1).
its corresponding angle of refraction. The two main equations give the first order dispersion for an array of m prisms at the exit surface of the mth prism. The plus sign in the second term in parenthesis refers to a positive dispersive configuration while the minus sign refers to a compensating configuration. The k factors are the corresponding beam expansions, and the H factors are additional geometrical quantities. It can also be seen that the dispersion of the mth prism depends on the dispersion of the previous prism (m - 1).
These equations can also be used to quantify the angular dispersion in prism arrays, as described in Isaac Newton
's book Opticks
, and as deployed in dispersive instrumentation such as multiple-prism spectrometers. A comprehensive review on practical multiple-prism beam expander
s and multiple-prism angular dispersion theory is given by Duarte.
More recently the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory has been extended to higher order phase derivatives using a Newtonian iterative approach. This extension of the theory enables the evaluation of the Nth higher derivative via an elegant mathematical framework. Applications include further refinements in the design of prism pulse compressors and nonlinear optics.
For a single right-angled prism (m = 1) with the beam exiting normal to the output face, that is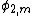 equal to zero, the Duarte-Piper equation reduces to
equal to zero, the Duarte-Piper equation reduces to
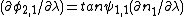
in multiple-prism grating laser oscillators. Adding the grating contribution to the dispersion renders an equation for the total intracavity angular dispersion. It is this total dispersion that plays an important role in the linewidth narrowing
of pulsed tunable lasers through the equation
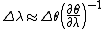
where the angular dispersion is the quantity in parenthesis (elevated to –1). Although originally classical in origin, in 1992 it was shown that this cavity linewidth equation can also be derived from quantum principles.
In 1987 the multiple-prism angular dispersion theory was extended to provide explicit second order equations directly applicable to the design of prismatic pulse compressors
.
The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory is applicable to:
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
in his book Opticks
Opticks
Opticks is a book written by English physicist Isaac Newton that was released to the public in 1704. It is about optics and the refraction of light, and is considered one of the great works of science in history...
. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster
David Brewster
Sir David Brewster KH PRSE FRS FSA FSSA MICE was a Scottish physicist, mathematician, astronomer, inventor, writer and university principal.-Early life:...
in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born
Max Born
Max Born was a German-born physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s...
and Wolf
Emil Wolf
Emil Wolf is a Czech born American physicist who made advancements in physical optics, including diffraction, coherence properties of optical fields, spectroscopy of partially coherent radiation, and the theory of direct scattering and inverse scattering. He is also the author of several works on...
in 1959. The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory was introduced by Duarte
F. J. Duarte
F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory and has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations...
and Piper in 1982.
Generalized multiple-prism dispersion equations
The generalized mathematical description of multiple-prism dispersion, as a function of the angle of incidence, prism geometry, prism refractive index, and number of prisms, was introduced as a design tool for multiple-prism grating laser oscillators by DuarteF. J. Duarte
F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory and has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations...
and Piper, and is given by
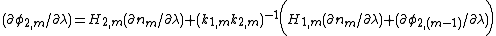
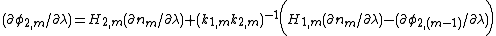

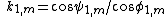
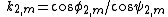
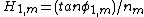
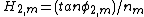
Here,
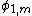 is the angle of incidence, at the mth prism, and
is the angle of incidence, at the mth prism, and 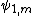 its corresponding angle of refraction. Similarly,
its corresponding angle of refraction. Similarly, 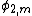 is the exit angle and
is the exit angle and 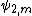 its corresponding angle of refraction. The two main equations give the first order dispersion for an array of m prisms at the exit surface of the mth prism. The plus sign in the second term in parenthesis refers to a positive dispersive configuration while the minus sign refers to a compensating configuration. The k factors are the corresponding beam expansions, and the H factors are additional geometrical quantities. It can also be seen that the dispersion of the mth prism depends on the dispersion of the previous prism (m - 1).
its corresponding angle of refraction. The two main equations give the first order dispersion for an array of m prisms at the exit surface of the mth prism. The plus sign in the second term in parenthesis refers to a positive dispersive configuration while the minus sign refers to a compensating configuration. The k factors are the corresponding beam expansions, and the H factors are additional geometrical quantities. It can also be seen that the dispersion of the mth prism depends on the dispersion of the previous prism (m - 1).These equations can also be used to quantify the angular dispersion in prism arrays, as described in Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
's book Opticks
Opticks
Opticks is a book written by English physicist Isaac Newton that was released to the public in 1704. It is about optics and the refraction of light, and is considered one of the great works of science in history...
, and as deployed in dispersive instrumentation such as multiple-prism spectrometers. A comprehensive review on practical multiple-prism beam expander
Beam expander
Beam expanders are used in laser physics either as intracavity or extracavity elements. They can be telescopic in nature or prismatic. Generally prismatic beam expanders use several prisms and are known as multiple-prism beam expanders....
s and multiple-prism angular dispersion theory is given by Duarte.
More recently the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory has been extended to higher order phase derivatives using a Newtonian iterative approach. This extension of the theory enables the evaluation of the Nth higher derivative via an elegant mathematical framework. Applications include further refinements in the design of prism pulse compressors and nonlinear optics.
For a single right-angled prism (m = 1) with the beam exiting normal to the output face, that is
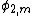 equal to zero, the Duarte-Piper equation reduces to
equal to zero, the Duarte-Piper equation reduces to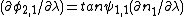
Applications
The first application of this theory was to evaluate the laser linewidthLaser linewidth
←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser...
in multiple-prism grating laser oscillators. Adding the grating contribution to the dispersion renders an equation for the total intracavity angular dispersion. It is this total dispersion that plays an important role in the linewidth narrowing
Laser linewidth
←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser...
of pulsed tunable lasers through the equation
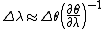
where the angular dispersion is the quantity in parenthesis (elevated to –1). Although originally classical in origin, in 1992 it was shown that this cavity linewidth equation can also be derived from quantum principles.
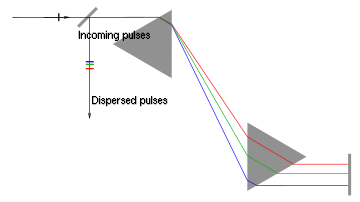
In 1987 the multiple-prism angular dispersion theory was extended to provide explicit second order equations directly applicable to the design of prismatic pulse compressors
Prism compressor
A prism compressor is an optical device used to shorten the duration of a positively chirped ultrashort laser pulse by giving different wavelength components a different time delay. It typically consists of two prisms and a mirror. Figure 1 shows the construction of such a compressor...
.
The generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory is applicable to:
- laser microscopyMicroscopyMicroscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
, - narrow-linewidth tunable laserTunable laserA tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range....
design, - prismatic beam expandersBeam expanderBeam expanders are used in laser physics either as intracavity or extracavity elements. They can be telescopic in nature or prismatic. Generally prismatic beam expanders use several prisms and are known as multiple-prism beam expanders....
- prism compressorPrism compressorA prism compressor is an optical device used to shorten the duration of a positively chirped ultrashort laser pulse by giving different wavelength components a different time delay. It typically consists of two prisms and a mirror. Figure 1 shows the construction of such a compressor...
s for femtosecond pulse lasers.
See also
- Beam expanderBeam expanderBeam expanders are used in laser physics either as intracavity or extracavity elements. They can be telescopic in nature or prismatic. Generally prismatic beam expanders use several prisms and are known as multiple-prism beam expanders....
- Laser linewidthLaser linewidth←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser...
- Multiple-prism grating laser oscillatorMultiple-prism grating laser oscillatorMultiple-prism grating laser oscillators, or MPG laser oscillators, use multiple-prism beam expansion to illuminate a diffraction grating mounted either in Littrow configuration or grazing-incidence configuration...

