
Prism compressor
Encyclopedia
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
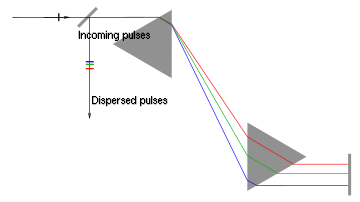
device used to shorten the duration of a positively chirped ultrashort laser pulse
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
by giving different wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
components a different time delay. It typically consists of two prisms and a mirror. Figure 1 shows the construction of such a compressor. Although the dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
of the prism material causes different wavelength components to travel along different paths, the compressor is built such that all wavelength components leave the compressor at different times, but in the same direction. If the different wavelength components of a laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
pulse were already separated in time, the prism compressor can make them overlap with each other, thus causing a shorter pulse.
Prism compressors are typically used to compensate for dispersion inside Ti:sapphire
Ti-sapphire laser
Ti:sapphire lasers are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses...
modelocked
Modelocking
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
laser. Each time the laser pulse inside travels through the optical components inside the laser cavity, it becomes stretched. A prism compressor inside the cavity can be designed such that it exactly compensates this intra-cavity dispersion. It can also be used to compensate for dispersion of ultrashort pulses outside laser cavities.
Prismatic pulse compression was first introduced, using a single prism, in 1983 by Dietel et al. and a four-prism pulse compressor was demonstrated in 1984 by Fork et al. Additional experimental developments include a prism-pair pulse compressor and a six-prism pulse compressor for semiconductor lasers. The multiple-prism dispersion theory
Multiple-prism dispersion theory
The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959...
, for pulse compression, was introduced in 1982 by Duarte
F. J. Duarte
F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory and has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations...
and Piper, extended to second derivatives in 1987, and further extended to higher order phase derivatives in 2009.
An additional compressor, using a large prism with lateral reflectors to enable a multi-pass arrangement at the prism, was introduced in 2006.
Principle of operation
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
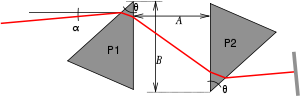
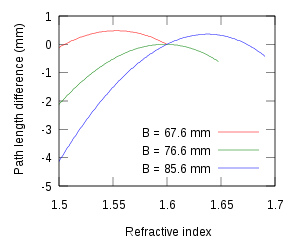
decreases with increasing wavelength. This means that longer wavelengths travel faster through these materials. The same is true for the prisms in a prism compressor. However, the positive dispersion of the prisms is offset by the extra distance that the longer wavelength components have to travel through the second prism. This is a rather delicate balance, since the shorter wavelengths travel a larger distance through air. However, with a careful choice of the geometry, it is possible to create a negative dispersion that can compensate positive dispersion from other optical components. This is shown in Figure 3. By shifting prism P2 up and down, the dispersion of the compressor can be both negative around refractive index n = 1.6 (red curve) and positive (blue curve). The range with a negative dispersion is relatively short since prism P2 can only be moved upwards over a short distance before the light ray misses it altogether.
In principle, the α angle can be varied to tune the dispersion properties of a prism compressor. In practice, however, the geometry is chosen such that the incident and refracted beam have the same angle at the central wavelength of the spectrum to be compressed. This configuration is known as the "angle of minimum deviation", and is easier to align than arbitrary angles.
The refractive index of typical materials such as BK7 glass changes only a small amount (0.01 – 0.02) within the few tens of nanometers that are covered by an ultrashort pulse. Within a practical size, a prism compressor can only compensate a few hundred µm of path length differences between the wavelength components. However, by using a large refractive index material (such as SF10, SF11, etc.) the compensation distance can be extended to mm level. This technology has been used successfully inside femtosecond laser cavity for compensation of the Ti:sapphire crystal, and outside for the compensation of dispersion introduced by other elements. However, high-order dispersion will be introduced by the prism compressor itself, as well as other optical elements. It can be corrected with careful measurement of the ultrashort pulse
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
and compensate the phase distortion. MIIPS is one of the pulse shaping
Femtosecond pulse shaping
In optics, femtosecond pulse shaping is a technique that modifies the temporal profile of an ultrashort pulse from a laser. Pulse shaping can be used to shorten/elongate the duration of optical pulse, or to generate more complex pulses.-Introduction:...
techniques which can measure and compensate high-order dispersion automatically. As a muddled version of pulse shaping the end mirror is sometimes tilted or even deformed, accepting that the rays do not travel back the same path or become divergent.
Comparison with other pulse compressors
The most common other pulse compressor is based on gratingsDiffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as...
(see Chirped pulse amplification
Chirped pulse amplification
Chirped pulse amplification is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally prior to amplification...
), which can easily create a much larger negative dispersion than a prism compressor (centimeters rather than tenths of millimeters). However, a grating compressor has losses of at least 30% due to higher-order diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
and absorption
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
losses in the metallic coating of the gratings. A prism compressor with an appropriate anti-reflection coating can have less than 2% loss, which makes it a feasible option inside a laser cavity. Moreover, a prism compressor is cheaper than a grating compressor.
Another pulse compression technique uses chirped mirrors, which are dielectric mirror
Dielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror is a type of a mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating with specified...
s that are designed such that the reflection has a negative dispersion. Chirped mirrors are difficult to manufacture; moreover the amount of dispersion is rather small, which means that the laser beam must be reflected a number of times in order to achieve the same amount of dispersion as with a single prism compressor. This means that it is hard to tune. On the other hand, the dispersion of a chirped-mirror compressor can be manufactured to have a specific dispersion curve, whereas a prism compressor offers much less freedom. Chirped-mirror compressors are used in applications where pulses with a very large bandwidth have to be compressed.
See also
- Chirped pulse amplificationChirped pulse amplificationChirped pulse amplification is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally prior to amplification...
- Ti:sapphire laserTi-sapphire laserTi:sapphire lasers are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses...
- ModelockingModelockingMode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
- Ultrashort pulseUltrashort pulseIn optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
- MIIPS, a technique to calibrate and correct the high-order distortion of femtosecond laser pulse.
- Multiple-prism dispersion theoryMultiple-prism dispersion theoryThe first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959...

