
Life Quality Index
Encyclopedia
The Life Quality Index (LQI) is a compound social indicator of human welfare
that reflects the expected length of life
in good health and enhancement of the quality of life through access to income
. The Life Quality Index combines two primary social indicators: the expectancy of healthy life at birth, E, and the real gross domestic product
per person, G, corrected for purchasing power parity
as appropriate. Both are widely available and accurate statistics
.
, the duration of life in good health and the time available to enjoy life. The amount of life available to enjoy wealth acts as a multiplying factor upon the value of that wealth. Conversely, the amount of income one has to enjoy that available lifetime acts as a multiplier on the expected duration of life.
Unlike the United Nation’s Human Development Index
(HDI), the LQI is derived rigorously from the economics of human welfare. Like the HDI it can be used to rank nations in order of human welfare (development). However, more important and unlike the HDI it can also serve as an objective function to be used in setting national or corporate goals for managing risk
and to guide effective allocation of society’s scarce resources for the mitigation of risks to life or health. The LQI is a summary indicator of net benefit to society for improving the overall public welfare by reducing risks to life in a cost-effective manner.
In the accounting and assessment of human development, we can view the role of individuals as the principal means, or contributors, to development as well as the ends. For example, the productivity of an individual contributes directly to the aggregate wealth creation in a society. However, the income so generated (to whomsoever it may accrue) increases the capacity of society to provide the necessary means such as the required infrastructure
(hospital
s, school
s, clean water
, safe road
s and structures). The adequacy of the infrastructure in turn benefits the individual via access to quality health and environment
, education
and means for cultural
expression and enrichment. The LQI enhances our decision-making capacity and helps brings into sharp focus the choices and trade-offs we have to make between extension of life and creation of productive wealth.
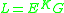
showing the LQI, L as a power function
of E, the health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) at birth and G, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per person. The parameter K is a constant based on time budget studies available for many countries. K is approximately equal to 5.0 for developed nations (Rackwitz 2005, Pandey et al. 2006).
Suppose a portion of GDP, dG, is invested in implementing a program that has an impact on public risk, thus modifying the life expectancy by a small amount dE. There is a net benefit if there is a net increase in LQI, dL. This criterion can be derived from the definition of L as:
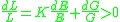
from which the Societal Capacity to Commit Resources to sustainable risk reduction follows as:
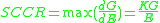
through better allocation of society’s scarce resources by reducing wasteful efforts on inefficient risk-reduction and identifying efficient alternatives.
Given that the Societal Capacity to Commit Resources (SCCR) is limited, the LQI is a powerful indicator of merit amongst competing but desirable goods, such as for example level of resources to be directed at air pollution
vs water pollution
vs low probability
, high consequence risks in the distant future.
The Life Quality Index may be thought of as refinement of monetary measures commonly used in cost-benefit analysis
.
, Waterloo, Ontario
, Canada in the early 1990s The two primary publications were:
Waterloo, ON, Canada, pp 230.
The principal investigators involved in the development of the Life Quality Index have been Professors Niels Lind, Jatin Nathwani and Mahesh Pandey.
Quality of life
The term quality of life is used to evaluate the general well-being of individuals and societies. The term is used in a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, and politics. Quality of life should not be confused with the concept of standard of...
that reflects the expected length of life
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
in good health and enhancement of the quality of life through access to income
Income
Income is the consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified time frame, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. However, for households and individuals, "income is the sum of all the wages, salaries, profits, interests payments, rents and other forms of earnings...
. The Life Quality Index combines two primary social indicators: the expectancy of healthy life at birth, E, and the real gross domestic product
Real GDP
Real Gross Domestic Product is a macroeconomic measure of the value of output economy adjusted for price changes . The adjustment transforms the money-value measure, called nominal GDP, into an index for quantity of total output...
per person, G, corrected for purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
as appropriate. Both are widely available and accurate statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
.
Basic concept
The three components of the Life Quality Index, G, E and K reflect three important human concerns: the creation of wealthWealth
Wealth is the abundance of valuable resources or material possessions. The word wealth is derived from the old English wela, which is from an Indo-European word stem...
, the duration of life in good health and the time available to enjoy life. The amount of life available to enjoy wealth acts as a multiplying factor upon the value of that wealth. Conversely, the amount of income one has to enjoy that available lifetime acts as a multiplier on the expected duration of life.
Unlike the United Nation’s Human Development Index
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
(HDI), the LQI is derived rigorously from the economics of human welfare. Like the HDI it can be used to rank nations in order of human welfare (development). However, more important and unlike the HDI it can also serve as an objective function to be used in setting national or corporate goals for managing risk
Risk management
Risk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities...
and to guide effective allocation of society’s scarce resources for the mitigation of risks to life or health. The LQI is a summary indicator of net benefit to society for improving the overall public welfare by reducing risks to life in a cost-effective manner.
In the accounting and assessment of human development, we can view the role of individuals as the principal means, or contributors, to development as well as the ends. For example, the productivity of an individual contributes directly to the aggregate wealth creation in a society. However, the income so generated (to whomsoever it may accrue) increases the capacity of society to provide the necessary means such as the required infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
(hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
s, school
School
A school is an institution designed for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is commonly compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools...
s, clean water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
, safe road
Road
A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places, which typically has been paved or otherwise improved to allow travel by some conveyance, including a horse, cart, or motor vehicle. Roads consist of one, or sometimes two, roadways each with one or more lanes and also any...
s and structures). The adequacy of the infrastructure in turn benefits the individual via access to quality health and environment
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
, education
Education
Education in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts...
and means for cultural
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
expression and enrichment. The LQI enhances our decision-making capacity and helps brings into sharp focus the choices and trade-offs we have to make between extension of life and creation of productive wealth.
Formulation
The mathematical expression for the Life-Quality Index L is: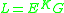
showing the LQI, L as a power function
Power function
In mathematics, a power function is a function of the form , where c and a are constant real numbers and x is a variable.Power functions are a special case of power law relationships, which appear throughout mathematics and statistics....
of E, the health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE) at birth and G, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per person. The parameter K is a constant based on time budget studies available for many countries. K is approximately equal to 5.0 for developed nations (Rackwitz 2005, Pandey et al. 2006).
Societal Capacity to Commit Resources (SCCR)
The LQI has been used to determine an acceptable level of expenditure that can be justifiably incurred on behalf of the public interest in exchange for a small reduction in the risk of death that results in improved life-quality for all. This value can be considered as the Societal Capacity to Commit Resources (SCCR) to sustainable risk reduction.Suppose a portion of GDP, dG, is invested in implementing a program that has an impact on public risk, thus modifying the life expectancy by a small amount dE. There is a net benefit if there is a net increase in LQI, dL. This criterion can be derived from the definition of L as:
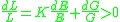
from which the Societal Capacity to Commit Resources to sustainable risk reduction follows as:
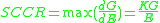
Application
The Life Quality Index is a decision tool serving to promote human developmentHuman development (humanity)
Human development in the scope of humanity, specifically international development, is an international and economic development paradigm that is about much more than the rise or fall of national incomes. People are the real wealth of nations...
through better allocation of society’s scarce resources by reducing wasteful efforts on inefficient risk-reduction and identifying efficient alternatives.
Given that the Societal Capacity to Commit Resources (SCCR) is limited, the LQI is a powerful indicator of merit amongst competing but desirable goods, such as for example level of resources to be directed at air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
vs water pollution
Water pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
vs low probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
, high consequence risks in the distant future.
Using the Life Quality Index or SCCR to Judge Risk
Risks influence the LQI via the age- and sex-specific mortality, calculated by changes in an actuarial life table. The safety benefit is the gain in health-adjusted life expectancy HALE, or life extension expected upon implementation of the program. The cost impacts must also be evaluated, measured as the impact on the real gross domestic product per person (with refinements that could include correction for purchasing power parity for international comparisons). The net benefit of a program is measured, according to the SCCR, by the resultant increases in real gross domestic product per capita and life expectancy, weighted by K, eq.(3).The Life Quality Index may be thought of as refinement of monetary measures commonly used in cost-benefit analysis
Cost-benefit analysis
Cost–benefit analysis , sometimes called benefit–cost analysis , is a systematic process for calculating and comparing benefits and costs of a project for two purposes: to determine if it is a sound investment , to see how it compares with alternate projects...
.
Net Benefit Criterion for Managing Risk
The objective is to maximize life expectancy subject to society’s capacity to commit resources in light of existing or future constraints. Reducing risk of death and disease translates into longer healthful lives. The length of life extension in good health for a population can be reliably measured as the impact on the gain in life expectancy (dE). Resources and monies (-dG) are required to achieve the gains, or increases, in life expectancy. If the resources are wisely spent, then the gains in life expectancy will be sufficiently large that there is a net increase in the Life Quality Index (LQI). In contrast, if inordinate sums are spent on activities that do not save lives or result in only meagre life extension then there is a net decrease in the LQI.Life Quality Index as a Tool for Managing Risk
Through case studies and worked examples, it has been shown how the Life Quality Index can be used to assist decision-makers in evaluating the effectiveness of regulations and activities aimed at reducing risk to life, health and the environment. The LQI is a versatile tool that can be used to assess a wide range of risk management problems. The examples of application of LQI include:- the effectiveness of standards and regulations for health and safety;
- harmonization of structural safety standardsBuilding codeA building code, or building control, is a set of rules that specify the minimum acceptable level of safety for constructed objects such as buildings and nonbuilding structures. The main purpose of building codes are to protect public health, safety and general welfare as they relate to the...
and design goals; - assessment of air pollution standards;
- efficiency of life-saving interventions and estimates of the societal willingness (or capacity) to commit resources for safety.
Development of the Life Quality Index
The concept of the Life Quality Index was first initiated at the Institute for Risk Researchhttp://www.irr-neram.ca/, University of WaterlooUniversity of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo is a comprehensive public university in the city of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The school was founded in 1957 by Drs. Gerry Hagey and Ira G. Needles, and has since grown to an institution of more than 30,000 students, faculty, and staff...
, Waterloo, Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, Canada in the early 1990s The two primary publications were:
- Lind, N.C., Nathwani, J.S. and Siddal, E. (1992). Managing Risks in the Public Interest, Institute of Risk Research, University of Waterloo Press, Waterloo, ON, Canada and
- Nathwani, J.S., Lind, N.C., and Pandey, M.D. (1997). Affordable Safety by Choice: The Life Quality Method. Institute for Risk Research, University of Waterloo Press,
Waterloo, ON, Canada, pp 230.
The principal investigators involved in the development of the Life Quality Index have been Professors Niels Lind, Jatin Nathwani and Mahesh Pandey.
See also
- Manchester Short Assessment of Quality of LifeMANSAMANSA is a scale used to assess quality of life. Its name is short for Manchester Short Assessment of Quality of Life. It was developed by Priebe et al. in 1999. The creators of the scale found the results of the scale to be comparable to the Lancashire Quality of Life Profile.The MANSA consists of...
- Nonlinear quality of life index

