List of videogame consoles palettes
Encyclopedia
This is a list of the full color palettes
for notable video game console
hardware.
For color palettes of early 8-bit
personal computer
s, see the List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For color palettes of 16-bit
personal computer
s, see the List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For current RGB display systems for 32-bit
and better PCs
(Super VGA
, etc.), see the 16-bit RGB for HighColor (thousands) and 24-bit RGB for TrueColor (millions of colors) modes.
For various software arrangements and sorts of colors, see the List of software palettes article.
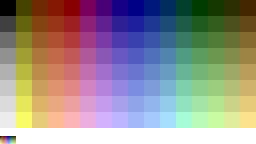
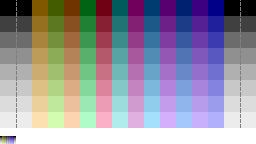
For each unique palette, an image color test chart and sample image (Truecolor original follows) rendered with that palette (without dither
ing) are given. The test chart shows the full 8-bits, 256 levels of the red, green and blue (RGB
) primary colors and cyan, magenta and yellow complementary colors, along with a full 8-bits, 256 levels grayscale. Gradients of RGB intermediate colors (orange, lime green, sea green, sky blue, violet and fucsia), and a full hue
's spectrum are also present. Color charts are not gamma
corrected.
These elements let to study the color depth
and distribution of the full colors of any given palette, and the sample image indicates how the full color selection of such palettes would represent real life images. These images are not necessarily representative of how the image would be displayed on the original graphics hardware, as the hardware may have additional limitations regarding the maximum display resolution
, pixel
aspect ratio
and color placement.
For specific models of videogame consoles, simulations of how the sample image would render in different graphic modes are provided, if available. These simulations are always up to the maximum vertical resolution of the given graphic mode or up to 200 scan lines, if vertical resolution is greater. So any of them could be properly padded, transcoded and dumped into the original hardware and/or software emulators without any other changes.
The sample images only try to show how a certain system is able to handle to an image in terms of color without improvements nor additional clever tricks of design like anti-aliasing
or dithering
. Doubtlessly a human artist is able to improve enormously the look of the simulated images to approximate them to the original one, but that is not the goal of this article.
Note: please do not change the compression scheme of every image by a lossy compression scheme (i.e. JPEG
) in order to improve their file size, nor change the thumbnail size of the images, nor gamma-correct them. They are didactical material AS IS, and they have been already optimized for this purpose.
used different YPbPr
color palettes dependent on the television signal format used.
With the NTSC
format, a 128-color palette was available, built based on eight luminance
values and fifteen combinations of Pb and Pr chroma
signals (plus Pb = Pr = 0 for a pure grayscale
):
The hardware supports 4 colors per scanline: a background, an arbitrary 40-pixel wide bitmapped playfield, and colors for the two players. Using just the first two, an NTSC console could draw the above.
With the PAL
format, a 104-color palette was available. 128-color entries were still selectable, but due to changes in color encoding schemes, 32 color entries results in the same eight shades of gray:
Using just the playfield and background controls, a PAL console could draw the above.
The SECAM
palette were reduced to a simple 3-bit RGB, contained only 8 colors:
(PPU) was used in the Nintendo Entertainment System
and had a YPbPr
64-color palette (plus color emphasis bits, not counted), eight of which are reserved, giving a total of 56 useful colors. The palette is built based on four luminance
values and twelve combinations of Pb and Pr chroma
signals (plus two series of Pb = Pr = 0 for eight pure grays). Some of the shades of gray are so similar, that sometimes the palette has been reported to have only 53 to 55 colors.
There are no current simulated screen images available for the NES.
has a 15-bit RGB (32,768 color) palette, with up to 256 simultaneous colors.
However, while the hardware palette can only contain 256 entries, in most display modes the graphics are arranged into between 2 and 4 layers, and these layers can be combined using additive or subtractive colour blending.
Because these blended colours are calculated by the hardware itself, and do not have to be represented by any of the existing palette entries, the actual number of visible colours onscreen at any one time can be much higher.
The exact number depends on the number of layers, and the combination of colours used by these layers, as well as what blending mode and graphical effects are in use. In theory it can show the entire 32,768 colours, but in practice this is rarely the case.
systems uses a 15-bit RGB (32,768 colours) palette.
When an older monochrome original Game Boy game catridge (Type 1) is plugged-in, if certain combinations of the controls are held during startup, the games are colourised with one of the factory 12 false colour palettes. In this mode, games can have from 4 to 10 colours, due 4 are for the background plane palette and there are two more hardware sprite planes palettes, with 3 colours plus transparent each.
The following shows these startup palettes (background plus both sprite planes) and the combination of controls used (the names are taken from the Game Boy user's manual; the colours are simulated):
The specific Game Boy Color (Type 3) game catridges presents up to 56 colors without the use special programming techniques from the full 32,768. From these, 32 are for a background palette, plus 8 hardware sprite palettes, with 3 colors plus transparent each. Typically, the sprite palettes shares some colors (black, white or others), so the total colors displayed are less than 56.
Here is the sample image shown in the non-backlighted color LCD display of the Game Boy Color (the colors are simulated):
Though there is a 56 color limit, this in of itself is a palette storage limit and not an actual hardware limitation. As such, the programmer can swap out the palettes on a per-scanline or even on a mid-scanline basis ("mode 3 mid-scanline rendering"). Because of this ability to swap out the palettes each scanline, over ten thousand colors can actually appear on screen per frame when programmed on a per-scanline basis.
/SP
/Micro
systems also uses a 15-bit RGB palette, and along with the original and Color modes, they have also a specific Highcolor 32,768 colors mode.
The color LCD displays of the SP and Micro are backlit, giving brighter images.
Here are sample images shown in the backlit color LCD display of the Game Boy Advance/SP/Micro in both Game Boy Color compatible mode and Game Boy Advance 32K color mode:
had a 6-bit RGB palette (64 colors), with 32 colors on-screen at once. It is possible to display all 64 colors at once using raster effects (line interrupts).
had a 12-bit RGB palette (4096 colors), with 32 colors on-screen at once.
used a 9-bit RGB palette, like the Sega Mega Drive/Genesis, consisting of 512 colors with 482 colors on-screen at once (16 background palettes of 16 colors each, with at least 1 common color among all background palettes, and 16 sprite palettes of 15 colors each, plus transparent which was visible as the overscan area).
Palette (computing)
In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
for notable video game console
Video game console
A video game console is an interactive entertainment computer or customized computer system that produces a video display signal which can be used with a display device to display a video game...
hardware.
For color palettes of early 8-bit
8-bit
The first widely adopted 8-bit microprocessor was the Intel 8080, being used in many hobbyist computers of the late 1970s and early 1980s, often running the CP/M operating system. The Zilog Z80 and the Motorola 6800 were also used in similar computers...
personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, see the List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For color palettes of 16-bit
16-bit
-16-bit architecture:The HP BPC, introduced in 1975, was the world's first 16-bit microprocessor. Prominent 16-bit processors include the PDP-11, Intel 8086, Intel 80286 and the WDC 65C816. The Intel 8088 was program-compatible with the Intel 8086, and was 16-bit in that its registers were 16...
personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, see the List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For current RGB display systems for 32-bit
32-bit
The range of integer values that can be stored in 32 bits is 0 through 4,294,967,295. Hence, a processor with 32-bit memory addresses can directly access 4 GB of byte-addressable memory....
and better PCs
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
(Super VGA
Super Video Graphics Array
Super Video Graphics Array or Ultra Video Graphics Array, almost always abbreviated to Super VGA, Ultra VGA or just SVGA or UVGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards....
, etc.), see the 16-bit RGB for HighColor (thousands) and 24-bit RGB for TrueColor (millions of colors) modes.
For various software arrangements and sorts of colors, see the List of software palettes article.
For each unique palette, an image color test chart and sample image (Truecolor original follows) rendered with that palette (without dither
Dither
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
ing) are given. The test chart shows the full 8-bits, 256 levels of the red, green and blue (RGB
RGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which red, green, and blue light is added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors...
) primary colors and cyan, magenta and yellow complementary colors, along with a full 8-bits, 256 levels grayscale. Gradients of RGB intermediate colors (orange, lime green, sea green, sky blue, violet and fucsia), and a full hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
's spectrum are also present. Color charts are not gamma
Gamma correction
Gamma correction, gamma nonlinearity, gamma encoding, or often simply gamma, is the name of a nonlinear operation used to code and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems...
corrected.
 |
 |
These elements let to study the color depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
and distribution of the full colors of any given palette, and the sample image indicates how the full color selection of such palettes would represent real life images. These images are not necessarily representative of how the image would be displayed on the original graphics hardware, as the hardware may have additional limitations regarding the maximum display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
, pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
and color placement.
For specific models of videogame consoles, simulations of how the sample image would render in different graphic modes are provided, if available. These simulations are always up to the maximum vertical resolution of the given graphic mode or up to 200 scan lines, if vertical resolution is greater. So any of them could be properly padded, transcoded and dumped into the original hardware and/or software emulators without any other changes.
The sample images only try to show how a certain system is able to handle to an image in terms of color without improvements nor additional clever tricks of design like anti-aliasing
Anti-aliasing
In digital signal processing, spatial anti-aliasing is the technique of minimizing the distortion artifacts known as aliasing when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution...
or dithering
Dither
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
. Doubtlessly a human artist is able to improve enormously the look of the simulated images to approximate them to the original one, but that is not the goal of this article.
Note: please do not change the compression scheme of every image by a lossy compression scheme (i.e. JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
) in order to improve their file size, nor change the thumbnail size of the images, nor gamma-correct them. They are didactical material AS IS, and they have been already optimized for this purpose.
Atari 2600
The Atari 2600Atari 2600
The Atari 2600 is a video game console released in October 1977 by Atari, Inc. It is credited with popularizing the use of microprocessor-based hardware and cartridges containing game code, instead of having non-microprocessor dedicated hardware with all games built in...
used different YPbPr
YPbPr
' is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. is the analog version of the YCBCR color space; the two are numerically equivalent, but YPBPR is designed for use in analog systems whereas YCBCR is intended for digital video. cables are also...
color palettes dependent on the television signal format used.
With the NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
format, a 128-color palette was available, built based on eight luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
values and fifteen combinations of Pb and Pr chroma
Chroma (software)
Chroma is a media player for Mac OS X.Features include playback of DivX/XviD, Quicktime, and other video codecs and support can be added for h264 video and Windows Media Format via third party plug-ins...
signals (plus Pb = Pr = 0 for a pure grayscale
Grayscale
In photography and computing, a grayscale or greyscale digital image is an image in which the value of each pixel is a single sample, that is, it carries only intensity information...
):
 |
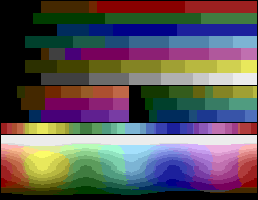 |
| hue / luminance | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||
| 15 |
The hardware supports 4 colors per scanline: a background, an arbitrary 40-pixel wide bitmapped playfield, and colors for the two players. Using just the first two, an NTSC console could draw the above.
With the PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
format, a 104-color palette was available. 128-color entries were still selectable, but due to changes in color encoding schemes, 32 color entries results in the same eight shades of gray:
 |
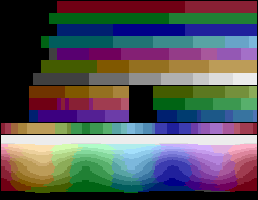 |
| hue / luminance | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,1,14,15 | ||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||
| 13 |
Using just the playfield and background controls, a PAL console could draw the above.
The SECAM
SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM , is an analog color television system first used in France....
palette were reduced to a simple 3-bit RGB, contained only 8 colors:
| 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
NES
The Picture Processing UnitPicture Processing Unit
The PPU , more specifically known as Ricoh RP2C02 / RP2C07 , is the microprocessor in the Nintendo Entertainment System responsible for generating video signals from graphic data stored in memory....
(PPU) was used in the Nintendo Entertainment System
Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System is an 8-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America during 1985, in Europe during 1986 and Australia in 1987...
and had a YPbPr
YPbPr
' is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. is the analog version of the YCBCR color space; the two are numerically equivalent, but YPBPR is designed for use in analog systems whereas YCBCR is intended for digital video. cables are also...
64-color palette (plus color emphasis bits, not counted), eight of which are reserved, giving a total of 56 useful colors. The palette is built based on four luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
values and twelve combinations of Pb and Pr chroma
Chrominance
Chrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
signals (plus two series of Pb = Pr = 0 for eight pure grays). Some of the shades of gray are so similar, that sometimes the palette has been reported to have only 53 to 55 colors.
 |
 |
| Hex Value Hexadecimal In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen... |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 00h | ||||||||||||||||
| 10h | ||||||||||||||||
| 20h | ||||||||||||||||
| 30h |
There are no current simulated screen images available for the NES.
SNES
The Picture Processing Unit (PPU) used in the Super Nintendo Entertainment SystemSuper Nintendo Entertainment System
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System is a 16-bit video game console that was released by Nintendo in North America, Europe, Australasia , and South America between 1990 and 1993. In Japan and Southeast Asia, the system is called the , or SFC for short...
has a 15-bit RGB (32,768 color) palette, with up to 256 simultaneous colors.
However, while the hardware palette can only contain 256 entries, in most display modes the graphics are arranged into between 2 and 4 layers, and these layers can be combined using additive or subtractive colour blending.
Because these blended colours are calculated by the hardware itself, and do not have to be represented by any of the existing palette entries, the actual number of visible colours onscreen at any one time can be much higher.
The exact number depends on the number of layers, and the combination of colours used by these layers, as well as what blending mode and graphical effects are in use. In theory it can show the entire 32,768 colours, but in practice this is rarely the case.
Original Game Boy
The original Game Boy uses a monochrome 4-shades palette. Due to the fact that the non-backlighted LCD display background is greenish, this results in a green-scale graphic display, as it is shown in the simulated image (at Game Boy display resolution), below.Game Boy Color
The Game Boy ColorGame Boy Color
The is Nintendo's successor to the 8-bit Game Boy handheld game console, and was released on October 21, 1998 in Japan, November 19, 1998 in North America, November 23, 1998 in Europe and November 27, 1998 in the United Kingdom. It features a color screen and is slightly thicker and taller than...
systems uses a 15-bit RGB (32,768 colours) palette.
When an older monochrome original Game Boy game catridge (Type 1) is plugged-in, if certain combinations of the controls are held during startup, the games are colourised with one of the factory 12 false colour palettes. In this mode, games can have from 4 to 10 colours, due 4 are for the background plane palette and there are two more hardware sprite planes palettes, with 3 colours plus transparent each.
The following shows these startup palettes (background plus both sprite planes) and the combination of controls used (the names are taken from the Game Boy user's manual; the colours are simulated):
| UP (Brown) |
UP+A (Red) |
UP+B (Dark brown) |
| DOWN (Pastel mix) |
DOWN+A (Orange) |
DOWN+B (Yellow) |
| LEFT (Blue) |
LEFT+A (Dark blue) |
LEFT+B (Gray) |
| RIGHT (Green) |
RIGHT+A (Dark green) |
RIGHT+B (Reverse) |
The specific Game Boy Color (Type 3) game catridges presents up to 56 colors without the use special programming techniques from the full 32,768. From these, 32 are for a background palette, plus 8 hardware sprite palettes, with 3 colors plus transparent each. Typically, the sprite palettes shares some colors (black, white or others), so the total colors displayed are less than 56.
Here is the sample image shown in the non-backlighted color LCD display of the Game Boy Color (the colors are simulated):
Though there is a 56 color limit, this in of itself is a palette storage limit and not an actual hardware limitation. As such, the programmer can swap out the palettes on a per-scanline or even on a mid-scanline basis ("mode 3 mid-scanline rendering"). Because of this ability to swap out the palettes each scanline, over ten thousand colors can actually appear on screen per frame when programmed on a per-scanline basis.
Game Boy Advance/SP/Micro
The Game Boy AdvanceGame Boy Advance
The is a 32-bit handheld video game console developed, manufactured, and marketed by Nintendo. It is the successor to the Game Boy Color. It was released in Japan on March 21, 2001; in North America on June 11, 2001; in Australia and Europe on June 22, 2001; and in the People's Republic of China...
/SP
Game Boy Advance SP
The , released in February 2003, is an upgraded version of Nintendo's Game Boy Advance. The "SP" in Game Boy Advance SP stands for Special. The SP was marketed at US$99.99 at launch. In September 2004, Nintendo lowered the price to US$79.99...
/Micro
Game Boy Micro
is a handheld game console developed and manufactured by Nintendo. It was first released in September 2005 in the market. The system is the last console of the Game Boy line...
systems also uses a 15-bit RGB palette, and along with the original and Color modes, they have also a specific Highcolor 32,768 colors mode.
The color LCD displays of the SP and Micro are backlit, giving brighter images.
Here are sample images shown in the backlit color LCD display of the Game Boy Advance/SP/Micro in both Game Boy Color compatible mode and Game Boy Advance 32K color mode:
Master System
The Sega Master SystemSega Master System
The is a third-generation video game console that was manufactured and released by Sega in 1985 in Japan , 1986 in North America and 1987 in Europe....
had a 6-bit RGB palette (64 colors), with 32 colors on-screen at once. It is possible to display all 64 colors at once using raster effects (line interrupts).
Game Gear
The Sega Game GearSega Game Gear
The was Sega's first handheld game console. It was the third commercially available color handheld console, after the Atari Lynx and the TurboExpress....
had a 12-bit RGB palette (4096 colors), with 32 colors on-screen at once.
Mega Drive/Genesis
The Sega Mega Drive/Sega Genesis used a 9-bit RGB palette (512 colors, 1536 including shadow and highlight mode) with up to 61 colors on-screen at once without raster effects (4 palette lines of 16 colors each, palette indices $x0 are definable but considered as transparent, and can only be used as the background color).PC-Engine/TurboGrafx 16
The PC-Engine/TurboGrafx 16TurboGrafx-16
TurboGrafx-16, fully titled as TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem and known in Japan as the , is a video game console developed by Hudson Soft and NEC, released in Japan on October 30, 1987, and in North America on August 29, 1989....
used a 9-bit RGB palette, like the Sega Mega Drive/Genesis, consisting of 512 colors with 482 colors on-screen at once (16 background palettes of 16 colors each, with at least 1 common color among all background palettes, and 16 sprite palettes of 15 colors each, plus transparent which was visible as the overscan area).
See also
- Palette (computing)Palette (computing)In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
- Indexed colorIndexed colorIn computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers...
- Color Lookup Table
- Color depthColor depthIn computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
- Computer display
- List of home computers by video hardware