
Local Government Commission for England (1992)
Encyclopedia
Local Government Boundary Commission for England (1972)
The Local Government Boundary Commission for England was the statutory body established under the Local Government Act 1972 to settle the boundaries, names and electoral arrangements of the non-metropolitan districts which came into existence in 1974, and for their periodic review...
. The Commission could be ordered by the Secretary of State
Secretary of State for the Environment
The Secretary of State for the Environment was a UK cabinet position, responsible for the Department of the Environment . This was created by Edward Heath as a combination of the Ministry of Housing and Local Government, the Ministry of Transport and the Ministry of Public Building and Works on 15...
to undertake "structural reviews" in specified areas and recommend the creation of unitary authorities
Unitary authority
A unitary authority is a type of local authority that has a single tier and is responsible for all local government functions within its area or performs additional functions which elsewhere in the relevant country are usually performed by national government or a higher level of sub-national...
in the two-tier shire counties
Shire county
A non-metropolitan county, or shire county, is a county-level entity in England that is not a metropolitan county. The counties typically have populations of 300,000 to 1.4 million. The term shire county is, however, an unofficial usage. Many of the non-metropolitan counties bear historic names...
of England. The Commission, chaired by John Banham
John Banham
Sir John Banham is a British business leader. He has been the chairman of Whitbread, a major brewer since 2000, and is also chairman of ECI Ventures and Johnson Matthey.- Biography :...
, conducted a review of all the non-metropolitan counties of England from 1993 to 1994, making various recommendations on their future.
After much political debate and several legal challenges, the Commission's proposals resulted in the abolition of Berkshire
Berkshire
Berkshire is a historic county in the South of England. It is also often referred to as the Royal County of Berkshire because of the presence of the royal residence of Windsor Castle in the county; this usage, which dates to the 19th century at least, was recognised by the Queen in 1957, and...
county council and the counties of Avon
Avon (county)
Avon was, from 1974 to 1996, a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in the west of England.The county was named after the River Avon, which runs through the area. It was formed from parts of the historic counties of Gloucestershire and Somerset, together with the City of Bristol...
, Cleveland
Cleveland, England
Cleveland is an area in the north east of England. Its name means literally "cliff-land", referring to its hilly southern areas, which rise to nearly...
, Hereford and Worcester
Hereford and Worcester
Hereford and Worcester was an English county created on 1 April 1974, by the Local Government Act 1972 from the area of the former administrative county of Herefordshire, most of Worcestershire and the county borough of Worcester.It bordered Shropshire, Staffordshire and the West Midlands to the...
and Humberside
Humberside
Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire...
(created in 1974). Combined with a second wave of reviews in 1995, under the chairmanship of David Cooksey
David Cooksey
Sir David James Scott Cooksey, GBE is a British businessman, venture capitalist and politician.David Cooksey gained a degree in metallurgy at St Edmund Hall, University of Oxford...
, the Commission's proposals led to the creation of unitary authorities covering many urban areas of England, including cities like Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
, Hull
Kingston upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull , usually referred to as Hull, is a city and unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Hull at its junction with the Humber estuary, 25 miles inland from the North Sea. Hull has a resident population of...
, Leicester
Leicester
Leicester is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England, and the county town of Leicestershire. The city lies on the River Soar and at the edge of the National Forest...
, Derby
Derby
Derby , is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands region of England. It lies upon the banks of the River Derwent and is located in the south of the ceremonial county of Derbyshire. In the 2001 census, the population of the city was 233,700, whilst that of the Derby Urban Area was 229,407...
, Nottingham
Nottingham
Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group...
, Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent , also called The Potteries is a city in Staffordshire, England, which forms a linear conurbation almost 12 miles long, with an area of . Together with the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme Stoke forms The Potteries Urban Area...
and Plymouth
Plymouth
Plymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound...
. Reforms in the rest of Great Britain
1990s UK local government reform
The structure of local government in the United Kingdom underwent large changes in the 1990s. The system of two-tier local government introduced in the 1970s by the Local Government Act 1972 and the Local Government Act 1973 was abolished in Scotland and Wales on April 1, 1996, and replaced with...
followed a different course.
Following the structural review, the Commission then reviewed electoral arrangements in English local authorities, re-warding
Redistricting
Redistricting is the process of drawing United States electoral district boundaries, often in response to population changes determined by the results of the decennial census. In 36 states, the state legislature has primary responsibility for creating a redistricting plan, in many cases subject to...
based on population changes. It was replaced by the Boundary Committee for England
Boundary Committee for England
The Boundary Committee for England was a statutory committee of the Electoral Commission, an independent body set up by the UK Parliament. The Committee’s aim was to conduct thorough, consultative and robust reviews of local government areas in England, and for its recommendations to be...
in 2002, which finished this review cycle in 2004.
Establishment
Local government was at the time organised under the Local Government Act 1972Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974....
, which had been passed during Edward Heath
Edward Heath
Sir Edward Richard George "Ted" Heath, KG, MBE, PC was a British Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and as Leader of the Conservative Party ....
's Conservative administration. Before this, local government in England had been a mixed system, with large urban areas being covered by unitary authorities called county borough
County borough
County borough is a term introduced in 1889 in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland , to refer to a borough or a city independent of county council control. They were abolished by the Local Government Act 1972 in England and Wales, but continue in use for lieutenancy and shrievalty in...
s, and the rest of the country having administrative county
Administrative counties of England
Administrative counties were a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government from 1889 to 1974. They were created by the Local Government Act 1888 as the areas for which county councils were elected. Some large counties were divided into several administrative...
councils and many smaller district councils, with different competences. The 1972 Act abolished county boroughs, making them districts in two-tier counties. This, and the consequent loss of education, social services and libraries to county control, was strongly regretted by the larger towns outside the new metropolitan counties
Metropolitan county
The metropolitan counties are a type of county-level administrative division of England. There are six metropolitan counties, which each cover large urban areas, typically with populations of 1.2 to 2.8 million...
, such as Bristol, Plymouth, Stoke, Leicester and Nottingham. The abolition of metropolitan county councils in 1986 left the metropolitan boroughs operating as unitary authorities.
Michael Heseltine
Michael Heseltine
Michael Ray Dibdin Heseltine, Baron Heseltine, CH, PC is a British businessman, Conservative politician and patron of the Tory Reform Group. He was a Member of Parliament from 1966 to 2001 and was a prominent figure in the governments of Margaret Thatcher and John Major...
, who had been a junior local government minister during the passage of the Local Government Act 1972, was appointed as Secretary of State for the Environment
Secretary of State for the Environment
The Secretary of State for the Environment was a UK cabinet position, responsible for the Department of the Environment . This was created by Edward Heath as a combination of the Ministry of Housing and Local Government, the Ministry of Transport and the Ministry of Public Building and Works on 15...
(and thus responsible for local government) in John Major
John Major
Sir John Major, is a British Conservative politician, who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990–1997...
's first cabinet of 1990. Heseltine was an enthusiast for unitary local government, and was also an early proponent of the idea of directly elected mayors
Elected mayors in the United Kingdom
Directly elected mayors are council leaders elected by the general electorate of a council area for local government, instead of being appointed by members of a local authority, which is common in the United Kingdom. The Elected Mayor is elected from a number of candidates who put themselves up for...
, to be taken up by Tony Blair
Tony Blair
Anthony Charles Lynton Blair is a former British Labour Party politician who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2 May 1997 to 27 June 2007. He was the Member of Parliament for Sedgefield from 1983 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007...
's government in the 2000s.
A wide range of political opinion had always favoured in principle the establishment of unitary authorities. The Labour Party
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a centre-left democratic socialist party in the United Kingdom. It surpassed the Liberal Party in general elections during the early 1920s, forming minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in 1924 and 1929-1931. The party was in a wartime coalition from 1940 to 1945, after...
had planned to implement the Redcliffe-Maud Report
Redcliffe-Maud Report
The Redcliffe–Maud Report is the name generally given to the report published by the Royal Commission on Local Government in England 1966–1969 under the chairmanship of Lord Redcliffe-Maud.-Terms of reference and membership:...
in the 1970s, and the party's 1982 statement of policy "Labour's Programme 1982" said "There is an irrational split of functions between the two tiers compounded by a confusing overlap of responsibilities ... We favour the creation in England and Wales of unitary authorities". Heseltine announced in 1991 that the government would be looking at the creation of unitary authorities in the non-metropolitan counties as part of a more general review of local government, including the abolition of the Community Charge
Community Charge
The Community Charge, popularly known as the "poll tax", was a system of taxation introduced in replacement of the rates to part fund local government in Scotland from 1989, and England and Wales from 1990. It provided for a single flat-rate per-capita tax on every adult, at a rate set by the...
, or poll tax, and oversaw the passage of the 1992 Act through Parliament.
Heseltine was replaced by Michael Howard
Michael Howard
Michael Howard, Baron Howard of Lympne, CH, QC, PC is a British politician, who served as the Leader of the Conservative Party and Leader of the Opposition from November 2003 to December 2005...
in April 1992 after the 1992 general election
United Kingdom general election, 1992
The United Kingdom general election of 1992 was held on 9 April 1992, and was the fourth consecutive victory for the Conservative Party. This election result was one of the biggest surprises in 20th Century politics, as polling leading up to the day of the election showed Labour under leader Neil...
. Whilst Heseltine had expressed a wish for most of the country to become unitary authorities, Howard issued revised guidance on the basis that the "two-tier structure may be appropriate in some areas", and that the costs of reorganisation might be too much for the recession-hit UK economy
Late 1980s recession
The recession of the early 1990s describes the period of economic downturn affecting much of the world in the late 1980s and early 1990s.-Causes:...
to take.
The Commission, chaired by John Banham
John Banham
Sir John Banham is a British business leader. He has been the chairman of Whitbread, a major brewer since 2000, and is also chairman of ECI Ventures and Johnson Matthey.- Biography :...
(named to the post in November 1991, before the legislation had been passed to create the Commission), started the reviews in July 1992. The process was originally supposed to take some years, with the shire counties being considered in five waves, or "tranches", and it was hoped that the reforms would come into effect from 1994 to 1998. The process took longer than expected, with the Commission unable to recruit enough staff until November 1992. The first tranche, covering Avon, Cleveland, Derbyshire
Derbyshire
Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire. The northern part of Derbyshire overlaps with the Pennines, a famous chain of hills and mountains. The county contains within its boundary of approx...
, County Durham
County Durham
County Durham is a ceremonial county and unitary district in north east England. The county town is Durham. The largest settlement in the ceremonial county is the town of Darlington...
, Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean....
, the Isle of Wight
Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
, Humberside
Humberside
Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire...
, Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire is a county in the east of England. It borders Norfolk to the south east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders...
, North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is a non-metropolitan or shire county located in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, and a ceremonial county primarily in that region but partly in North East England. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972 it covers an area of , making it the largest...
and Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
was nearly done by the end of 1993. Banham had said that the Commission was expecting "early wins" in Cleveland, Humberside and Avon: three counties created in 1974, based on rivers, that had not achieved public acceptance.
Although Cleveland was and continues to be lumped together with Avon and Humberside, in reality it was a very different case, having achieved widespread acceptance amongst its residents and lacking any significant movement for abolition as in for example Humberside. Fears that the abolition of Cleveland would lead to a general lack of identity and a greatly reduced public voice appear to have been well founded and continues to rankle with residents.
The first recommendation, published in 1993, was the quite uncontroversial one to make Isle of Wight
Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
a unitary authority. The island had been split between South Wight
South Wight
South Wight was a non-metropolitan district with the status of a borough on the Isle of Wight in England from 1974 to 1995.The district was formed by the Local Government Act 1972, and was a merger of Sandown-Shanklin and Ventnor urban districts and Isle of Wight Rural District...
and Medina boroughs, with an Isle of Wight County Council, since 1974.
Acceleration

A new Secretary of State, John Selwyn Gummer
John Gummer
John Selwyn Gummer, Baron Deben, PC is a British Conservative Party politician, formerly Member of Parliament for Suffolk Coastal, now a member of the House of Lords. He is Chairman of the environmental consultancy company Sancroft International and Chairman of Veolia Water...
, had taken over in May, and he did not like these proposals, or the long time it took to produce them. Gummer sped-up the work plan and directed that all remaining reviews should start in December and be complete by the end of 1994. Gummer also issued new guidance, making it clear that wholly unitary solutions should be preferred, particularly ones smaller than existing counties but larger than existing districts. He further announced that Derbyshire and Durham would be referred back to the Commission for consideration under the new guidance. Gummer accepted the Commission's proposal to abolish Cleveland, but asked the Commission to consider Durham and Derbyshire again under the new guidance. The Labour Party, while remaining broadly in favour of unitary authorities, attacked the Commission for inconsistency. The leader of the Labour-controlled Derbyshire County Council questioned the inclusion of Derbyshire in the first tranche, which otherwise consisted mainly of counties newly created in 1974 and their neighbours.
The revised guidance included wording as follows:
In some areas the commission may wish to recommend a continuation of the existing two-tier structure. But the government expects that to be the exception, and that the result will be a substantial increase in the number of unitary authorities in both urban and rural areas.
Lancashire and Derbyshire County Councils, fearing their abolition under the new guidance, took a case to the High Court
High Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice is, together with the Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, one of the Senior Courts of England and Wales...
, seeking a judicial review
Judicial review
Judicial review is the doctrine under which legislative and executive actions are subject to review by the judiciary. Specific courts with judicial review power must annul the acts of the state when it finds them incompatible with a higher authority...
that it was illegal. On 28 January, the High Court ruled in their favour, deleting the sentence in dispute, implying that the Commission should consider retaining the status quo, either in part or wholly, as an option as well.
The commission recommended that Avon
Avon (county)
Avon was, from 1974 to 1996, a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in the west of England.The county was named after the River Avon, which runs through the area. It was formed from parts of the historic counties of Gloucestershire and Somerset, together with the City of Bristol...
and Humberside
Humberside
Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire...
should be abolished and broken up into four unitary authorities each. It also recommended that the rump Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
be broken up into three unitary authorities (West, South and Mid). It suggested that North Yorkshire be split into three unitary authorities – one for York
York
York is a walled city, situated at the confluence of the Rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. The city has a rich heritage and has provided the backdrop to major political events throughout much of its two millennia of existence...
, and two others to be called "West Riding of Yorkshire" and "North Riding of Yorkshire" (the proposed West Riding would have taken in only a small part of the historic West Riding of Yorkshire
West Riding of Yorkshire
The West Riding of Yorkshire is one of the three historic subdivisions of Yorkshire, England. From 1889 to 1974 the administrative county, County of York, West Riding , was based closely on the historic boundaries...
, while the proposed North Riding would have included most of the historic North Riding of Yorkshire
North Riding of Yorkshire
The North Riding of Yorkshire was one of the three historic subdivisions of the English county of Yorkshire, alongside the East and West Ridings. From the Restoration it was used as a Lieutenancy area. The three ridings were treated as three counties for many purposes, such as having separate...
). It recommended no change in Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire is a county in the east of England. It borders Norfolk to the south east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean....
. The County Councils of Avon, Cleveland and Somerset sought judicial review to stop these proposals going forward, but the High Court found them within the law.
The government accepted most of these recommendations, but also kept the status quo in Somerset ("after taking account of the number and strength of the representations which I received opposing the recommendations"), and in North Yorkshire retained a rump two-tier North Yorkshire without York ("in the light of the strong representations which I have received opposing the Commission's recommendations for North and West Riding") – both reportedly the subject of strong lobbying by local Conservative MPs. The government did not accept the recommendations of the Commission on Gloucestershire, and announced its intention to refer the county back. These changes were implemented in 1996.
Remaining tranches
MORI
Ipsos MORI is the second largest market research organisation in the United Kingdom, formed by a merger of Ipsos UK and MORI, two of the Britain's leading survey companies in October 2005...
polling in each of the local areas affected to determine which options were more popular locally. For example, in Cambridgeshire, the Commission outlined three options for a split of the county into unitary authorities, the preferred option being a three-way split between the "City & County of Cambridge" (consisting of Cambridge
Cambridge
The city of Cambridge is a university town and the administrative centre of the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It lies in East Anglia about north of London. Cambridge is at the heart of the high-technology centre known as Silicon Fen – a play on Silicon Valley and the fens surrounding the...
, South Cambridgeshire
South Cambridgeshire
South Cambridgeshire is a mostly rural local government district of Cambridgeshire, England. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Chesterton Rural District and South Cambridgeshire Rural District. It surrounds the city of Cambridge, which is administered separately from the district by...
, East Cambridgeshire
East Cambridgeshire
East Cambridgeshire is a local government district in Cambridgeshire, England. Its council is based in Ely....
), Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, covering the area around Huntingdon. Traditionally it is a county in its own right...
and Peterborough
Peterborough
Peterborough is a cathedral city and unitary authority area in the East of England, with an estimated population of in June 2007. For ceremonial purposes it is in the county of Cambridgeshire. Situated north of London, the city stands on the River Nene which flows into the North Sea...
& The Fens
Fenland
Fenland is a local government district in Cambridgeshire, England. Its council is based in March, and covers the neighbouring market towns of Chatteris, Whittlesey, and Wisbech, often called the "capital of the fens"...
.
In final reports delivered in October 1994, the Commission recommended Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan home county in South East England. The county town is Aylesbury, the largest town in the ceremonial county is Milton Keynes and largest town in the non-metropolitan county is High Wycombe....
and Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.It borders Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the west and Hertfordshire to the south-east....
county councils be abolished and replaced with four and three unitary authorities respectively. In other counties, it backed down from more radical draft proposals, and it recommended no change in Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire is a county in England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the northeast, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west...
, Cheshire
Cheshire
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow...
, Cumbria
Cumbria
Cumbria , is a non-metropolitan county in North West England. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local authority, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's largest settlement and county town is Carlisle. It consists of six districts, and in...
, Lancashire
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
, Kent
Kent
Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of...
and Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a county in the South East region of England, bordering on Warwickshire and Northamptonshire , Buckinghamshire , Berkshire , Wiltshire and Gloucestershire ....
. In Hampshire
Hampshire
Hampshire is a county on the southern coast of England in the United Kingdom. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, a historic cathedral city that was once the capital of England. Hampshire is notable for housing the original birthplaces of the Royal Navy, British Army, and Royal Air Force...
it recommended that Southampton
Southampton
Southampton is the largest city in the county of Hampshire on the south coast of England, and is situated south-west of London and north-west of Portsmouth. Southampton is a major port and the closest city to the New Forest...
, Portsmouth
Portsmouth
Portsmouth is the second largest city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire on the south coast of England. Portsmouth is notable for being the United Kingdom's only island city; it is located mainly on Portsea Island...
and New Forest
New Forest (district)
New Forest is a local government district in Hampshire, England. It is named after the New Forest.It was created on 1 April 1974, and was a merger of the borough of Lymington, New Forest Rural District and part of Ringwood and Fordingbridge Rural District....
become unitary authorities.
A further batch of reports was delivered in December, recommending that Norfolk
Norfolk
Norfolk is a low-lying county in the East of England. It has borders with Lincolnshire to the west, Cambridgeshire to the west and southwest and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea coast and to the north-west the county is bordered by The Wash. The county...
, Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire is a landlocked county in the English East Midlands, with a population of 629,676 as at the 2001 census. It has boundaries with the ceremonial counties of Warwickshire to the west, Leicestershire and Rutland to the north, Cambridgeshire to the east, Bedfordshire to the south-east,...
, Northumberland
Northumberland
Northumberland is the northernmost ceremonial county and a unitary district in North East England. For Eurostat purposes Northumberland is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three boroughs or unitary districts that comprise the "Northumberland and Tyne and Wear" NUTS 2 region...
, Suffolk
Suffolk
Suffolk is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in East Anglia, England. It has borders with Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south. The North Sea lies to the east...
, Surrey
Surrey
Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
, Warwickshire
Warwickshire
Warwickshire is a landlocked non-metropolitan county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, although the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare...
, West Sussex
West Sussex
West Sussex is a county in the south of England, bordering onto East Sussex , Hampshire and Surrey. The county of Sussex has been divided into East and West since the 12th century, and obtained separate county councils in 1888, but it remained a single ceremonial county until 1974 and the coming...
should remained unchanged. In Hereford and Worcester
Hereford and Worcester
Hereford and Worcester was an English county created on 1 April 1974, by the Local Government Act 1972 from the area of the former administrative county of Herefordshire, most of Worcestershire and the county borough of Worcester.It bordered Shropshire, Staffordshire and the West Midlands to the...
, Worcestershire
Worcestershire
Worcestershire is a non-metropolitan county, established in antiquity, located in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire" NUTS 2 region...
would become a two-tier county whilst Herefordshire
Herefordshire
Herefordshire is a historic and ceremonial county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire" NUTS 2 region. It also forms a unitary district known as the...
become a unitary authority. In Leicestershire
Leicestershire
Leicestershire is a landlocked county in the English Midlands. It takes its name from the heavily populated City of Leicester, traditionally its administrative centre, although the City of Leicester unitary authority is today administered separately from the rest of Leicestershire...
, Leicester
Leicester
Leicester is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England, and the county town of Leicestershire. The city lies on the River Soar and at the edge of the National Forest...
and Rutland
Rutland
Rutland is a landlocked county in central England, bounded on the west and north by Leicestershire, northeast by Lincolnshire and southeast by Peterborough and Northamptonshire....
would become unitary authorities, with the rest of the county remaining two-tier – a pattern followed also in County Durham
County Durham
County Durham is a ceremonial county and unitary district in north east England. The county town is Durham. The largest settlement in the ceremonial county is the town of Darlington...
(Darlington
Darlington (borough)
Darlington is a local government district and borough in North East England. In 2008 it had a resident population of 100,500 It borders County Durham to the north and west, North Yorkshire to the south along the line of the River Tees, and Stockton-on-Tees to the east.-Council:Traditionally part of...
), Devon
Devon
Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
(Plymouth
Plymouth
Plymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound...
and Torbay
Torbay
Torbay is an east-facing bay and natural harbour, at the western most end of Lyme Bay in the south-west of England, situated roughly midway between the cities of Exeter and Plymouth. Part of the ceremonial county of Devon, Torbay was made a unitary authority on 1 April 1998...
), East Sussex
East Sussex
East Sussex is a county in South East England. It is bordered by the counties of Kent, Surrey and West Sussex, and to the south by the English Channel.-History:...
(Brighton & Hove
Brighton & Hove
Brighton and Hove is a unitary authority area and city on the south coast of England. It is England's most populous seaside resort.In 1997 Brighton and Hove were joined to form the unitary authority of Brighton and Hove, which was granted city status by Queen Elizabeth II as part of the millennium...
), Essex
Essex
Essex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England, and one of the home counties. It is located to the northeast of Greater London. It borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent to the South and London to the south west...
(Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea
Southend-on-Sea is a unitary authority area, town, and seaside resort in Essex, England. The district has Borough status, and comprises the towns of Chalkwell, Eastwood, Leigh-on-Sea, North Shoebury, Prittlewell, Shoeburyness, Southchurch, Thorpe Bay, and Westcliff-on-Sea. The district is situated...
), Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire is a county in the East Midlands of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west...
(Nottingham
Nottingham
Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group...
), Staffordshire
Staffordshire
Staffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes, the county is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. Part of the National Forest lies within its borders...
(Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent , also called The Potteries is a city in Staffordshire, England, which forms a linear conurbation almost 12 miles long, with an area of . Together with the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme Stoke forms The Potteries Urban Area...
) and Wiltshire
Wiltshire
Wiltshire is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset, Somerset, Hampshire, Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire and Berkshire. It contains the unitary authority of Swindon and covers...
(Thamesdown
Swindon (borough)
The Borough of Swindon is a local government authority in South West England. It is centred on the town of Swindon and forms part of the ceremonial county of Wiltshire...
). The Commission recommended the abolition of two county councils – Berkshire (which was to have five unitary authorities) and Dorset (which was to have four).
The final batch of recommendations was published in January 1995, slightly missing the deadline, and recommended no change for Cornwall, Gloucestershire, Hertfordshire and Shropshire. In Derbyshire it recommended the creation of a unitary city of Derby
Derby
Derby , is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands region of England. It lies upon the banks of the River Derwent and is located in the south of the ceremonial county of Derbyshire. In the 2001 census, the population of the city was 233,700, whilst that of the Derby Urban Area was 229,407...
with the remainder of the county remaining two-tier.
In a January 1995 interview, Banham explained the decision-making process of the Commission was based strongly on local opinion, noting that although a fully unitary solution for much of the country would commend all-party support in the House of Commons, he thought it would cause "mayhem" when implemented. He also advocated the creation of more parish councils
Civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a territorial designation and, where they are found, the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties...
in unparished area
Unparished area
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish. Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unparished. Many towns and some cities in otherwise rural districts are also unparished areas and therefore no longer have a town council or city...
s. In a letter to The Times
The Times
The Times is a British daily national newspaper, first published in London in 1785 under the title The Daily Universal Register . The Times and its sister paper The Sunday Times are published by Times Newspapers Limited, a subsidiary since 1981 of News International...
in March 1994, he noted he had the attitude that "if it ain't broke, don't fix it".
Government reaction
On 2 March 1995, Gummer announced to the Commons that the government would not fully accept the Commission's proposals and certain districts would be referred to the Commission for a further review. He also announced John Banham's resignation in protest at this.For Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan home county in South East England. The county town is Aylesbury, the largest town in the ceremonial county is Milton Keynes and largest town in the non-metropolitan county is High Wycombe....
, Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.It borders Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the west and Hertfordshire to the south-east....
and Dorset
Dorset
Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
the government did not accept the Commission's recommendations for an entirely unitary structure, and decided to only make Luton
Luton
Luton is a large town and unitary authority of Bedfordshire, England, 30 miles north of London. Luton and its near neighbours, Dunstable and Houghton Regis, form the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area with a population of about 250,000....
, Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes (borough)
The Borough of Milton Keynes is a unitary authority and borough in south central England, at the northern tip of the South East England Region. For ceremonial purposes, it is in the county of Buckinghamshire...
, Bournemouth
Bournemouth (borough)
Bournemouth Borough Council is the local authority of Bournemouth in Dorset, England. The council is now a unitary authority, although between 1974 and 1997 it was an administrative district council with Dorset...
and Poole
Poole
Poole is a large coastal town and seaport in the county of Dorset, on the south coast of England. The town is east of Dorchester, and Bournemouth adjoins Poole to the east. The Borough of Poole was made a unitary authority in 1997, gaining administrative independence from Dorset County Council...
unitary, with the rest of those counties remaining two-tier.
The proposal to abolish Berkshire County Council was accepted by the government. The Commission had recommended five unitary authorities in Berkshire, based on the districts of Newbury
West Berkshire
West Berkshire is a local government district in the ceremonial county of Berkshire, England, governed by a unitary authority . Its administrative capital is Newbury, located almost equidistantly between Bristol and London.-Geography:...
, Reading
Reading, Berkshire
Reading is a large town and unitary authority area in England. It is located in the Thames Valley at the confluence of the River Thames and River Kennet, and on both the Great Western Main Line railway and the M4 motorway, some west of London....
, Wokingham
Wokingham (district)
Wokingham is a local government district in Berkshire, United Kingdom. It is named after its main town, Wokingham. Other places in the district include Arborfield, Barkham, Charvil, Earley, Finchampstead, Hurst, Sonning, Remenham, Ruscombe, Shinfield, Twyford, Wargrave, Three Mile Cross, Winnersh,...
, Slough
Slough
Slough is a borough and unitary authority within the ceremonial county of Royal Berkshire, England. The town straddles the A4 Bath Road and the Great Western Main Line, west of central London...
, with Bracknell Forest
Bracknell Forest
Bracknell Forest is a unitary authority and borough in Berkshire in southern England. It covers the towns of Bracknell, North Ascot, Sandhurst, Crowthorne and surrounding villages and hamlets.-History:...
and Windsor and Maidenhead districts merging to form a "Royal East Berkshire". Gummer decided to make each district a unitary authority. The proposal for an entirely unitary structure had been strongly supported by the County Council earlier, though with time and a change in political composition of the Council, it changed its mind and took this decision to court, seeking to have the entire Order declared invalid. The High Court ruled in their favour, but the Court of Appeal quashed this decision. This led to the implementation of unitary authorities of Berkshire to be delayed from 1997 to 1998.
In Hampshire, the Commission had proposed unitary authorities for the cities of Portsmouth
Portsmouth
Portsmouth is the second largest city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire on the south coast of England. Portsmouth is notable for being the United Kingdom's only island city; it is located mainly on Portsea Island...
and Southampton
Southampton
Southampton is the largest city in the county of Hampshire on the south coast of England, and is situated south-west of London and north-west of Portsmouth. Southampton is a major port and the closest city to the New Forest...
, which were accepted by the government, and the larger and more rural New Forest
New Forest (district)
New Forest is a local government district in Hampshire, England. It is named after the New Forest.It was created on 1 April 1974, and was a merger of the borough of Lymington, New Forest Rural District and part of Ringwood and Fordingbridge Rural District....
district, which the government did not accept.
In many counties that were to remain unchanged, the government had reservations about specific districts. Gummer identified as candidates on his 2 March statement the districts of Basildon
Basildon (district)
Basildon is a local government district in south Essex in the East of England, centred around the town of Basildon. The district was formed under the Local Government Act 1972 on 1 April 1974 from the former area of Basildon Urban District and the part of Thurrock Urban District that was within the...
, Blackburn
Blackburn with Darwen
Blackburn with Darwen is a unitary authority area in Lancashire, North West England. It consists of Blackburn, the small town of Darwen to the south of it, and the surrounding countryside.-Formation:...
, Blackpool
Blackpool
Blackpool is a borough, seaside town, and unitary authority area of Lancashire, in North West England. It is situated along England's west coast by the Irish Sea, between the Ribble and Wyre estuaries, northwest of Preston, north of Liverpool, and northwest of Manchester...
, Broxtowe
Broxtowe
Broxtowe is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England, west of the City of Nottingham. It is part of the Greater Nottingham metropolitan area...
, Dartford
Dartford (borough)
Dartford is the name given to a local government district and borough in north west Kent, England, which takes its name from its administrative capital. It borders Thurrock, to the north across the River Thames; to the west lies the London Borough of Bexley; to the south Sevenoaks district; and the...
, Exeter
Exeter
Exeter is a historic city in Devon, England. It lies within the ceremonial county of Devon, of which it is the county town as well as the home of Devon County Council. Currently the administrative area has the status of a non-metropolitan district, and is therefore under the administration of the...
, Gedling
Gedling
Gedling is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England. Its council is based in Arnold. It is part of the Greater Nottingham metropolitan area lying to the North and East of the City of Nottingham....
, Gillingham, Gloucester
Gloucester
Gloucester is a city, district and county town of Gloucestershire in the South West region of England. Gloucester lies close to the Welsh border, and on the River Severn, approximately north-east of Bristol, and south-southwest of Birmingham....
, Gravesham
Gravesham
Gravesham is a local government district and borough in North West Kent, England. It has borders with the River Thames to the north; the City of Rochester and Medway to the east; the borough of Tonbridge and Malling ; and the boroughs of Sevenoaks and Dartford to the west.Its council is based at...
, Halton
Halton (borough)
Halton is a local government district in North West England, with borough status and administered by a unitary authority. It was created in 1974 as a district of Cheshire, and became a unitary authority area on 1 April 1998. It consists of the towns of Widnes and Runcorn and the civil parishes of...
, Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire
Huntingdonshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, covering the area around Huntingdon. Traditionally it is a county in its own right...
, Northampton
Northampton
Northampton is a large market town and local government district in the East Midlands region of England. Situated about north-west of London and around south-east of Birmingham, Northampton lies on the River Nene and is the county town of Northamptonshire. The demonym of Northampton is...
, Peterborough
Peterborough
Peterborough is a cathedral city and unitary authority area in the East of England, with an estimated population of in June 2007. For ceremonial purposes it is in the county of Cambridgeshire. Situated north of London, the city stands on the River Nene which flows into the North Sea...
, Rochester upon Medway, Rushcliffe
Rushcliffe
Rushcliffe is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England. Its council is based in West Bridgford. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by merging the West Bridgford Urban District, the Bingham Rural District and part of Basford Rural District.-Political representation:The...
, Thurrock
Thurrock
Thurrock is a unitary authority with borough status in the English ceremonial county of Essex. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The local authority is Thurrock Council....
, Warrington
Warrington
Warrington is a town, borough and unitary authority area of Cheshire, England. It stands on the banks of the River Mersey, which is tidal to the west of the weir at Howley. It lies 16 miles east of Liverpool, 19 miles west of Manchester and 8 miles south of St Helens...
. Shadow Environment Secretary Frank Dobson
Frank Dobson
Frank Gordon Dobson, is a British Labour Party politician who has been the Member of Parliament for Holborn and St. Pancras since 1979...
suggested that Cambridge
Cambridge
The city of Cambridge is a university town and the administrative centre of the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It lies in East Anglia about north of London. Cambridge is at the heart of the high-technology centre known as Silicon Fen – a play on Silicon Valley and the fens surrounding the...
, Ipswich
Ipswich
Ipswich is a large town and a non-metropolitan district. It is the county town of Suffolk, England. Ipswich is located on the estuary of the River Orwell...
, Norwich
Norwich
Norwich is a city in England. It is the regional administrative centre and county town of Norfolk. During the 11th century, Norwich was the largest city in England after London, and one of the most important places in the kingdom...
, Oxford
Oxford
The city of Oxford is the county town of Oxfordshire, England. The city, made prominent by its medieval university, has a population of just under 165,000, with 153,900 living within the district boundary. It lies about 50 miles north-west of London. The rivers Cherwell and Thames run through...
and The Wrekin
Telford and Wrekin
Telford and Wrekin is a unitary district with borough status in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. The district was created in 1974 as The...
be added to this list: Norwich and the Wrekin were. Spelthorne
Spelthorne
Spelthorne is a local government district and borough in Surrey, England. It includes the towns of Ashford, Laleham, Shepperton, Staines, Stanwell and Sunbury...
was added at the request of the local MP, David Wilshire
David Wilshire
David Wilshire is a Conservative Party politician in the United Kingdom. He was the Member of Parliament for Spelthorne in Surrey from 1987 to 2010....
.
Cooksey commission
The new commission was under the chairmanship of Sir David CookseyDavid Cooksey
Sir David James Scott Cooksey, GBE is a British businessman, venture capitalist and politician.David Cooksey gained a degree in metallurgy at St Edmund Hall, University of Oxford...
, previously the chairman of the Audit Commission
Audit Commission
The Audit Commission is a public corporation in the United Kingdom.The Commission’s primary objective is to improve economy, efficiency and effectiveness in local government, housing and the health service, directly through the audit and inspection process and also through value for money...
. The commission published draft proposals on the districts referred back to it in September 1995. It recommended unitary status for Blackpool, Blackburn, Halton, Northampton, Peterborough, Thurrock, Warrington and the Wrekin, and also that Rochester upon Medway and Gillingham should form a Medway Towns
Medway
Medway is a conurbation and unitary authority in South East England. The Unitary Authority was formed in 1998 when the City of Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with Gillingham Borough Council and part of Kent County Council to form Medway Council, a unitary authority independent of Kent County...
unitary authority.
The final recommendations deleted Northampton from this list, deciding that "as with Exeter and Gloucester, the separation of Northampton from its county would have a significant and detrimental effect". The government announced its acceptance of these recommendations in March 1996, and these changes were implemented in 1998.
The Commission decided against unitary status for the three districts around Nottingham: Gedling, Broxtowe and Rushcliffe. Of the three, only Rushcliffe Borough Council supported a change. It considered but came down against unifying Dartford
Dartford (borough)
Dartford is the name given to a local government district and borough in north west Kent, England, which takes its name from its administrative capital. It borders Thurrock, to the north across the River Thames; to the west lies the London Borough of Bexley; to the south Sevenoaks district; and the...
and Gravesham
Gravesham
Gravesham is a local government district and borough in North West Kent, England. It has borders with the River Thames to the north; the City of Rochester and Medway to the east; the borough of Tonbridge and Malling ; and the boroughs of Sevenoaks and Dartford to the west.Its council is based at...
as a unitary authority (supported by Dartford but rejected by Gravesham). Exeter was considered too small. The Commission noted that Gloucester
Gloucester
Gloucester is a city, district and county town of Gloucestershire in the South West region of England. Gloucester lies close to the Welsh border, and on the River Severn, approximately north-east of Bristol, and south-southwest of Birmingham....
's proximity to Cheltenham
Cheltenham
Cheltenham , also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a large spa town and borough in Gloucestershire, on the edge of the Cotswolds in the South-West region of England. It is the home of the flagship race of British steeplechase horse racing, the Gold Cup, the main event of the Cheltenham Festival held...
would cause issues and that the two towns should be governed together. The Commission rejected the case of Huntingdonshire (a historic county
Historic counties of England
The historic counties of England are subdivisions of England established for administration by the Normans and in most cases based on earlier Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and shires...
, and the constituency of the Prime Minister, John Major
John Major
Sir John Major, is a British Conservative politician, who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990–1997...
), noting that there was "no exceptional county allegiance" and doubting the capacity of Huntingdonshire and the viability of the remaining Cambridgeshire. The Commission noted that tight boundaries for Norwich would cause a problem for unitary government, but that an extension would likely be strongly opposed. In Spelthorne the Commission was concerned about the lack of "internal coherence of the area" and its size.
While finding against a Basildon unitary authority, the Commission recommended the removal of Billericay
Billericay
Billericay is a town and civil parish in the Basildon borough of Essex, England. It lies within the London Basin, has a population of 40,000, and constitutes a commuter town east of central London. The town has three secondary schools and a variety of open spaces...
and Wickford
Wickford
Wickford is a town in the south of the English county of Essex, with a population of more than 32,500. Located approximately 30 miles east of London, it falls within the District of Basildon along with Basildon, Billericay, Laindon and Pitsea....
from Basildon district and their addition to Brentwood
Brentwood (borough)
Brentwood is a local government district and borough in Essex in the East of England.-History & Geography:The borough is named after the town of Brentwood which is the main development in the area. There are still large areas of woodland including Shenfield Common, Hartswood , Weald Country Park,...
and Rochford
Rochford (district)
Rochford is a local government district in Essex, England. It is named for one of its main settlements, Rochford, though the major centre of population in the district is the town of Rayleigh...
districts, leaving Basildon district focused on the Basildon New Town. The boundary alterations proposed between Basildon, Rochford and Brentwood were never implemented.
The Commission also recommended boundary revisions between Peterborough and Huntingdonshire to incorporate the entire southern township of Peterborough in the city, and also boundary changes between Spelthorne
Spelthorne
Spelthorne is a local government district and borough in Surrey, England. It includes the towns of Ashford, Laleham, Shepperton, Staines, Stanwell and Sunbury...
and Runnymede
Runnymede
Runnymede is a water-meadow alongside the River Thames in the English county of Berkshire, and just over west of central London. It is notable for its association with the sealing of Magna Carta, and as a consequence is the site of a collection of memorials...
as a result of changes in the path of the River Thames
River Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
. The Peterborough changes were implemented as part of the Order for Peterborough, coming into force in 1998, and the alterations to the boundary between Runnymede and Spelthorne were implemented on 1 April 1997.
The Commission was directed in 1996 to review local government in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in Merseyside
Merseyside
Merseyside is a metropolitan county in North West England, with a population of 1,365,900. It encompasses the metropolitan area centred on both banks of the lower reaches of the Mersey Estuary, and comprises five metropolitan boroughs: Knowsley, St Helens, Sefton, Wirral, and the city of Liverpool...
, as a result of local demand for Southport
Southport
Southport is a seaside town in the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton in Merseyside, England. During the 2001 census Southport was recorded as having a population of 90,336, making it the eleventh most populous settlement in North West England...
to be removed from that borough. The final report recommended no change in the existing structure of local government in Sefton.
In 1996, the Commission began a periodic electoral review of every local authority in England, reviewing the existing wards and electoral divisions and altering them to take into account changes in the electorate. This work was taken over by the Boundary Committee for England
Boundary Committee for England
The Boundary Committee for England was a statutory committee of the Electoral Commission, an independent body set up by the UK Parliament. The Committee’s aim was to conduct thorough, consultative and robust reviews of local government areas in England, and for its recommendations to be...
in 2002, and completed in 2004.
Summary of proposals
| County | Commission recommendations | Government reaction | Date in force |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avon Avon (county) Avon was, from 1974 to 1996, a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in the west of England.The county was named after the River Avon, which runs through the area. It was formed from parts of the historic counties of Gloucestershire and Somerset, together with the City of Bristol... |
four unitary authorities (Bristol Bristol Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007... , North Somerset North Somerset North Somerset is a unitary authority in England. Its area covers part of the ceremonial county of Somerset but it is administered independently of the non-metropolitan county. Its administrative headquarters is in the town hall in Weston-super-Mare.... , Bath and North East Somerset Bath and North East Somerset Bath and North East Somerset is a unitary authority that was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the County of Avon. It is part of the Ceremonial county of Somerset... , South Gloucestershire South Gloucestershire South Gloucestershire is a unitary district in the ceremonial county of Gloucestershire, in South West England.-History:The district was created in 1996, when the county of Avon was abolished, by the merger of former area of the districts of Kingswood and Northavon... ) |
accepted | 1996 |
| Bedfordshire Bedfordshire Bedfordshire is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.It borders Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the west and Hertfordshire to the south-east.... |
three unitary authorities (Bedford Bedford (borough) Bedford is a unitary authority with the status of a borough in the ceremonial county of Bedfordshire, England. Its council is based at Bedford, which is also the county town of Bedfordshire. The borough contains a single urban area, the 69th largest in the United Kingdom that comprises Bedford and... , Luton Luton Luton is a large town and unitary authority of Bedfordshire, England, 30 miles north of London. Luton and its near neighbours, Dunstable and Houghton Regis, form the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area with a population of about 250,000.... and Mid & South Beds South Bedfordshire South Bedfordshire was, from 1974 to 2009, a non-metropolitan district of Bedfordshire, in the East of England. Its main towns were Dunstable, Houghton Regis and Leighton Buzzard.-Creation:... ) |
Luton Luton Luton is a large town and unitary authority of Bedfordshire, England, 30 miles north of London. Luton and its near neighbours, Dunstable and Houghton Regis, form the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area with a population of about 250,000.... unitary authority only; two-tier remainder |
1997 |
| Berkshire Berkshire Berkshire is a historic county in the South of England. It is also often referred to as the Royal County of Berkshire because of the presence of the royal residence of Windsor Castle in the county; this usage, which dates to the 19th century at least, was recognised by the Queen in 1957, and... |
five unitary authorities (existing districts, with merger of Bracknell Forest Bracknell Forest Bracknell Forest is a unitary authority and borough in Berkshire in southern England. It covers the towns of Bracknell, North Ascot, Sandhurst, Crowthorne and surrounding villages and hamlets.-History:... and Windsor and Maidenhead as Royal East Berkshire) |
six unitary authorities (one for each district) | 1998 |
| Buckinghamshire Buckinghamshire Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan home county in South East England. The county town is Aylesbury, the largest town in the ceremonial county is Milton Keynes and largest town in the non-metropolitan county is High Wycombe.... |
four unitary authorities | Milton Keynes Milton Keynes (borough) The Borough of Milton Keynes is a unitary authority and borough in south central England, at the northern tip of the South East England Region. For ceremonial purposes, it is in the county of Buckinghamshire... unitary authority only; two-tier remainder |
1997 |
| Cambridgeshire Cambridgeshire Cambridgeshire is a county in England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the northeast, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west... |
no change | Huntingdonshire Huntingdonshire Huntingdonshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, covering the area around Huntingdon. Traditionally it is a county in its own right... and Peterborough Peterborough Peterborough is a cathedral city and unitary authority area in the East of England, with an estimated population of in June 2007. For ceremonial purposes it is in the county of Cambridgeshire. Situated north of London, the city stands on the River Nene which flows into the North Sea... referred back; Peterborough accepted |
1998 |
| Cheshire Cheshire Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow... |
no change | Halton Halton (borough) Halton is a local government district in North West England, with borough status and administered by a unitary authority. It was created in 1974 as a district of Cheshire, and became a unitary authority area on 1 April 1998. It consists of the towns of Widnes and Runcorn and the civil parishes of... and Warrington Warrington Warrington is a town, borough and unitary authority area of Cheshire, England. It stands on the banks of the River Mersey, which is tidal to the west of the weir at Howley. It lies 16 miles east of Liverpool, 19 miles west of Manchester and 8 miles south of St Helens... referred back; both accepted |
1998 |
| Cleveland Cleveland, England Cleveland is an area in the north east of England. Its name means literally "cliff-land", referring to its hilly southern areas, which rise to nearly... |
four unitary authorities (Hartlepool Hartlepool (borough) Hartlepool is a unitary authority in the ceremonial county of County Durham, north east England. In 2003 it had a resident population of 90,161. It borders the non-metropolitan county of County Durham to the north, Stockton-on-Tees to the south and Redcar and Cleveland to the south-east along the... , Middlesbrough Middlesbrough (borough) -External links:*... , Redcar and Cleveland Redcar and Cleveland The borough of Redcar & Cleveland is a unitary authority in the ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, England consisting of Redcar, Saltburn-by-the-Sea, Guisborough, and small towns such as Brotton, Eston, Skelton and Loftus. It had a resident population of 139,132 in 2001, and is part of the Tees... , Stockton-on-Tees Stockton-on-Tees (borough) Stockton-on-Tees is a unitary authority area and borough in the Tees Valley area of north east England, with a population in 2001 of 178,408, rising to 185,880 in 2005 estimates.... ) |
accepted | 1996 |
| Cornwall Cornwall Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Cumbria Cumbria Cumbria , is a non-metropolitan county in North West England. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local authority, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's largest settlement and county town is Carlisle. It consists of six districts, and in... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Derbyshire Derbyshire Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire. The northern part of Derbyshire overlaps with the Pennines, a famous chain of hills and mountains. The county contains within its boundary of approx... |
Derby Derby Derby , is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands region of England. It lies upon the banks of the River Derwent and is located in the south of the ceremonial county of Derbyshire. In the 2001 census, the population of the city was 233,700, whilst that of the Derby Urban Area was 229,407... and North East Derbyshire (North East Derbyshire North East Derbyshire North East Derbyshire is a local government district in Derbyshire, England. It borders the districts of Chesterfield, Bolsover, Amber Valley and Derbyshire Dales in Derbyshire, and Sheffield and Rotherham in South Yorkshire.... , Bolsover Bolsover (district) Bolsover is a local government district in Derbyshire, England. Its main town is Bolsover.There are fourteen town and parish councils within the district.In addition to the town councils of Old Bolsover and Shirebrook, there are the parish councils of:... , Chesterfield); two-tier reminder |
referred back under new guidelines | – |
| Derby Derby Derby , is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands region of England. It lies upon the banks of the River Derwent and is located in the south of the ceremonial county of Derbyshire. In the 2001 census, the population of the city was 233,700, whilst that of the Derby Urban Area was 229,407... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
accepted | 1997 | |
| Devon Devon Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with... |
Plymouth Plymouth Plymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound... and Torbay Torbay Torbay is an east-facing bay and natural harbour, at the western most end of Lyme Bay in the south-west of England, situated roughly midway between the cities of Exeter and Plymouth. Part of the ceremonial county of Devon, Torbay was made a unitary authority on 1 April 1998... unitary authorities; two-tier remainder |
Exeter Exeter Exeter is a historic city in Devon, England. It lies within the ceremonial county of Devon, of which it is the county town as well as the home of Devon County Council. Currently the administrative area has the status of a non-metropolitan district, and is therefore under the administration of the... referred back; rejected |
1998 |
| Dorset Dorset Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974... |
four unitary authorities (Bournemouth Bournemouth Bournemouth is a large coastal resort town in the ceremonial county of Dorset, England. According to the 2001 Census the town has a population of 163,444, making it the largest settlement in Dorset. It is also the largest settlement between Southampton and Plymouth... , Poole Poole Poole is a large coastal town and seaport in the county of Dorset, on the south coast of England. The town is east of Dorchester, and Bournemouth adjoins Poole to the east. The Borough of Poole was made a unitary authority in 1997, gaining administrative independence from Dorset County Council... , East Dorset and West Dorset) |
Bournemouth and Poole unitary authorities only; two-tier remainder | 1997 |
| Durham County Durham County Durham is a ceremonial county and unitary district in north east England. The county town is Durham. The largest settlement in the ceremonial county is the town of Darlington... |
Darlington Darlington (borough) Darlington is a local government district and borough in North East England. In 2008 it had a resident population of 100,500 It borders County Durham to the north and west, North Yorkshire to the south along the line of the River Tees, and Stockton-on-Tees to the east.-Council:Traditionally part of... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
referred back under new guidelines | – |
| Darlington Darlington (borough) Darlington is a local government district and borough in North East England. In 2008 it had a resident population of 100,500 It borders County Durham to the north and west, North Yorkshire to the south along the line of the River Tees, and Stockton-on-Tees to the east.-Council:Traditionally part of... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
accepted | 1997 | |
| East Sussex East Sussex East Sussex is a county in South East England. It is bordered by the counties of Kent, Surrey and West Sussex, and to the south by the English Channel.-History:... |
Brighton and Hove unitary authority; two-tier remainder | accepted | 1997 |
| Essex Essex Essex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England, and one of the home counties. It is located to the northeast of Greater London. It borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent to the South and London to the south west... |
Southend-on-Sea Southend-on-Sea Southend-on-Sea is a unitary authority area, town, and seaside resort in Essex, England. The district has Borough status, and comprises the towns of Chalkwell, Eastwood, Leigh-on-Sea, North Shoebury, Prittlewell, Shoeburyness, Southchurch, Thorpe Bay, and Westcliff-on-Sea. The district is situated... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
Basildon Basildon (district) Basildon is a local government district in south Essex in the East of England, centred around the town of Basildon. The district was formed under the Local Government Act 1972 on 1 April 1974 from the former area of Basildon Urban District and the part of Thurrock Urban District that was within the... and Thurrock Thurrock Thurrock is a unitary authority with borough status in the English ceremonial county of Essex. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The local authority is Thurrock Council.... referred back; Thurrock accepted |
1998 |
| Gloucestershire Gloucestershire Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean.... |
no change | referred back under new guidance | – |
| no change | Gloucester Gloucester Gloucester is a city, district and county town of Gloucestershire in the South West region of England. Gloucester lies close to the Welsh border, and on the River Severn, approximately north-east of Bristol, and south-southwest of Birmingham.... referred back; rejected |
– | |
| Hampshire Hampshire Hampshire is a county on the southern coast of England in the United Kingdom. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, a historic cathedral city that was once the capital of England. Hampshire is notable for housing the original birthplaces of the Royal Navy, British Army, and Royal Air Force... |
Southampton Southampton Southampton is the largest city in the county of Hampshire on the south coast of England, and is situated south-west of London and north-west of Portsmouth. Southampton is a major port and the closest city to the New Forest... , Portsmouth Portsmouth Portsmouth is the second largest city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire on the south coast of England. Portsmouth is notable for being the United Kingdom's only island city; it is located mainly on Portsea Island... and New Forest New Forest (district) New Forest is a local government district in Hampshire, England. It is named after the New Forest.It was created on 1 April 1974, and was a merger of the borough of Lymington, New Forest Rural District and part of Ringwood and Fordingbridge Rural District.... unitary authorities; remainder two-tier |
Southampton and Portsmouth unitary authorities only; two-tier remainder | 1997 |
| Hereford and Worcester Hereford and Worcester Hereford and Worcester was an English county created on 1 April 1974, by the Local Government Act 1972 from the area of the former administrative county of Herefordshire, most of Worcestershire and the county borough of Worcester.It bordered Shropshire, Staffordshire and the West Midlands to the... |
Herefordshire Herefordshire Herefordshire is a historic and ceremonial county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire" NUTS 2 region. It also forms a unitary district known as the... unitary authority; two-tier Worcestershire Worcestershire Worcestershire is a non-metropolitan county, established in antiquity, located in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire" NUTS 2 region... |
accepted | 1998 |
| Hertfordshire Hertfordshire Hertfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England. The county town is Hertford.The county is one of the Home Counties and lies inland, bordered by Greater London , Buckinghamshire , Bedfordshire , Cambridgeshire and... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Humberside Humberside Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire... |
four unitary authorities (East Riding of Yorkshire East Riding of Yorkshire The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Yorkshire, is a local government district with unitary authority status, and a ceremonial county of England. For ceremonial purposes the county also includes the city of Kingston upon Hull, which is a separate unitary authority... , Hull Kingston upon Hull Kingston upon Hull , usually referred to as Hull, is a city and unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Hull at its junction with the Humber estuary, 25 miles inland from the North Sea. Hull has a resident population of... , North Lincolnshire North Lincolnshire North Lincolnshire is a unitary authority area in the region of Yorkshire and the Humber in England. For ceremonial purposes it is part of Lincolnshire.... , North East Lincolnshire North East Lincolnshire North East Lincolnshire is a unitary authority in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, bordering the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire and the administrative county of Lincolnshire... ) |
accepted † | 1996 |
| Isle of Wight Isle of Wight The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent... |
one unitary authority | accepted | 1995 |
| Kent Kent Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of... |
no change | Dartford Dartford (borough) Dartford is the name given to a local government district and borough in north west Kent, England, which takes its name from its administrative capital. It borders Thurrock, to the north across the River Thames; to the west lies the London Borough of Bexley; to the south Sevenoaks district; and the... , Gillingham, Gravesham Gravesham Gravesham is a local government district and borough in North West Kent, England. It has borders with the River Thames to the north; the City of Rochester and Medway to the east; the borough of Tonbridge and Malling ; and the boroughs of Sevenoaks and Dartford to the west.Its council is based at... and Rochester upon Medway referred back; Dartford and Gravesham rejected, Gillingham and Rochester joined to form Medway Towns unitary authority |
1998 |
| Lancashire Lancashire Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston... |
no change | Blackpool Blackpool Blackpool is a borough, seaside town, and unitary authority area of Lancashire, in North West England. It is situated along England's west coast by the Irish Sea, between the Ribble and Wyre estuaries, northwest of Preston, north of Liverpool, and northwest of Manchester... and Blackburn Blackburn with Darwen Blackburn with Darwen is a unitary authority area in Lancashire, North West England. It consists of Blackburn, the small town of Darwen to the south of it, and the surrounding countryside.-Formation:... referred back; accepted |
1998 |
| Leicestershire Leicestershire Leicestershire is a landlocked county in the English Midlands. It takes its name from the heavily populated City of Leicester, traditionally its administrative centre, although the City of Leicester unitary authority is today administered separately from the rest of Leicestershire... |
Leicester Leicester Leicester is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England, and the county town of Leicestershire. The city lies on the River Soar and at the edge of the National Forest... and Rutland Rutland Rutland is a landlocked county in central England, bounded on the west and north by Leicestershire, northeast by Lincolnshire and southeast by Peterborough and Northamptonshire.... unitary authorities; two-tier remainder |
accepted | 1997 |
| Lincolnshire Lincolnshire Lincolnshire is a county in the east of England. It borders Norfolk to the south east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Norfolk Norfolk Norfolk is a low-lying county in the East of England. It has borders with Lincolnshire to the west, Cambridgeshire to the west and southwest and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea coast and to the north-west the county is bordered by The Wash. The county... |
no change | Norwich Norwich Norwich is a city in England. It is the regional administrative centre and county town of Norfolk. During the 11th century, Norwich was the largest city in England after London, and one of the most important places in the kingdom... referred back; rejected |
– |
| North Yorkshire North Yorkshire North Yorkshire is a non-metropolitan or shire county located in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, and a ceremonial county primarily in that region but partly in North East England. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972 it covers an area of , making it the largest... |
three unitary authorities (West Riding of Yorkshire, North Riding of Yorkshire, York York York is a walled city, situated at the confluence of the Rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. The city has a rich heritage and has provided the backdrop to major political events throughout much of its two millennia of existence... ) |
York unitary authority accepted; two-tier remainder | 1996 |
| Northamptonshire Northamptonshire Northamptonshire is a landlocked county in the English East Midlands, with a population of 629,676 as at the 2001 census. It has boundaries with the ceremonial counties of Warwickshire to the west, Leicestershire and Rutland to the north, Cambridgeshire to the east, Bedfordshire to the south-east,... |
no change | Northampton Northampton Northampton is a large market town and local government district in the East Midlands region of England. Situated about north-west of London and around south-east of Birmingham, Northampton lies on the River Nene and is the county town of Northamptonshire. The demonym of Northampton is... referred back; rejected |
– |
| Northumberland Northumberland Northumberland is the northernmost ceremonial county and a unitary district in North East England. For Eurostat purposes Northumberland is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three boroughs or unitary districts that comprise the "Northumberland and Tyne and Wear" NUTS 2 region... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Nottinghamshire Nottinghamshire Nottinghamshire is a county in the East Midlands of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west... |
Nottingham Nottingham Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
Broxtowe Broxtowe Broxtowe is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England, west of the City of Nottingham. It is part of the Greater Nottingham metropolitan area... , Gedling Gedling Gedling is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England. Its council is based in Arnold. It is part of the Greater Nottingham metropolitan area lying to the North and East of the City of Nottingham.... , Rushcliffe Rushcliffe Rushcliffe is a local government district with borough status in Nottinghamshire, England. Its council is based in West Bridgford. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by merging the West Bridgford Urban District, the Bingham Rural District and part of Basford Rural District.-Political representation:The... referred back; rejected |
1998 |
| Oxfordshire Oxfordshire Oxfordshire is a county in the South East region of England, bordering on Warwickshire and Northamptonshire , Buckinghamshire , Berkshire , Wiltshire and Gloucestershire .... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Shropshire Shropshire Shropshire is a county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes, the county is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. It borders Wales to the west... |
no change | The Wrekin Telford and Wrekin Telford and Wrekin is a unitary district with borough status in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. The district was created in 1974 as The... referred back; accepted |
1998 |
| Somerset Somerset The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the... |
three unitary authorities (West, Mid and South) | rejected; two-tier status quo kept | – |
| Staffordshire Staffordshire Staffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes, the county is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. Part of the National Forest lies within its borders... |
Stoke-on-Trent Stoke-on-Trent Stoke-on-Trent , also called The Potteries is a city in Staffordshire, England, which forms a linear conurbation almost 12 miles long, with an area of . Together with the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme Stoke forms The Potteries Urban Area... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
accepted | 1998 |
| Suffolk Suffolk Suffolk is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in East Anglia, England. It has borders with Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south. The North Sea lies to the east... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Surrey Surrey Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of... |
no change | Spelthorne Spelthorne Spelthorne is a local government district and borough in Surrey, England. It includes the towns of Ashford, Laleham, Shepperton, Staines, Stanwell and Sunbury... referred back; rejected |
– |
| Warwickshire Warwickshire Warwickshire is a landlocked non-metropolitan county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, although the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare... |
no change | accepted | – |
| West Sussex West Sussex West Sussex is a county in the south of England, bordering onto East Sussex , Hampshire and Surrey. The county of Sussex has been divided into East and West since the 12th century, and obtained separate county councils in 1888, but it remained a single ceremonial county until 1974 and the coming... |
no change | accepted | – |
| Wiltshire Wiltshire Wiltshire is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset, Somerset, Hampshire, Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire and Berkshire. It contains the unitary authority of Swindon and covers... |
Thamesdown Swindon (borough) The Borough of Swindon is a local government authority in South West England. It is centred on the town of Swindon and forms part of the ceremonial county of Wiltshire... unitary authority; two-tier remainder |
accepted | 1998 |
† since the government rejected the Commission's proposal for a West Riding of Yorkshire authority to include parts of North Yorkshire and the Goole
Goole
Goole is a town, civil parish and port located approximately inland on the confluence of the rivers Don and Ouse in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England...
area of Humberside, Goole became part of the new East Riding of Yorkshire instead.
Timetable
| On 1 April 1995, the Isle of Wight Isle of Wight The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent... became a unitary authority. Two small areas were ceded from Surrey Surrey Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of... and Buckinghamshire Buckinghamshire Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan home county in South East England. The county town is Aylesbury, the largest town in the ceremonial county is Milton Keynes and largest town in the non-metropolitan county is High Wycombe.... to Berkshire Berkshire Berkshire is a historic county in the South of England. It is also often referred to as the Royal County of Berkshire because of the presence of the royal residence of Windsor Castle in the county; this usage, which dates to the 19th century at least, was recognised by the Queen in 1957, and... , giving it a border with Greater London Greater London Greater London is the top-level administrative division of England covering London. It was created in 1965 and spans the City of London, including Middle Temple and Inner Temple, and the 32 London boroughs. This territory is coterminate with the London Government Office Region and the London... . |
 |
|
| On 1 April 1996, the unpopular counties of Avon, Humberside Humberside Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire... and Cleveland Cleveland, England Cleveland is an area in the north east of England. Its name means literally "cliff-land", referring to its hilly southern areas, which rise to nearly... were split into unitary authorities. Avon became Bath and North East Somerset Bath and North East Somerset Bath and North East Somerset is a unitary authority that was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the County of Avon. It is part of the Ceremonial county of Somerset... , North Somerset North Somerset North Somerset is a unitary authority in England. Its area covers part of the ceremonial county of Somerset but it is administered independently of the non-metropolitan county. Its administrative headquarters is in the town hall in Weston-super-Mare.... , South Gloucestershire South Gloucestershire South Gloucestershire is a unitary district in the ceremonial county of Gloucestershire, in South West England.-History:The district was created in 1996, when the county of Avon was abolished, by the merger of former area of the districts of Kingswood and Northavon... and Bristol Bristol Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007... . Each of Cleveland's four districts became a unitary authority. The part of Humberside Humberside Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East and West ridings of Yorkshire and parts of Lindsey, Lincolnshire... north of the River Humber became part of the new East Riding of Yorkshire East Riding of Yorkshire The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Yorkshire, is a local government district with unitary authority status, and a ceremonial county of England. For ceremonial purposes the county also includes the city of Kingston upon Hull, which is a separate unitary authority... , apart from Hull Kingston upon Hull Kingston upon Hull , usually referred to as Hull, is a city and unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Hull at its junction with the Humber estuary, 25 miles inland from the North Sea. Hull has a resident population of... , which constituted a unitary authority itself. In the Lincolnshire part of Humberside, two new unitary authorities, North Lincolnshire North Lincolnshire North Lincolnshire is a unitary authority area in the region of Yorkshire and the Humber in England. For ceremonial purposes it is part of Lincolnshire.... and North East Lincolnshire North East Lincolnshire North East Lincolnshire is a unitary authority in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, bordering the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire and the administrative county of Lincolnshire... , were formed. Also at this time, the City of York York York is a walled city, situated at the confluence of the Rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. The city has a rich heritage and has provided the backdrop to major political events throughout much of its two millennia of existence... was expanded and separated from North Yorkshire North Yorkshire North Yorkshire is a non-metropolitan or shire county located in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, and a ceremonial county primarily in that region but partly in North East England. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972 it covers an area of , making it the largest... . |
||
 |
On 1 April 1997, the districts of Bournemouth Bournemouth Bournemouth is a large coastal resort town in the ceremonial county of Dorset, England. According to the 2001 Census the town has a population of 163,444, making it the largest settlement in Dorset. It is also the largest settlement between Southampton and Plymouth... , Darlington Darlington (borough) Darlington is a local government district and borough in North East England. In 2008 it had a resident population of 100,500 It borders County Durham to the north and west, North Yorkshire to the south along the line of the River Tees, and Stockton-on-Tees to the east.-Council:Traditionally part of... , Derby, Leicester Leicester Leicester is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England, and the county town of Leicestershire. The city lies on the River Soar and at the edge of the National Forest... , Luton Luton Luton is a large town and unitary authority of Bedfordshire, England, 30 miles north of London. Luton and its near neighbours, Dunstable and Houghton Regis, form the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area with a population of about 250,000.... , Milton Keynes Milton Keynes (borough) The Borough of Milton Keynes is a unitary authority and borough in south central England, at the northern tip of the South East England Region. For ceremonial purposes, it is in the county of Buckinghamshire... , Poole Poole Poole is a large coastal town and seaport in the county of Dorset, on the south coast of England. The town is east of Dorchester, and Bournemouth adjoins Poole to the east. The Borough of Poole was made a unitary authority in 1997, gaining administrative independence from Dorset County Council... , Portsmouth Portsmouth Portsmouth is the second largest city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire on the south coast of England. Portsmouth is notable for being the United Kingdom's only island city; it is located mainly on Portsea Island... , Rutland Rutland Rutland is a landlocked county in central England, bounded on the west and north by Leicestershire, northeast by Lincolnshire and southeast by Peterborough and Northamptonshire.... and Southampton Southampton Southampton is the largest city in the county of Hampshire on the south coast of England, and is situated south-west of London and north-west of Portsmouth. Southampton is a major port and the closest city to the New Forest... became unitary authorities. Brighton Brighton Brighton is the major part of the city of Brighton and Hove in East Sussex, England on the south coast of Great Britain... and Hove were merged to form the Brighton and Hove unitary authority. |
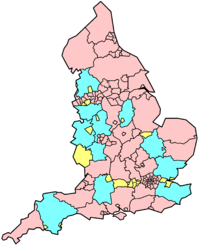 |
| On 1 April 1998, Blackpool Blackpool Blackpool is a borough, seaside town, and unitary authority area of Lancashire, in North West England. It is situated along England's west coast by the Irish Sea, between the Ribble and Wyre estuaries, northwest of Preston, north of Liverpool, and northwest of Manchester... , Blackburn with Darwen Blackburn with Darwen Blackburn with Darwen is a unitary authority area in Lancashire, North West England. It consists of Blackburn, the small town of Darwen to the south of it, and the surrounding countryside.-Formation:... (a renamed Blackburn), Halton Halton (borough) Halton is a local government district in North West England, with borough status and administered by a unitary authority. It was created in 1974 as a district of Cheshire, and became a unitary authority area on 1 April 1998. It consists of the towns of Widnes and Runcorn and the civil parishes of... , Nottingham Nottingham Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group... , Peterborough, Plymouth Plymouth Plymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound... , Stoke-on-Trent Stoke-on-Trent Stoke-on-Trent , also called The Potteries is a city in Staffordshire, England, which forms a linear conurbation almost 12 miles long, with an area of . Together with the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme Stoke forms The Potteries Urban Area... , Southend-on-Sea Southend-on-Sea Southend-on-Sea is a unitary authority area, town, and seaside resort in Essex, England. The district has Borough status, and comprises the towns of Chalkwell, Eastwood, Leigh-on-Sea, North Shoebury, Prittlewell, Shoeburyness, Southchurch, Thorpe Bay, and Westcliff-on-Sea. The district is situated... , Swindon Swindon (borough) The Borough of Swindon is a local government authority in South West England. It is centred on the town of Swindon and forms part of the ceremonial county of Wiltshire... (Thamesdown), Telford and Wrekin Telford and Wrekin Telford and Wrekin is a unitary district with borough status in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of four counties or unitary districts that comprise the "Shropshire and Staffordshire" NUTS 2 region. The district was created in 1974 as The... (The Wrekin), Torbay Torbay Torbay is an east-facing bay and natural harbour, at the western most end of Lyme Bay in the south-west of England, situated roughly midway between the cities of Exeter and Plymouth. Part of the ceremonial county of Devon, Torbay was made a unitary authority on 1 April 1998... , Thurrock Thurrock Thurrock is a unitary authority with borough status in the English ceremonial county of Essex. It is part of the London commuter belt and an area of regeneration within the Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The local authority is Thurrock Council.... and Warrington Warrington Warrington is a town, borough and unitary authority area of Cheshire, England. It stands on the banks of the River Mersey, which is tidal to the west of the weir at Howley. It lies 16 miles east of Liverpool, 19 miles west of Manchester and 8 miles south of St Helens... became unitary authorities. Rochester upon Medway and Gillingham were merged to form the Medway Medway Medway is a conurbation and unitary authority in South East England. The Unitary Authority was formed in 1998 when the City of Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with Gillingham Borough Council and part of Kent County Council to form Medway Council, a unitary authority independent of Kent County... unitary authority. Also, Hereford and Worcester Hereford and Worcester Hereford and Worcester was an English county created on 1 April 1974, by the Local Government Act 1972 from the area of the former administrative county of Herefordshire, most of Worcestershire and the county borough of Worcester.It bordered Shropshire, Staffordshire and the West Midlands to the... was abolished and replaced by the unitary authority of Herefordshire Herefordshire Herefordshire is a historic and ceremonial county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire" NUTS 2 region. It also forms a unitary district known as the... and the shire county of Worcestershire Worcestershire Worcestershire is a non-metropolitan county, established in antiquity, located in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire" NUTS 2 region... . Berkshire Berkshire Berkshire is a historic county in the South of England. It is also often referred to as the Royal County of Berkshire because of the presence of the royal residence of Windsor Castle in the county; this usage, which dates to the 19th century at least, was recognised by the Queen in 1957, and... was split into six unitary authorities, but not formally abolished. |
Other changes
The local government reform did not affect police areas, or fire and rescue service areas, but resulted in the setting of many more joint boards for such authorities: previously county councils were represented on these bodies, and the creation of new unitary authorities meant that the apportionment of representatives was adjusted.In addition to having their county councils abolished, Avon, Humberside and Cleveland were abolished as non-metropolitan counties. This, and the fact that many of the new unitary authorities were in themselves non-metropolitan counties, led to the concept of ceremonial counties
Ceremonial counties of England
The ceremonial counties are areas of England to which are appointed a Lord Lieutenant, and are defined by the government as counties and areas for the purposes of the Lieutenancies Act 1997 with reference to the metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties of England and Lieutenancies Act 1997...
for the Lieutenancy
Lord Lieutenant
The title Lord Lieutenant is given to the British monarch's personal representatives in the United Kingdom, usually in a county or similar circumscription, with varying tasks throughout history. Usually a retired local notable, senior military officer, peer or business person is given the post...
, which would include the areas made part of unitary authorities. In Avon, Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
became a ceremonial county in itself, with the other parts allocated to Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn, and the entire Forest of Dean....
. Cleveland was simply partitioned between County Durham
County Durham
County Durham is a ceremonial county and unitary district in north east England. The county town is Durham. The largest settlement in the ceremonial county is the town of Darlington...
and North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is a non-metropolitan or shire county located in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England, and a ceremonial county primarily in that region but partly in North East England. Created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972 it covers an area of , making it the largest...
, along the line of the River Tees
River Tees
The River Tees is in Northern England. It rises on the eastern slope of Cross Fell in the North Pennines, and flows eastwards for 85 miles to reach the North Sea between Hartlepool and Redcar.-Geography:...
. Humberside was split between Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire is a county in the east of England. It borders Norfolk to the south east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders...
and the new ceremonial East Riding of Yorkshire
East Riding of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Yorkshire, is a local government district with unitary authority status, and a ceremonial county of England. For ceremonial purposes the county also includes the city of Kingston upon Hull, which is a separate unitary authority...
(including Hull). In 1997, Rutland
Rutland
Rutland is a landlocked county in central England, bounded on the west and north by Leicestershire, northeast by Lincolnshire and southeast by Peterborough and Northamptonshire....
became a ceremonial county as well as a unitary authority, to be followed in 1998 by Herefordshire
Herefordshire
Herefordshire is a historic and ceremonial county in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire" NUTS 2 region. It also forms a unitary district known as the...
and Worcestershire
Worcestershire
Worcestershire is a non-metropolitan county, established in antiquity, located in the West Midlands region of England. For Eurostat purposes it is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three counties that comprise the "Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire" NUTS 2 region...
.
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics
NUTS:UK
In the NUTS codes of the United Kingdom , the three levels are:-NUTS codes:...
used for European regional statistics were also altered, in part to be consistent with the new local government boundaries.

