
Locomotive classification of the Deutsche Bundesbahn
Encyclopedia
Originally, both Deutsche Bundesbahn
and Deutsche Reichsbahn
continued the classification system of the Deutsche Reichsbahn (DRG)
- see also a short overview of the numbering system of the German railways
. When UIC
introduced a new classification system that could be processed by the computers of the late 1960s, DB did a major modification of their system, effective 1 January 1968. This system is still in use and now includes the engines of the former GDR railways as well. (See List of Deutsche Bahn AG locomotives and railbuses for a current list.)
Series that contain more than 1,000 vehicles are assigned ascending numbers.
The first number denotes the type of the vehicle, replacing the DRG convention of using letters to differentiate between the vehicle types.
The letters of the DRG schema are not officially used any more since the introduction of computer numbers, however they can often be found in informal writing and spoken conversation. So if somebody is talking of an E110, they likely mean an E10 / 110, if a V216 is mentioned, it is likely the author is intending the V160 / 216.
Tenders are not assigned a number of their own, as they are regarded a part of the vehicle they are coupled to.
Cab cars and intermediate cars of multiple unit
s receive the numbers 8 if they belong to an EMU, 9 if they belong to a DMU
. If another powered car or engine is present in the multiple unit, its serial number usually is offset by 500, but it is still assigned into the original class.
For example, a two-car Class 628
DMU would look like:
A class 420
commuter EMU, for example, would look like this:

for the origins of the system.
The number 0 was assigned to steam locomotives, as their end of duty was already foreseeable. The schematics are largely derivative of the DRG system of classification, therefore like in the older system the class numbers were grouped by locomotive types:
 Steam locomotives that had been converted to oil fuelling received separate class numbers from their coal-fuelled counterparts, e. g. oil-fuelled units from the old class 44
Steam locomotives that had been converted to oil fuelling received separate class numbers from their coal-fuelled counterparts, e. g. oil-fuelled units from the old class 44
were assigned to class 043 while coal-fuelled ones were assigned to class 044 under the new numbering plan. The DRB Class 50
(with originally more than 3,000 units, of which DB still had more than 1,000 by the end of 1967) gave rise to BR 050, 051, 052 and 053.
A noteworthy change from the old system was that four-digit engine numbers were no longer possible. Locomotives with such a number would either be put into an overflow class (e. g. 50 3097 became 053 097-2) or have their number abbreviated to three digits. The latter solution could lead to number conflicts in cases where the original (sub)class had comprised more than 1,000 units. These were dealt with by adjusting one of the numbers involved, e. g., 38 3711 became 038 711-8 while 38 1711 became 038 710-0. This also means that for some classes it is not possible to reconstruct the old number from the new one in a purely systematic way.
The last steam locomotives in the Deutsche Bundesbahn
were decommissioned on 26 October 1977 at Rheine und Emden locomotive depot (Bahnbetriebswerk
or Bw). These were the 043 903, 043 315 and 043 196 .
They usually were relabelled by replacing the letter "E" with the number "1".
For example, the Einheits-Elektrolokomotive
n were relabelled from E 40 into 140, E 10 into 110 and E 10.12 into 112.
 In the pre-1968 scheme, diesel engines were assigned the letter "V" (as in the German term Verbrennungsmotor for combustion engine). The old numbers were directly proportional with the engine power, so that two- and three-digit codes existed. Two-digit codes were transposed one by one (Examples: Class V60 became Class 260, Class V80 became Class 280). Three digit codes generally lost their last digit (V 160 became DB Class 216). Variants of the previously same class were also assigned individual subclasses, the V 160 family, consisting of V 160, V 160 long, V 162, V 164, V 168 and V 169 were assigned the numbers 210, 215, 216, 217, 218 and 219, for example.)
In the pre-1968 scheme, diesel engines were assigned the letter "V" (as in the German term Verbrennungsmotor for combustion engine). The old numbers were directly proportional with the engine power, so that two- and three-digit codes existed. Two-digit codes were transposed one by one (Examples: Class V60 became Class 260, Class V80 became Class 280). Three digit codes generally lost their last digit (V 160 became DB Class 216). Variants of the previously same class were also assigned individual subclasses, the V 160 family, consisting of V 160, V 160 long, V 162, V 164, V 168 and V 169 were assigned the numbers 210, 215, 216, 217, 218 and 219, for example.)
became Class 329. In 1987 the DB Class 260/261
were also assigned to the small locomotives and labelled as Class 360/361.
Deutsche Bundesbahn
The Deutsche Bundesbahn or DB was formed as the state railway of the newly established Federal Republic of Germany on September 7, 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft '...
and Deutsche Reichsbahn
Deutsche Reichsbahn of the GDR
The Deutsche Reichsbahn or DR was the operating name of state owned railways in the German Democratic Republic ....
continued the classification system of the Deutsche Reichsbahn (DRG)
Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft
The Deutsche Reichsbahn – was the name of the German national railway created from the railways of the individual states of the German Empire following the end of World War I....
- see also a short overview of the numbering system of the German railways
Numbering scheme of the German railways
The different railway companies in Germany have used various schemes to classify their rolling stock.-From the beginning:As widely known the first few locomotives had names. The first locomotive in public service in Germany from 1835 was named Adler. The first railway lines were built by privately...
. When UIC
International Union of Railways
The UIC , or International Union of Railways, is an international rail transport industry body.- Brief history :The railways of Europe originated as separate concerns. There were many border changes after World War I and the Treaty of Versailles. Colonial railways were the responsibility of the...
introduced a new classification system that could be processed by the computers of the late 1960s, DB did a major modification of their system, effective 1 January 1968. This system is still in use and now includes the engines of the former GDR railways as well. (See List of Deutsche Bahn AG locomotives and railbuses for a current list.)
Basics
Since January 1, 1968, all vehicles are denoted by a seven-digit vehicle number. It consists of a three-digit class number, a three-digit serial number and a check digit separated by a dash. The check digit is calculated by multiplying the first six digits by 1 and 2 alternately, the difference of the result to the next multitude of ten is the check digit. The check digit is used to perform a cross-check to ensure the correct number, for example in computer systems.Series that contain more than 1,000 vehicles are assigned ascending numbers.
The first number denotes the type of the vehicle, replacing the DRG convention of using letters to differentiate between the vehicle types.
| Number | Letter(s) | Vehicle type |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Steam locomotive Steam locomotive A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine... s |
|
| 1 | E | Electric locomotive Electric locomotive An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or an on-board energy storage device... s |
| 2 | V | Diesel locomotive Diesel locomotive A diesel locomotive is a type of railroad locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine, a reciprocating engine operating on the Diesel cycle as invented by Dr. Rudolf Diesel... s |
| 3 | K | Small shunting locomotives |
| 4 | ET | Electric multiple units, not including battery powered |
| 5 | ETA | Battery powered railcar Railcar A railcar, in British English and Australian English, is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach , with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railways, e.g., the Great Western... s |
| 6 | VT | Diesel multiple units |
| 7 | Railbus Railbus A railbus is a very lightweight type passenger rail vehicle that shares many aspects of their construction with a bus, usually having a bus, or modified bus body, and having four wheels on a fixed base, instead of on bogies... es and work vehicles |
|
| 8 | ES, EB | Cab cars and accompanying cars to electric railcars |
| 9 | VS, VB | Cab cars and accompanying cars to diesel railcars and railbuses |
The letters of the DRG schema are not officially used any more since the introduction of computer numbers, however they can often be found in informal writing and spoken conversation. So if somebody is talking of an E110, they likely mean an E10 / 110, if a V216 is mentioned, it is likely the author is intending the V160 / 216.
Tenders are not assigned a number of their own, as they are regarded a part of the vehicle they are coupled to.
Cab cars and intermediate cars of multiple unit
Multiple unit
The term multiple unit or MU is used to describe a self-propelled carriages capable of coupling with other units of the same or similar type and still being controlled from one driving cab. The term is commonly used to denote passenger trainsets consisting of more than one carriage...
s receive the numbers 8 if they belong to an EMU, 9 if they belong to a DMU
Diesel multiple unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple unit train consisting of multiple carriages powered by one or more on-board diesel engines. They may also be referred to as a railcar or railmotor, depending on country.-Design:...
. If another powered car or engine is present in the multiple unit, its serial number usually is offset by 500, but it is still assigned into the original class.
For example, a two-car Class 628
DB Class 628
The DB Class 628 is a twin-car, diesel multiple unit operated by the Deutsche Bahn AG for local passenger rail services.- Design :...
DMU would look like:
- 628 210-7 (powered cab car)
- 928 210-4 (non-powered cab, hence 9 instead of 6)
A class 420
DB Class 420
The Baureihe 420 is a light-weight commuter electric multiple unit developed for the S-Bahn networks in Germany and was originally commissioned by the Deutsche Bundesbahn for the Munich, Stuttgart and Frankfurt networks. It could seat 194 second class, 17 or 33 first class, depending on series. The...
commuter EMU, for example, would look like this:
- 420 210-1 (powered cab car)
- 421 210-2 (powered intermediate car)
- 420 710-7 (powered cab car, +500)
Example: 110 494-2

| Meaning of 110 494-2 | |
|---|---|
| 110 | Class number → first number (1) meaning electric locomotive Electric locomotive An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or an on-board energy storage device... |
| 494 | Serial number |
| 2 | Check digit |
| How to calculate the check digit | |
 |
Add 1st, 3rd and 5th number. |
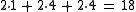 |
Digit sum of the double of 2nd, 4th and 6th number. |
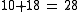 |
Add both results. |
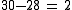 |
Difference of the result to the next multiple of ten is the check digit. |
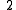 |
check digit |
Steam locomotives
See also: DRG locomotive classificationDRG locomotive classification
The DRG locomotive classification system was developed by the German Imperial Railway Company or Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft , which was formed in 1924 following the merger of the German state railways in 1920...
for the origins of the system.
The number 0 was assigned to steam locomotives, as their end of duty was already foreseeable. The schematics are largely derivative of the DRG system of classification, therefore like in the older system the class numbers were grouped by locomotive types:
| Number | Vehicle types |
|---|---|
| 001–019 | Express train Express train Express trains are a form of rail service. Express trains make only a small number of stops, instead of stopping at every single station... tender locomotive Tender locomotive A tender or coal-car is a special rail vehicle hauled by a steam locomotive containing the locomotive's fuel and water. Steam locomotives consume large quantities of water compared to the quantity of fuel, so tenders are necessary to keep the locomotive running over long distances. A locomotive... s |
| 020–039 | Other Passenger train tender locomotives |
| 040–059 | Freight train Freight train A freight train or goods train is a group of freight cars or goods wagons hauled by one or more locomotives on a railway, ultimately transporting cargo between two points as part of the logistics chain... tender locomotives |
| 060–079 | Passenger train tank locomotives |
| 080–096 | Freight train tank locomotives |
| 097 | Rack Rack railway A rack-and-pinion railway is a railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with this rack rail... locomotives (in theory only - none were left by 1968) |
| 098 | Lokalbahn (branch line) engines |
| 099 | narrow gauge locomotives |

DRG Class 44
The Class 44 was a ten-coupled, heavy goods train steam locomotive built for the Deutsche Reichsbahn as a standard steam engine class . Its sub-class was G 56.20 and it had triple cylinders...
were assigned to class 043 while coal-fuelled ones were assigned to class 044 under the new numbering plan. The DRB Class 50
DRB Class 50
Because the Deutsche Bundesbahn had sufficient goods train locomotives, they could quickly phase out the DRB Class 52 engines, so that the ageing boilers on the Class 50s could be replaced by those of the Class 52s. Even the 'bathtub' tender of the Kriegslokomotiven was used by the 50s amongst...
(with originally more than 3,000 units, of which DB still had more than 1,000 by the end of 1967) gave rise to BR 050, 051, 052 and 053.
A noteworthy change from the old system was that four-digit engine numbers were no longer possible. Locomotives with such a number would either be put into an overflow class (e. g. 50 3097 became 053 097-2) or have their number abbreviated to three digits. The latter solution could lead to number conflicts in cases where the original (sub)class had comprised more than 1,000 units. These were dealt with by adjusting one of the numbers involved, e. g., 38 3711 became 038 711-8 while 38 1711 became 038 710-0. This also means that for some classes it is not possible to reconstruct the old number from the new one in a purely systematic way.
The last steam locomotives in the Deutsche Bundesbahn
Deutsche Bundesbahn
The Deutsche Bundesbahn or DB was formed as the state railway of the newly established Federal Republic of Germany on September 7, 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft '...
were decommissioned on 26 October 1977 at Rheine und Emden locomotive depot (Bahnbetriebswerk
Bahnbetriebswerk
A Bahnbetriebswerk is the equivalent of a locomotive depot on the German and Austrian railways. It is an installation that carries out the maintenance, minor repairs, refuelling and cleaning of locomotives and other motive power. In addition it organises the deployment of locomotives and crews...
or Bw). These were the 043 903, 043 315 and 043 196 .
Electric engines
Electric engines were considered the most important method of traction, and hence were assigned the number 1.They usually were relabelled by replacing the letter "E" with the number "1".
For example, the Einheits-Elektrolokomotive
Einheits-Elektrolokomotive
Einheits-Elektrolokomotive is a German railroad term for the Class E10, Class E40, Class E41 and Class E50 locomotives that were commissioned after World War II by the Deutsche Bundesbahn of West Germany...
n were relabelled from E 40 into 140, E 10 into 110 and E 10.12 into 112.
Diesel engines

Small locomotives
Small shunting locomotives were assigned the number "3". The second number indicates the engine power (according to 1955 standards). The third number differentiates between brakes and transmission (chain drive or Cardan shafts). Small locomotives of the former Ka series were given the new class numbers 381 (pre-war models) and 382 (new models). The existing narrow gauge locomotives of the Wangerooge Island RailwayWangerooge Island Railway
The single track Wangerooge Island Railway is an unelectrified narrow gauge railway with a rail gauge of 1,000 mm located on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge off the northwestern coast of Germany...
became Class 329. In 1987 the DB Class 260/261
DB Class V 60
The DB Class V 60 is a German diesel locomotive operated by the Deutsche Bundesbahn and later, the Deutsche Bahn AG , which is used particularly for shunting duties, but also for hauling light goods trains. Seventeen locomotives were bought used by the Norwegian State Railways and designated NSB...
were also assigned to the small locomotives and labelled as Class 360/361.
See also
- History of rail transport in GermanyHistory of rail transport in GermanyGerman Railway history began with the opening of the steam-hauled Bavarian Ludwig Railway between Nuremberg and Fürth on 7 December 1835. This had been preceded by the opening of the horse-hauled Prince William Railway on 20 September 1831...
- Deutsche BundesbahnDeutsche BundesbahnThe Deutsche Bundesbahn or DB was formed as the state railway of the newly established Federal Republic of Germany on September 7, 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft '...
- UIC classificationUIC classificationThe UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...

