
Luddite
Encyclopedia

Social movement
Social movements are a type of group action. They are large informal groupings of individuals or organizations focused on specific political or social issues, in other words, on carrying out, resisting or undoing a social change....
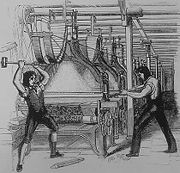
of 19th-century English textile artisans who protested – often by destroying mechanised loom
Loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads...
s – against the changes produced by the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
, which they felt were leaving them without work and changing their way of life. The movement was named after General Ned Ludd
Ned Ludd
Ned Ludd or Ned Lud, possibly born Ned Ludlam or Edward Ludlam, is the person from whom the Luddites took their name. His actions inspirated the folkloric character of Captain Ludd, also known as King Ludd or General Ludd, who became the Luddites' alleged leader and founder.It is believed that Ned...
or King Ludd, a mythical figure who, like Robin Hood
Robin Hood
Robin Hood was a heroic outlaw in English folklore. A highly skilled archer and swordsman, he is known for "robbing from the rich and giving to the poor", assisted by a group of fellow outlaws known as his "Merry Men". Traditionally, Robin Hood and his men are depicted wearing Lincoln green clothes....
, was reputed to live in Sherwood Forest
Sherwood Forest
Sherwood Forest is a Royal Forest in Nottinghamshire, England, that is famous through its historical association with the legend of Robin Hood. Continuously forested since the end of the Ice Age, Sherwood Forest National Nature Reserve today encompasses 423 hectares surrounding the village of...
.
Background
The movement emerged in the harsh economic climate of the Napoleonic WarsNapoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
and difficult working conditions in the new textile factories. The principal objection of the Luddites was to the introduction of new wide-framed automated looms that could be operated by cheap, relatively unskilled labour, resulting in the loss of jobs for many skilled textile workers. The movement began in Nottingham
Nottingham
Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group...
in 1811 and spread rapidly throughout England in 1811 and 1812. Mills and pieces of factory machinery were burned by handloom weavers, and for a short time Luddites were so strong that they clashed in battles with the British Army
British Army
The British Army is the land warfare branch of Her Majesty's Armed Forces in the United Kingdom. It came into being with the unification of the Kingdom of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England...
. Many wool
Wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and certain other animals, including cashmere from goats, mohair from goats, qiviut from muskoxen, vicuña, alpaca, camel from animals in the camel family, and angora from rabbits....
and cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
mills were destroyed until the British government suppressed the movement.
Formation of movement
The Luddites met at night on the moors surrounding the industrial towns, practising drills and manoeuvres, and often enjoyed local support. The main areas of the disturbances were NottinghamshireNottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire is a county in the East Midlands of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west...
in November 1811, followed by the West Riding of Yorkshire
West Riding of Yorkshire
The West Riding of Yorkshire is one of the three historic subdivisions of Yorkshire, England. From 1889 to 1974 the administrative county, County of York, West Riding , was based closely on the historic boundaries...
in early 1812 and Lancashire
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
from March 1813. Battles between Luddites and the military occurred at Burton's Mill in Middleton
Middleton, Greater Manchester
Middleton is a town within the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, in Greater Manchester, England. It stands on the River Irk, south-southwest of Rochdale, and north-northeast of the city of Manchester...
, and at Westhoughton Mill
Westhoughton Mill
Westhoughton Mill , situated in Mill Street in the town of Westhoughton, near Bolton in Lancashire, was in 1812 the site of a Luddite arson attack. It had been built in 1804 by Richard Johnson Lockett, a Macclesfield man who had bought and lived in Westhoughton Hall, and leased out in 1808 to...
, both in Lancashire
Lancashire
Lancashire is a non-metropolitan county of historic origin in the North West of England. It takes its name from the city of Lancaster, and is sometimes known as the County of Lancaster. Although Lancaster is still considered to be the county town, Lancashire County Council is based in Preston...
. It was rumoured at the time that agents provocateurs
Agent provocateur
Traditionally, an agent provocateur is a person employed by the police or other entity to act undercover to entice or provoke another person to commit an illegal act...
employed by the magistrates were involved in provoking the attacks. Magistrates and food merchants were also objects of death threats and attacks by the anonymous King Ludd and his supporters. Some industrialists even had secret chambers constructed in their buildings, which may have been used as hiding places.
Government response
York
York is a walled city, situated at the confluence of the Rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. The city has a rich heritage and has provided the backdrop to major political events throughout much of its two millennia of existence...
in 1812 that resulted in many executions and penal transportation
Penal transportation
Transportation or penal transportation is the deporting of convicted criminals to a penal colony. Examples include transportation by France to Devil's Island and by the UK to its colonies in the Americas, from the 1610s through the American Revolution in the 1770s, and then to Australia between...
s. The Luddite movement can also be seen as part of a rising tide of English working-class discontent in the early 19th century (see also, for example, the Pentridge or Pentrich Rising
Pentrich, Derbyshire
-Pentrich Revolution:The village gave its name to the Pentrich Revolution, which occurred on the night of 9/10 June 1817. A gathering of some two or three hundred men , led by Jeremiah Brandreth , , set out to march to Nottingham...
of 1817, which was a general uprising but led by an unemployed Nottingham stockinger and probable ex-Luddite, Jeremiah Brandreth
Jeremiah Brandreth
Jeremiah Brandreth was an out-of-work stocking maker who lived in Sutton-in-Ashfield, Nottinghamshire, who was hanged for treason. He was known as "The Nottingham Captain"...
.) An agricultural variant of Luddism, centring on the breaking of threshing machines, was crucial to the widespread Swing Riots
Swing Riots
The Swing Riots were a widespread uprising by agricultural workers; it began with the destruction of threshing machines in the Elham Valley area of East Kent in the summer of 1830, and by early December had spread throughout the whole of southern England and East Anglia.As well as the attacks on...
of 1830 in southern and eastern England. Research by Kevin Binfield is particularly useful in placing the Luddite movement in historical context – as organised action by stockingers had occurred at various times since 1675, and the present action had to be seen in the context of the hardships suffered by the working class during the Napoleonic Wars.
"Machine breaking" (industrial sabotage
Sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening another entity through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. In a workplace setting, sabotage is the conscious withdrawal of efficiency generally directed at causing some change in workplace conditions. One who engages in sabotage is...
) was subsequently made a capital crime by the Frame Breaking Act, 52 Geo. 3, c. 16 and the Malicious Damage Act of 1812, 52 Geo. 3, c. 130 – legislation which was opposed by Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron, later George Gordon Noel, 6th Baron Byron, FRS , commonly known simply as Lord Byron, was a British poet and a leading figure in the Romantic movement...
, one of the few prominent defenders of the Luddites – and 17 men were executed after an 1813 trial in York
York
York is a walled city, situated at the confluence of the Rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. The city has a rich heritage and has provided the backdrop to major political events throughout much of its two millennia of existence...
. Many others were transported as prisoners
Penal transportation
Transportation or penal transportation is the deporting of convicted criminals to a penal colony. Examples include transportation by France to Devil's Island and by the UK to its colonies in the Americas, from the 1610s through the American Revolution in the 1770s, and then to Australia between...
to Australia. At one time, there were more British soldiers fighting the Luddites than Napoleon I
Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte was a French military and political leader during the latter stages of the French Revolution.As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1815...
on the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
. Three Luddites, led by George Mellor, ambushed and assassinated a mill owner (William Horsfall from Ottiwells Mill in Marsden
Marsden, West Yorkshire
Marsden is a large village within the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees, in West Yorkshire, England, west of Huddersfield and located at the confluence of the River Colne and the Wessenden Brook...
) at Crosland Moor
Crosland Moor
Crosland Moor is a district of the town of Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, England.It begins 1 mile to the south west of Huddersfield town centre. The electoral ward of Crosland Moor and Netherton, in the Colne Valley constituency...
, Huddersfield
Huddersfield
Huddersfield is a large market town within the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees, in West Yorkshire, England, situated halfway between Leeds and Manchester. It lies north of London, and south of Bradford, the nearest city....
, Mellor firing the shot to the groin which would prove fatal. Horsfall had remarked that he would "Ride up to his saddle in Luddite blood". The Luddites responsible were hanged in York, and shortly thereafter "Luddism" began to wane.
In contemporary thought
Many of the ideas that were encompassed within the Luddite Movement have been studied and evaluated in modern economics literature. The concept of "Skill Biased Technological Change" (SBTC) posits that technology contributes to the de-skilling of routine, manual tasks.In modern usage, "Luddite" is a term describing those opposed to industrialisation
Industrialisation
Industrialization is the process of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial one...
, automation
Automation
Automation is the use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods and services. In the scope of industrialization, automation is a step beyond mechanization...
, computerisation or new technologies
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
in general.
External links
- The Luddite Link - Comprehensive historical resources for the original West Yorkshire Luddites, University of Huddersfield.
- Is it O.K. to be a Luddite? by Thomas Pynchon
- Luddism and the Neo-Luddite Reaction by Martin Ryder, University of Colorado at Denver School of Education
- The Luddites and the Combination Acts from the Marxists Internet Archive

