
Lymphadenopathy
Encyclopedia
Lymphadenopathy is a term meaning "disease
of the lymph nodes." It is, however, almost synonymously used with "swollen/enlarged lymph nodes". It could be due to infection
, auto-immune disease, or malignancy.
Inflammation of a lymph node is called lymphadenitis. In practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made. (Inflammation of lymph channels is called lymphangitis
.)
Tangier disease (ABCA1 deficiency) may also cause this
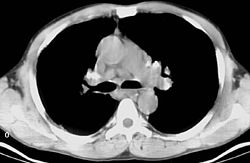 Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (BHL) is a radiographic
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (BHL) is a radiographic
term that describes the enlargement of mediastinal lymph
nodes. It is easily and most commonly identified by a chest x-ray
.
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
of the lymph nodes." It is, however, almost synonymously used with "swollen/enlarged lymph nodes". It could be due to infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, auto-immune disease, or malignancy.
Inflammation of a lymph node is called lymphadenitis. In practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made. (Inflammation of lymph channels is called lymphangitis
Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an inflammation of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. The most common cause of lymphangitis in humans is Streptococcus pyogenes...
.)
Types
- Localized lymphadenopathy : due to localized spot of infection e.g. an infected spot on the scalp will cause lymph nodes in the neck on that same side to swell up
- Generalized lymphadenopathyGeneralized lymphadenopathyLymph nodes or 'glands' or nodes or lymphoid tissue.are nodular bodies located throughout the body but clustering in certain areas such as the armpit, back of the neck and the groin. They are part of the lymphatic system....
: due to generalized infection all over the body e.g. influenza- persistent generalized lymphadenopathyPersistent generalized lymphadenopathyThe lymphatic system is part of the immune surveillance system. Blood contains fluid and blood cells. The fluid, which may contain suspended foreign material such as bacteria and viruses, seeps through blood vessel walls into the tissues, where it bathes the body cells and exchanges substances with...
(PGL) : persisting for a long time, possibly without an apparent cause
- persistent generalized lymphadenopathy
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathyDermatopathic lymphadenopathyIn pathology, dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, also dermatopathic lymphadenitis, is lymph node pathology due to skin disease.-Associations/differential diagnosis:*Cutaneous T cell lymphoma*Hodgkin's lymphoma*Melanoma- Diagnosis :...
: lymphadenopathy associated with skin disease.
Tangier disease (ABCA1 deficiency) may also cause this
Cause
Enlarged lymph nodes are a common symptom in a number of infectious and malignant diseases. It is a recognized symptom of many diseases, of which some are as follows:- Reactive: acute infectionInfectionAn infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
(e.g. bacterial, or viralVirusA virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
), or chronic infections (tuberculous lymphadenitisTuberculous lymphadenitisTuberculous lymphadenitis is a chronic specific granulomatous inflammation with caseation necrosis of the lymph node....
, cat-scratch disease).- The most distinctive symptom of bubonic plagueBubonic plaguePlague is a deadly infectious disease that is caused by the enterobacteria Yersinia pestis, named after the French-Swiss bacteriologist Alexandre Yersin. Primarily carried by rodents and spread to humans via fleas, the disease is notorious throughout history, due to the unrivaled scale of death...
is extreme swelling of one or more lymph nodes that bulge out of the skin as "buboes." The buboes often become necrotic and may even rupture. - Infectious mononucleosisInfectious mononucleosisInfectious mononucleosis is an infectious, widespread viral...
is an acute viral infection, the hallmark of which is marked enlargement of the cervical lymph nodesCervical lymph nodesCervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck.-Classification:There are approximately 300 lymph nodes in the neck, and they can be classified in many different ways.Henri Rouvière produced an influential classification in 1938...
. - It is also a symptom of cutaneous anthraxAnthraxAnthrax is an acute disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Most forms of the disease are lethal, and it affects both humans and other animals...
, measlesMeaslesMeasles, also known as rubeola or morbilli, is an infection of the respiratory system caused by a virus, specifically a paramyxovirus of the genus Morbillivirus. Morbilliviruses, like other paramyxoviruses, are enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses...
and Human African trypanosomiasis, the latter two giving lymphadenopathy in lymph nodes in the neck. - ToxoplasmosisToxoplasmosisToxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii. The parasite infects most genera of warm-blooded animals, including humans, but the primary host is the felid family. Animals are infected by eating infected meat, by ingestion of feces of a cat that has itself...
, a parasitic diseaseParasitic diseaseA parasitic disease is an infectious disease caused or transmitted by a parasite. Many parasites do not cause diseases. Parasitic diseases can affect practically all living organisms, including plants and mammals...
, gives a generalized lymphadenopathy (Piringer-Kuchinka lymphadenopathy). - Plasma cell variant of Castleman's diseaseCastleman's diseaseCastleman's disease is an uncommon lymphoproliferative disorder that can involve single lymph node stations or...
- associated with HHV-8 infection and HIVHIVHuman immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
infection. - Mesenteric lymphadenitis after viral systemic infection (particularly in the GALT in the appendix) can commonly present like appendicitis.
- The most distinctive symptom of bubonic plague
- Tumoral:
- Primary: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphomaNon-Hodgkin lymphomaThe non-Hodgkin lymphomas are a diverse group of blood cancers that include any kind of lymphoma except Hodgkin's lymphomas. Types of NHL vary significantly in their severity, from indolent to very aggressive....
give lymphadenopathy in all or a few lymph nodes. - Secondary: metastasisMetastasisMetastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
, Virchow's NodeVirchow's nodeVirchow's node is a lymph node in the left supraclavicular fossa . It takes its supply from lymph vessels in the abdominal cavity...
, NeuroblastomaNeuroblastomaNeuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid cancer in childhood and the most common cancer in infancy, with an annual incidence of about 650 cases per year in the US , and 100 cases per year in the UK . Close to 50 percent of neuroblastoma cases occur in children younger than two years old...
, and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
- Primary: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Autoimmune etiology: systemic lupus erythematosusSystemic lupus erythematosusSystemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage...
, rheumatoid arthritisRheumatoid arthritisRheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
all giving a generalized lymphadenopathy.
- Immunocompromised etiology: AIDSAIDSAcquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
. Generalized lymphadenopathy is an early sign of infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). "Lymphadenopathy syndrome" has been used to describe the first symptomatic stage of HIVHIVHuman immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
progression, preceding a diagnosis of AIDSAIDSAcquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
.
- Bites from certain venomous snakes, most notably the black mambaBlack mambaThe black mamba , also called the common black mamba or black-mouthed mamba, is the longest venomous snake in Africa, averaging around in length, and sometimes growing to lengths of...
, kraits, Australian brown snakesPseudonajaPseudonaja is a genus of venomous elapid snakes native to Australia. Members are known commonly as brown snakes and are considered to be one of the most dangerous snakes in the country; even young snakes are capable of delivering a fatal envenomation to a human.- Species :* Dugite or Spotted...
, coral snakeCoral snakeThe coral snakes are a large group of elapid snakes that can be subdivided into two distinct groups, Old World coral snakes and New World coral snakes...
s, tiger snakes, taipanTaipanThe taipans are a genus of large, fast, highly venomous Australasian snakes of the elapid family.-Overview:The taipan was named by Donald Thomson after the word used by the Wik-Mungkan Aboriginal people of central Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia.There are three known species: the coastal...
s, death adderAcanthophisAcanthophis is a genus of elapid snakes. Commonly called death adders, they are native to Australia, New Guinea and nearby islands, and are among the most venomous snakes in the world...
s, and some of the more toxic species of cobraCobraCobra is a venomous snake belonging to the family Elapidae. However, not all snakes commonly referred to as cobras are of the same genus, or even of the same family. The name is short for cobra capo or capa Snake, which is Portuguese for "snake with hood", or "hood-snake"...
.
- Unknown etiology: Kikuchi diseaseKikuchi diseaseKikuchi's disease, also known as histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis and Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, is a rare, non-cancerous enlargement of the lymph nodes....
, progressive transformation of germinal centresProgressive transformation of germinal centresProgressive transformation of germinal centres, abbreviated PTGCs and also progressive transformation of germinal centers, is a reactive lymph node process of undetermined etiology.-Symptoms:...
, sarcoidosisSarcoidosisSarcoidosis , also called sarcoid, Besnier-Boeck disease or Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease, is a disease in which abnormal collections of chronic inflammatory cells form as nodules in multiple organs. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown...
, hyaline-vascular variant of Castleman's diseaseCastleman's diseaseCastleman's disease is an uncommon lymphoproliferative disorder that can involve single lymph node stations or...
, Rosai-Dorfman diseaseRosai-Dorfman diseaseRosai–Dorfman disease, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare disorder of unknown etiology that is characterized by the overproduction of histiocytes, which accumulate in lymph nodes throughout the body. Lymphadenopathy of the neck is the most common place of...
, Kawasaki diseaseKawasaki diseaseKawasaki disease , also known as Kawasaki syndrome, lymph node syndrome and mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is an autoimmune disease in which the medium-sized blood vessels throughout the body become inflamed. It is largely seen in children under five years of age...
Benign (reactive) lymphadenopathy
There are three distinct patterns of benign lymphadenopathy:- Follicular hyperplasia - Seen in infections, autoimmune disorders, and nonspecific reactions.
- Paracortical hyperplasia - Seen in viral infections, skin diseases, and nonspecific reactions.
- Sinus histiocytosis - Seen in lymph nodes draining limbs, inflammatory lesions, and malignancies.
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy

Radiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
term that describes the enlargement of mediastinal lymph
Lymph
Lymph is considered a part of the interstitial fluid, the fluid which lies in the interstices of all body tissues. Interstitial fluid becomes lymph when it enters a lymph capillary...
nodes. It is easily and most commonly identified by a chest x-ray
Chest X-ray
In medicine, a chest radiograph, commonly called a chest X-ray , is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures...
.
Causes of BHL
The following are causes of BHL:- SarcoidosisSarcoidosisSarcoidosis , also called sarcoid, Besnier-Boeck disease or Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease, is a disease in which abnormal collections of chronic inflammatory cells form as nodules in multiple organs. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown...
- Infection
- TuberculosisTuberculosisTuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
- MycoplasmaMycoplasmaMycoplasma refers to a genus of bacteria that lack a cell wall. Without a cell wall, they are unaffected by many common antibiotics such as penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. They can be parasitic or saprotrophic. Several species are pathogenic in humans,...
- Intestinal Lipodystrophy (Whipple's Disease)
- Tuberculosis
- Malignancy
- LymphomaLymphomaLymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
- CarcinomaCarcinomaCarcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
- Mediastinal tumors
- Lymphoma
- Organic dust disease
- SilicosisSilicosisSilicosis, also known as Potter's rot, is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust, and is marked by inflammation and scarring in forms of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs...
- BerylliosisBerylliosisBerylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease , is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds. As an occupational lung disease, it is most classically associated with beryllium mining or manufacturing of fluorescent light bulbs...
- Silicosis
- Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- Such as bird fancier's lungBird fancier's lungBird fancier's lung is a type of hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by bird droppings. The lungs become inflamed with granuloma formation.Bird Fancier's Lung , also called bird-breeder's lung and pigeon-breeder's lung, is a subset of Hypersensitivity pneumonitis...
- Such as bird fancier's lung
- Less common causes also exist:
- Churg-Strauss syndromeChurg-Strauss syndromeChurg–Strauss syndrome is a medium and small vessel autoimmune vasculitis, leading to necrosis. It involves mainly the blood vessels of the lungs , gastrointestinal system, and peripheral nerves, but also affects the heart, skin and kidneys. It is a rare disease that is non-inheritable and...
- Human immunodeficiency virus
- Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- PneumoconiosisPneumoconiosisPneumoconiosis is an occupational lung disease and a restrictive lung disease caused by the inhalation of dust, often in mines.-Types:Depending upon the type of dust, the disease is given different names:...
- Adult-onset Still's diseaseAdult-onset Still's diseaseAdult-onset Still's disease is a rare form of inflammatory arthritis that was characterized by EG Bywaters in 1971. The underlying cause is unknown. It usually presents with high spiking fevers, joint and muscle pains, a salmon colored rash and other symptoms of systemic inflammation.- History...
- Churg-Strauss syndrome

