Lysis
Encyclopedia
Lysis refers to the breaking down of a cell, often by viral
, enzymic
, or osmotic
mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate".
Many species of bacteria
are subject to lysis by the enzyme lysozyme
, found in animal saliva
, egg white
, and other secretion
s. Phage lytic enzymes (lysins) produced during bacteriophage
infection are responsible for the ability of these viruses to lyse bacterial cells. Penicillin
and related β-lactam antibiotic
s cause the death of bacteria through enzyme-mediated lysis that occurs after the drug causes the bacterium to form a defective cell wall
. If cell wall is completely lost, the bacterium is referred as a protoplast
if penicillin was used on gram-positive bacteria, and spheroplast
when used on gram-negative bacteria.
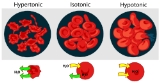
in a hypotonic environment (the surrounding fluid has a lower salt concentration than the cell interior). Cytolysis is caused by excessive osmosis
, or movement of water, towards the inside of a cell (hyperhydration). The cell membrane
cannot withstand the osmotic pressure
of the water inside, and so it explodes. Osmosis occurs from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential passing through a semipermeable membrane
, so these bursting cells are located in hypotonic environments.
Cytolysis can be prevented by several different mechanisms, including the contractile vacuole
that exists in some paramecia
which rapidly pump water out of the cell.
Cytolysis does not occur under normal conditions in plant cells because plant cells have a strong cell wall that contains the osmotic pressure, or turgor pressure, that would otherwise cause cytolysis to occur.
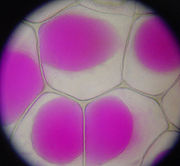
Plasmolysis is the contraction of cell
s within plants due to the loss of water through osmosis
. In a hypertonic environment, the cell membrane peels off of the cell wall
and the vacuole
collapses. These cells will eventually wilt and die unless the flow of water caused by osmosis can stop the contraction of the cell membrane
.
Erythrocytes' hemoglobin release free radicals in response to pathogens when lysed by them. This can damage the pathogens.
. Depending upon the detergent
used, either all or some membranes are lysed. For example, if the cell membrane
only is lysed then gradient centrifugation can be used to collect certain organelle
s.
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
, enzymic
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
, or osmotic
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate".
Many species of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
are subject to lysis by the enzyme lysozyme
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
, found in animal saliva
Saliva
Saliva , referred to in various contexts as spit, spittle, drivel, drool, or slobber, is the watery substance produced in the mouths of humans and most other animals. Saliva is a component of oral fluid. In mammals, saliva is produced in and secreted from the three pairs of major salivary glands,...
, egg white
Egg white
Egg white is the common name for the clear liquid contained within an egg. In chickens it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms around either fertilized or unfertilized egg yolks...
, and other secretion
Secretion
Secretion is the process of elaborating, releasing, and oozing chemicals, or a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast to excretion, the substance may have a certain function, rather than being a waste product...
s. Phage lytic enzymes (lysins) produced during bacteriophage
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage is any one of a number of viruses that infect bacteria. They do this by injecting genetic material, which they carry enclosed in an outer protein capsid...
infection are responsible for the ability of these viruses to lyse bacterial cells. Penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
and related β-lactam antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s cause the death of bacteria through enzyme-mediated lysis that occurs after the drug causes the bacterium to form a defective cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
. If cell wall is completely lost, the bacterium is referred as a protoplast
Protoplast
Protoplast, from the ancient Greek πρῶτον + verb πλάθω or πλάττω , initially referred to the first organized body of a species.Protoplast has several biological definitions:...
if penicillin was used on gram-positive bacteria, and spheroplast
Spheroplast
A spheroplast is a cell from which the cell wall has been almost completely removed, as by the action of penicillin. The name stems from the fact that after a microbe's cell wall is digested, membrane tension causes the cell to acquire a characteristic spherical shape...
when used on gram-negative bacteria.
Cytolysis
Cytolysis is the lysis of cellsCell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
in a hypotonic environment (the surrounding fluid has a lower salt concentration than the cell interior). Cytolysis is caused by excessive osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
, or movement of water, towards the inside of a cell (hyperhydration). The cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
cannot withstand the osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane....
of the water inside, and so it explodes. Osmosis occurs from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential passing through a semipermeable membrane
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
, so these bursting cells are located in hypotonic environments.
Cytolysis can be prevented by several different mechanisms, including the contractile vacuole
Contractile vacuole
A contractile vacuole is a sub-cellular structure involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists and in unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole....
that exists in some paramecia
Paramecium
Paramecium is a group of unicellular ciliate protozoa, which are commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group, and range from about 0.05 to 0.35 mm in length. Simple cilia cover the body, which allow the cell to move with a synchronous motion at speeds of approximately 12 body...
which rapidly pump water out of the cell.
Cytolysis does not occur under normal conditions in plant cells because plant cells have a strong cell wall that contains the osmotic pressure, or turgor pressure, that would otherwise cause cytolysis to occur.
Plasmolysis

Plasmolysis is the contraction of cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s within plants due to the loss of water through osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
. In a hypertonic environment, the cell membrane peels off of the cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
and the vacuole
Vacuole
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain...
collapses. These cells will eventually wilt and die unless the flow of water caused by osmosis can stop the contraction of the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
.
Immune response
- Main article: Red blood cell#Secondary functions
Erythrocytes' hemoglobin release free radicals in response to pathogens when lysed by them. This can damage the pathogens.
Applications
Cell lysis (splitting of cells) is used to break open cells when it is desirable to avoid shear forces that would denature or degrade sensitive macromolecules, such as proteins and DNA. For example, lysis is used in western and Southern blotting to analyze the composition of specific proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids individually or as complexesProtein complex
A multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. If the different polypeptide chains contain different protein domain, the resulting multiprotein complex can have multiple catalytic functions...
. Depending upon the detergent
Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with "cleaning properties in dilute solutions." In common usage, "detergent" refers to alkylbenzenesulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are less affected by hard water...
used, either all or some membranes are lysed. For example, if the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
only is lysed then gradient centrifugation can be used to collect certain organelle
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
s.

