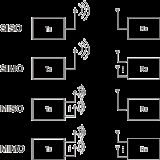
MIMO
Encyclopedia
In radio
, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (commonly pronounced my-moh or me-moh), is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna
technology. Note that the terms input and output refer to the radio channel
carrying the signal, not to the devices having antennas.
MIMO technology has attracted attention in wireless
communications, because it offers significant increases in data throughput and link range without additional bandwidth, though extra transmit power is needed since multiple transmit antennas are employed instead of only one as in SISO systems. It achieves this by higher spectral efficiency (more bits per second per hertz of bandwidth) and link reliability or diversity (reduced fading
). Because of these properties, MIMO is an important part of modern wireless communication standards such as IEEE 802.11n
(Wifi), 4G
, 3GPP Long Term Evolution
, WiMAX
and HSPA+
.
published several papers on beamforming
related applications in 1984 and 1986.
and Thomas Kailath
proposed the concept of spatial multiplexing
(SM) using MIMO in 1993. Their US Patent No. 5,345,599 on Spatial Multiplexing issued 1994 emphasized applications to wireless broadcast.
In 1996, Greg Raleigh and Gerard J. Foschini
refined new approaches to MIMO technology, considering a configuration where multiple transmit antennas are co-located at one transmitter to improve the link throughput effectively.
Bell Labs was the first to demonstrate a laboratory prototype of spatial multiplexing in 1998, where spatial multiplexing is a principal technology to improve the performance of MIMO communication systems.
had developed an IEEE 802.11n
precursor implementation based on their patents on MIMO. Following that in 2006, several companies (including at least Broadcom
, Intel
, and Marvell
) have fielded a MIMO-OFDM solution based on a pre-standard for 802.11n WiFi standard. Also in 2006, several companies (Beceem Communications, Samsung, Runcom Technologies, etc.) have developed MIMO-OFDMA based solutions for IEEE 802.16
e WiMAX broadband mobile standard. All upcoming 4G
systems will also employ MIMO technology. Several research groups have demonstrated over 1 Gbit/s prototypes.
, spatial multiplexing
or SM, and diversity coding
.
Precoding
is multi-stream beamforming
, in the narrowest definition. In more general terms, it is considered to be all spatial processing that occurs at the transmitter. In (single-layer) beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate phase (and sometimes gain) weighting such that the signal power is maximized at the receiver input. The benefits of beamforming are to increase the received signal gain, by making signals emitted from different antennas add up constructively, and to reduce the multipath fading effect. In the absence of scattering, beamforming results in a well defined directional pattern, but in typical cellular conventional beams are not a good analogy. When the receiver has multiple antennas, the transmit beamforming cannot simultaneously maximize the signal level at all of the receive antennas, and precoding with multiple streams is used. Note that precoding requires knowledge of channel state information
(CSI) at the transmitter.
Spatial multiplexing
requires MIMO antenna configuration. In spatial multiplexing, a high rate signal is split into multiple lower rate streams and each stream is transmitted from a different transmit antenna in the same frequency channel. If these signals arrive at the receiver antenna array with sufficiently different spatial signatures, the receiver can separate these streams into (almost) parallel channels. Spatial multiplexing is a very powerful technique for increasing channel capacity at higher signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The maximum number of spatial streams is limited by the lesser in the number of antennas at the transmitter or receiver. Spatial multiplexing can be used with or without transmit channel knowledge. Spatial multiplexing can also be used for simultaneous transmission to multiple receivers, known as space-division multiple access
. By scheduling receivers with different spatial signatures, good separability can be assured.
Diversity Coding
techniques are used when there is no channel knowledge
at the transmitter. In diversity methods, a single stream (unlike multiple streams in spatial multiplexing) is transmitted, but the signal is coded using techniques called space-time coding. The signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with full or near orthogonal coding. Diversity coding exploits the independent fading in the multiple antenna links to enhance signal diversity. Because there is no channel knowledge, there is no beamforming or array gain
from diversity coding.
Spatial multiplexing can also be combined with precoding when the channel is known at the transmitter or combined with diversity coding when decoding reliability is in trade-off.
(OFDM) or with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) modulation, where the problems created by multi-path channel are handled efficiently. The IEEE 802.16e standard incorporates MIMO-OFDMA. The IEEE 802.11n standard, released in October 2009, recommends MIMO-OFDM.
MIMO is also planned to be used in Mobile radio telephone standards such as recent 3GPP
and 3GPP2 standards. In 3GPP, High-Speed Packet Access plus (HSPA+) and Long Term Evolution (LTE)
standards take MIMO into account. Moreover, to fully support cellular environments MIMO research consortia including IST-MASCOT propose to develop advanced MIMO techniques, i.e., multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO)
.
MIMO technology can be used in non-wireless communications systems. One example is the home networking standard ITU-T
G.9963
, which defines a powerline communications system that uses MIMO techniques to transmit multiple signals over multiple AC wires (phase, neutral and ground).
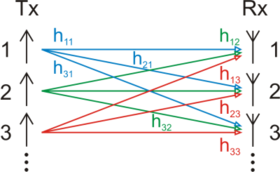 In MIMO systems, a transmitter sends multiple streams by multiple transmit antennas. The transmit streams go through a matrix
In MIMO systems, a transmitter sends multiple streams by multiple transmit antennas. The transmit streams go through a matrix
channel which consists of all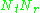 paths between the
paths between the  transmit antennas at the transmitter and
transmit antennas at the transmitter and 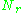 receive antennas at the receiver. Then, the receiver gets the received signal vectors
receive antennas at the receiver. Then, the receiver gets the received signal vectors
by the multiple receive antennas and decodes the received signal vectors into the original information. A narrowband
flat fading MIMO system is modelled as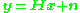
where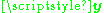 and
and 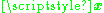 are the receive and transmit vectors, respectively, and
are the receive and transmit vectors, respectively, and 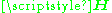 and
and 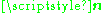 are the channel matrix and the noise vector, respectively.
are the channel matrix and the noise vector, respectively.
Referring to information theory
, the ergodic channel capacity
of MIMO systems where both the transmitter and the receiver have perfect instantaneous channel state information
is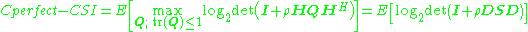
where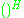 denotes Hermitian transpose
denotes Hermitian transpose
and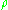 is the ratio between transmit power and noise power (i.e., transmit SNR
is the ratio between transmit power and noise power (i.e., transmit SNR
). The optimal signal covariance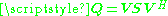 is achieved through singular value decomposition
is achieved through singular value decomposition
of the channel matrix and an optimal diagonal power allocation matrix
and an optimal diagonal power allocation matrix 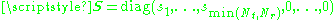 . The optimal power allocation is achieved through waterfilling, that is
. The optimal power allocation is achieved through waterfilling, that is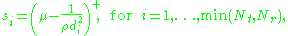
where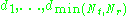 are the diagonal elements of
are the diagonal elements of 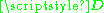 ,
, 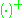 is zero if its argument is negative, and
is zero if its argument is negative, and 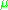 is selected such that
is selected such that  .
.
If the transmitter has only statistical channel state information
, then the ergodic channel capacity
will decrease as the signal covariance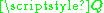 can only be optimized in terms of the average mutual information
can only be optimized in terms of the average mutual information
as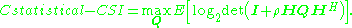
The spatial correlation
of the channel have a strong impact on the ergodic channel capacity
with statistical information.
If the transmitter has no channel state information
it can select the signal covariance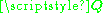 to maximize channel capacity under worst-case statistics, which means
to maximize channel capacity under worst-case statistics, which means 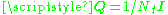 and accordingly
and accordingly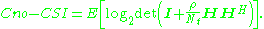
Depending on the statistical properties of the channel, the ergodic capacity is no greater than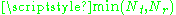 times larger than that of a SISO system.
times larger than that of a SISO system.
Knowing the quality of the signal channel is also critical. A channel emulator
can simulate how a device performs at the cell edge, can add noise or can simulate what the channel looks like at speed. To fully qualify the performance of a receiver, a calibrated transmitter, such as a vector signal generator (VSG), and channel emulator can be used to test the receiver under a variety of different conditions. Conversely, the transmitter's performance under a number of different conditions can be verified using a channel emulator and a calibrated receiver, such as a vector signal analyzer
(VSA).
Understanding the channel allows for manipulation of the phase and amplitude of each transmitter in order to form a beam. To correctly form a beam, the transmitter needs to understand the characteristics of the channel. This process is called channel sounding or channel estimation. A known signal is sent to the mobile device that enables it to build a picture of the channel environment. The phone then sends back the channel characteristics to the transmitter. The transmitter then can apply the correct phase and amplitude adjustments to form a beam directed at the mobile device. This is called a closed-loop MIMO system. For beamforming
, it is required to adjust the phases and amplitude of each transmitter. In a beamformer optimized for spatial diversity or spatial multiplexing, each antenna element simultaneously transmits a weighted combination of two data symbols.
(a theoretical upper bound on system throughput) for a MIMO system is increased as the number of antennas is increased, proportional to the minimum number of transmit and receive antennas. This basic finding in information theory
is what led to a spurt of research in this area. A text book by A. Paulraj, R. Nabar and D. Gore has published an introduction to this area. Mobile Experts has published a research report which predicts the use of MIMO technology in 500 million PCs, tablets, and smartphones by 2016. link
.
.
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (commonly pronounced my-moh or me-moh), is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna
Smart antenna
Smart antennas are antenna arrays with smart signal processing algorithms used to identify spatial signal signature such as the direction of arrival of the signal, and use it to calculate beamforming vectors, to track and locate the antenna beam on the mobile/target...
technology. Note that the terms input and output refer to the radio channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
carrying the signal, not to the devices having antennas.
MIMO technology has attracted attention in wireless
Wireless
Wireless telecommunications is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not physically connected. Distances can be short, such as a few meters for television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications...
communications, because it offers significant increases in data throughput and link range without additional bandwidth, though extra transmit power is needed since multiple transmit antennas are employed instead of only one as in SISO systems. It achieves this by higher spectral efficiency (more bits per second per hertz of bandwidth) and link reliability or diversity (reduced fading
Fading
In wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
). Because of these properties, MIMO is an important part of modern wireless communication standards such as IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n-2009 is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard to improve network throughput over the two previous standards—802.11a and 802.11g—with a significant increase in the maximum net data rate from 54 Mbit/s to 600 Mbit/s with the use of four...
(Wifi), 4G
4G
In telecommunications, 4G is the fourth generation of cellular wireless standards. It is a successor to the 3G and 2G families of standards. In 2009, the ITU-R organization specified the IMT-Advanced requirements for 4G standards, setting peak speed requirements for 4G service at 100 Mbit/s...
, 3GPP Long Term Evolution
3GPP Long Term Evolution
3GPP Long Term Evolution, usually referred to as LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals. It is based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA network technologies, increasing the capacity and speed using new modulation techniques...
, WiMAX
WiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
and HSPA+
Evolved HSPA
HSPA+, or Evolved High-Speed Packet Access, is a technical standard for wireless, broadband telecommunication. HSPA+ was first defined in the technical standard 3GPP release 7....
.
Background technologies
The earliest ideas in this field go back to work by A.R. Kaye and D.A. George (1970) and W. van Etten (1975, 1976). Jack Winters and Jack Salz at Bell LaboratoriesBell Labs
Bell Laboratories is the research and development subsidiary of the French-owned Alcatel-Lucent and previously of the American Telephone & Telegraph Company , half-owned through its Western Electric manufacturing subsidiary.Bell Laboratories operates its...
published several papers on beamforming
Beamforming
Beamforming is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in the array in a way where signals at particular angles experience constructive interference and while others experience destructive...
related applications in 1984 and 1986.
Principle
Arogyaswami PaulrajArogyaswami Paulraj
Prof. Arogyaswami Paulraj was born in Pollachi near Coimbatore, India. He joined the Indian Navy at age 15 through the National Defence Academy, Kharakvalsa and served the Navy for 30 years. He is currently a Professor Emeritus at the Dept. of Elect. Engineering, Stanford University...
and Thomas Kailath
Thomas Kailath
Thomas Kailath is an Indian electrical engineer, information theorist, control engineer, entrepreneur and the Hitachi America Professor of Engineering, Emeritus, at Stanford University...
proposed the concept of spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
(SM) using MIMO in 1993. Their US Patent No. 5,345,599 on Spatial Multiplexing issued 1994 emphasized applications to wireless broadcast.
In 1996, Greg Raleigh and Gerard J. Foschini
Gerard J. Foschini
Gerard Joseph Foschini , is an American telecommunications engineer who has worked for Bell Laboratories since 1961. His research has covered many kinds of data communications, particularly wireless communications and optical communications. Foschini has also worked on point-to-point systems and...
refined new approaches to MIMO technology, considering a configuration where multiple transmit antennas are co-located at one transmitter to improve the link throughput effectively.
Bell Labs was the first to demonstrate a laboratory prototype of spatial multiplexing in 1998, where spatial multiplexing is a principal technology to improve the performance of MIMO communication systems.
Wireless standards
In the commercial arena, Iospan Wireless Inc. developed the first commercial system in 2001 that used MIMO with Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access technology (MIMO-OFDMA). Iospan technology supported both diversity coding and spatial multiplexing. In 2005, Airgo NetworksAirgo Networks
Airgo Networks , is a Palo Alto, California-based company specializing in the development of multiple-input multiple-output wireless technology. Founded in 2001, Airgo is a lead proponent of the 802.11n standard....
had developed an IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n-2009 is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard to improve network throughput over the two previous standards—802.11a and 802.11g—with a significant increase in the maximum net data rate from 54 Mbit/s to 600 Mbit/s with the use of four...
precursor implementation based on their patents on MIMO. Following that in 2006, several companies (including at least Broadcom
Broadcom
Broadcom Corporation is a fabless semiconductor company in the wireless and broadband communication business. The company is headquartered in Irvine, California, USA. Broadcom was founded by a professor-student pair Henry Samueli and Henry T. Nicholas III from the University of California, Los...
, Intel
Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation is an American multinational semiconductor chip maker corporation headquartered in Santa Clara, California, United States and the world's largest semiconductor chip maker, based on revenue. It is the inventor of the x86 series of microprocessors, the processors found in most...
, and Marvell
Marvell Technology Group
Marvell is an American producer of storage, communications and consumer semiconductor products.Founded in 1995, Marvell Technology Group Ltd. has operations worldwide and approximately 5,700 employees. Marvell’s U.S. operating subsidiary is based in Santa Clara, California and Marvell has...
) have fielded a MIMO-OFDM solution based on a pre-standard for 802.11n WiFi standard. Also in 2006, several companies (Beceem Communications, Samsung, Runcom Technologies, etc.) have developed MIMO-OFDMA based solutions for IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16 is a series of Wireless Broadband standards authored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . The IEEE Standards Board in established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks...
e WiMAX broadband mobile standard. All upcoming 4G
4G
In telecommunications, 4G is the fourth generation of cellular wireless standards. It is a successor to the 3G and 2G families of standards. In 2009, the ITU-R organization specified the IMT-Advanced requirements for 4G standards, setting peak speed requirements for 4G service at 100 Mbit/s...
systems will also employ MIMO technology. Several research groups have demonstrated over 1 Gbit/s prototypes.
Functions of MIMO
MIMO can be sub-divided into three main categories, precodingPrecoding
Precoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
, spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
or SM, and diversity coding
Diversity Coding
Diversity coding is a particular technique for antenna diversity and is implemented by space–time coding....
.
Precoding
Precoding
Precoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
is multi-stream beamforming
Beamforming
Beamforming is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in the array in a way where signals at particular angles experience constructive interference and while others experience destructive...
, in the narrowest definition. In more general terms, it is considered to be all spatial processing that occurs at the transmitter. In (single-layer) beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate phase (and sometimes gain) weighting such that the signal power is maximized at the receiver input. The benefits of beamforming are to increase the received signal gain, by making signals emitted from different antennas add up constructively, and to reduce the multipath fading effect. In the absence of scattering, beamforming results in a well defined directional pattern, but in typical cellular conventional beams are not a good analogy. When the receiver has multiple antennas, the transmit beamforming cannot simultaneously maximize the signal level at all of the receive antennas, and precoding with multiple streams is used. Note that precoding requires knowledge of channel state information
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
(CSI) at the transmitter.
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
requires MIMO antenna configuration. In spatial multiplexing, a high rate signal is split into multiple lower rate streams and each stream is transmitted from a different transmit antenna in the same frequency channel. If these signals arrive at the receiver antenna array with sufficiently different spatial signatures, the receiver can separate these streams into (almost) parallel channels. Spatial multiplexing is a very powerful technique for increasing channel capacity at higher signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The maximum number of spatial streams is limited by the lesser in the number of antennas at the transmitter or receiver. Spatial multiplexing can be used with or without transmit channel knowledge. Spatial multiplexing can also be used for simultaneous transmission to multiple receivers, known as space-division multiple access
Space-division multiple access
Space-Division Multiple Access is a channel access method based on creating parallel spatial pipes next to higher capacity pipes through spatial multiplexing and/or diversity, by which it is able to offer superior performance in radio multiple access communication systems...
. By scheduling receivers with different spatial signatures, good separability can be assured.
Diversity Coding
Diversity Coding
Diversity coding is a particular technique for antenna diversity and is implemented by space–time coding....
techniques are used when there is no channel knowledge
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
at the transmitter. In diversity methods, a single stream (unlike multiple streams in spatial multiplexing) is transmitted, but the signal is coded using techniques called space-time coding. The signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with full or near orthogonal coding. Diversity coding exploits the independent fading in the multiple antenna links to enhance signal diversity. Because there is no channel knowledge, there is no beamforming or array gain
Array gain
In MIMO communication systems, array gain means a power gain of transmitted signals that is achieved by using multiple-antennas at transmitter and/or receiver, with respect to SISO case. It can be simply called power gain. In a broadside array, the array gain is almost exactly proportional to the...
from diversity coding.
Spatial multiplexing can also be combined with precoding when the channel is known at the transmitter or combined with diversity coding when decoding reliability is in trade-off.
Multi-antenna types
Multi-antenna MIMO (or Single user MIMO) technology has been developed and implemented in some standards, e.g. 802.11n products.- SISO/SIMO/MISO are degenerateDegeneracy (mathematics)In mathematics, a degenerate case is a limiting case in which a class of object changes its nature so as to belong to another, usually simpler, class....
cases of MIMO- Multiple-input and single-output (MISO) is a degenerate case when the receiver has a single antenna.
- Single-input and multiple-output (SIMO) is a degenerate case when the transmitter has a single antenna.
- single-input single-output (SISO) is a radio system where neither the transmitter nor receiver have multiple antenna.
- Principal single-user MIMO techniques
- Bell Laboratories Layered Space-Time (BLAST)Bell Laboratories Layered Space-TimeBell Laboratories Layered Space-Time is a transceiver architecture for offering spatial multiplexing over multiple-antenna wireless communication systems. Such systems have multiple antennas at both the transmitter and the receiver in an effort to exploit the many different paths between the two...
, Gerard. J. Foschini (1996) - Per Antenna Rate Control (PARC), Varanasi, Guess (1998), Chung, Huang, Lozano (2001)
- Selective Per Antenna Rate Control (SPARC), Ericsson (2004)
- Bell Laboratories Layered Space-Time (BLAST)
- Some limitations
- The physical antenna spacing are selected to be large; multiple wavelengths at the base station. The antenna separation at the receiver is heavily space constrained in hand sets, though advanced antenna design and algorithm techniques are under discussion. Refer to: Advanced MIMO
Multi-user types
Recently, the research on multi-user MIMO technology has been emerging. While full multi-user MIMO (or network MIMO) can have higher potentials, from its practicality the research on (partial) multi-user MIMO (or multi-user and multi-antenna MIMO) technology is more active.- Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO)Multi-user MIMOIn radio, multi-user MIMO is a set of advanced MIMO, multiple-input and multiple-output , technologies that exploit the availability of multiple independent radio terminals in order to enhance the communication capabilities of each individual terminal...
- In recent 3GPP3GPPThe 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations, known as the Organizational Partners...
and WiMAXWiMAXWiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
standards, MU-MIMO is being treated as one of candidate technologies adoptable in the specification by a lot of companies including Samsung, Intel, Qualcomm, Ericsson, TI, Huawei, Philips, Alcatel-Lucent, Freescale, et al. since MU-MIMO is more feasible to low complexity mobiles with small number of reception antennas than SU-MIMO with the high system throughput capability. - PU2RCPU2RCPer-User Unitary Rate Control is the advanced multi-user MIMO technique which utilizes the concept of both pre-coding matrices and scheduling to enhance the system performance of multiple antenna wireless networks....
allows the network to allocate each antenna to the different users instead of allocating only single user as in single-user MIMO scheduling. The network can transmit user data through a codebook-based spatial beam or a virtual antenna. Efficient user scheduling, such as pairing spatially distinguishable users with codebook based spatial beams, are additionally discussed for the simplification of wireless networks in terms of additional wireless resource requirements and complex protocol modification. Recently, PU2RC is included the system description documentation (SDD) of IEEE 802.16m (WiMAX evolution to meet the ITU-R's IMT-Advance requirements). - Enhanced multiuser MIMO: 1)Employ advanced decoding techniques, 2) Employ advanced precoding techniques
- SDMA represents either space-division multiple accessSpace-division multiple accessSpace-Division Multiple Access is a channel access method based on creating parallel spatial pipes next to higher capacity pipes through spatial multiplexing and/or diversity, by which it is able to offer superior performance in radio multiple access communication systems...
or super-division multiple access where super emphasises that orthogonal division such as frequency and time division is not used but non-orthogonal approaches such as super-position coding are used.
- In recent 3GPP
- Cooperative MIMO (CO-MIMO)
- Utilizes distributed antennas which belong to other users.
- MIMO RoutingRoutingRouting is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network , electronic data networks , and transportation networks...
- Routing a cluster by a cluster in each hop, where the number of nodes in each cluster is larger or equal to one. MIMO routing is different from conventional (SISO) routing since conventional routing protocols route a node by a node in each hop.
Applications of MIMO
Spatial multiplexing techniques makes the receivers very complex, and therefore it is typically combined with Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexingOrthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
(OFDM) or with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) modulation, where the problems created by multi-path channel are handled efficiently. The IEEE 802.16e standard incorporates MIMO-OFDMA. The IEEE 802.11n standard, released in October 2009, recommends MIMO-OFDM.
MIMO is also planned to be used in Mobile radio telephone standards such as recent 3GPP
3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations, known as the Organizational Partners...
and 3GPP2 standards. In 3GPP, High-Speed Packet Access plus (HSPA+) and Long Term Evolution (LTE)
3GPP Long Term Evolution
3GPP Long Term Evolution, usually referred to as LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals. It is based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA network technologies, increasing the capacity and speed using new modulation techniques...
standards take MIMO into account. Moreover, to fully support cellular environments MIMO research consortia including IST-MASCOT propose to develop advanced MIMO techniques, i.e., multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO)
Multi-user MIMO
In radio, multi-user MIMO is a set of advanced MIMO, multiple-input and multiple-output , technologies that exploit the availability of multiple independent radio terminals in order to enhance the communication capabilities of each individual terminal...
.
MIMO technology can be used in non-wireless communications systems. One example is the home networking standard ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
G.9963
G.9963
Recommendation G.9963 is a home networking standard under development at ITU-T.It was begun in 2010 by ITU-T to add multiple-input and multiple-output capabilities to the G.hn standard originally defined in Recommendation G.9960. The standard is also known as "G.hn-mimo".As part of the family of...
, which defines a powerline communications system that uses MIMO techniques to transmit multiple signals over multiple AC wires (phase, neutral and ground).
Mathematical description

Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
channel which consists of all
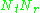 paths between the
paths between the  transmit antennas at the transmitter and
transmit antennas at the transmitter and 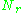 receive antennas at the receiver. Then, the receiver gets the received signal vectors
receive antennas at the receiver. Then, the receiver gets the received signal vectorsVector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
by the multiple receive antennas and decodes the received signal vectors into the original information. A narrowband
Narrowband
In radio, narrowband describes a channel in which the bandwidth of the message does not significantly exceed the channel's coherence bandwidth. It is a common misconception that narrowband refers to a channel which occupies only a "small" amount of space on the radio spectrum.The opposite of...
flat fading MIMO system is modelled as
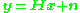
where
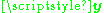 and
and 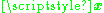 are the receive and transmit vectors, respectively, and
are the receive and transmit vectors, respectively, and 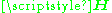 and
and 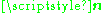 are the channel matrix and the noise vector, respectively.
are the channel matrix and the noise vector, respectively.Referring to information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
, the ergodic channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
of MIMO systems where both the transmitter and the receiver have perfect instantaneous channel state information
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
is
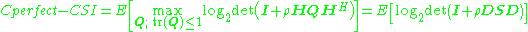
where
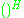 denotes Hermitian transpose
denotes Hermitian transposeConjugate transpose
In mathematics, the conjugate transpose, Hermitian transpose, Hermitian conjugate, or adjoint matrix of an m-by-n matrix A with complex entries is the n-by-m matrix A* obtained from A by taking the transpose and then taking the complex conjugate of each entry...
and
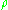 is the ratio between transmit power and noise power (i.e., transmit SNR
is the ratio between transmit power and noise power (i.e., transmit SNRSignal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
). The optimal signal covariance
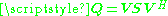 is achieved through singular value decomposition
is achieved through singular value decompositionSingular value decomposition
In linear algebra, the singular value decomposition is a factorization of a real or complex matrix, with many useful applications in signal processing and statistics....
of the channel matrix
 and an optimal diagonal power allocation matrix
and an optimal diagonal power allocation matrix 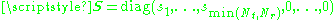 . The optimal power allocation is achieved through waterfilling, that is
. The optimal power allocation is achieved through waterfilling, that is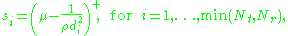
where
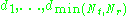 are the diagonal elements of
are the diagonal elements of  ,
, 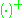 is zero if its argument is negative, and
is zero if its argument is negative, and 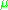 is selected such that
is selected such that  .
.If the transmitter has only statistical channel state information
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
, then the ergodic channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
will decrease as the signal covariance
 can only be optimized in terms of the average mutual information
can only be optimized in terms of the average mutual informationMutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
as
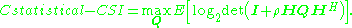
The spatial correlation
Spatial Correlation
Theoretically, the performance of wireless communication systems can be improved by having multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver. The idea is that if the propagation channels between each pair of transmit and receive antennas are statistically independent and identically...
of the channel have a strong impact on the ergodic channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
with statistical information.
If the transmitter has no channel state information
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
it can select the signal covariance
 to maximize channel capacity under worst-case statistics, which means
to maximize channel capacity under worst-case statistics, which means 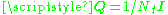 and accordingly
and accordingly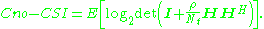
Depending on the statistical properties of the channel, the ergodic capacity is no greater than
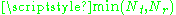 times larger than that of a SISO system.
times larger than that of a SISO system.MIMO testing
MIMO signal testing focuses first on the transmitter/receiver system. The random phases of the sub-carrier signals can produce instantaneous power levels that cause the amplifier to compress, momentarily causing distortion and ultimately symbol errors. Signals with a high PAR (peak-to-average ratio) can cause amplifiers to compress unpredictably during transmission. OFDM signals are very dynamic and compression problems can be hard to detect because of their noise-like nature.Knowing the quality of the signal channel is also critical. A channel emulator
Radio channel emulator
Radio channel emulators or radio channel simulators are tools for air interface testing in wireless communication. In a test environment, radio channel emulators replace the real-world radio channel between a radio transmitter and a receiver by providing a faded representation of a transmitted...
can simulate how a device performs at the cell edge, can add noise or can simulate what the channel looks like at speed. To fully qualify the performance of a receiver, a calibrated transmitter, such as a vector signal generator (VSG), and channel emulator can be used to test the receiver under a variety of different conditions. Conversely, the transmitter's performance under a number of different conditions can be verified using a channel emulator and a calibrated receiver, such as a vector signal analyzer
Vector signal analyzer
A vector signal analyzer is an instrument that measures the magnitude and phase of the input signal at a single frequency within the IF bandwidth of the instrument...
(VSA).
Understanding the channel allows for manipulation of the phase and amplitude of each transmitter in order to form a beam. To correctly form a beam, the transmitter needs to understand the characteristics of the channel. This process is called channel sounding or channel estimation. A known signal is sent to the mobile device that enables it to build a picture of the channel environment. The phone then sends back the channel characteristics to the transmitter. The transmitter then can apply the correct phase and amplitude adjustments to form a beam directed at the mobile device. This is called a closed-loop MIMO system. For beamforming
Beamforming
Beamforming is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in the array in a way where signals at particular angles experience constructive interference and while others experience destructive...
, it is required to adjust the phases and amplitude of each transmitter. In a beamformer optimized for spatial diversity or spatial multiplexing, each antenna element simultaneously transmits a weighted combination of two data symbols.
Principal researches
Papers by Gerard J. Foschini and Michael J. Gans, Foschini and Emre Telatar have shown that the channel capacityChannel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
(a theoretical upper bound on system throughput) for a MIMO system is increased as the number of antennas is increased, proportional to the minimum number of transmit and receive antennas. This basic finding in information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
is what led to a spurt of research in this area. A text book by A. Paulraj, R. Nabar and D. Gore has published an introduction to this area. Mobile Experts has published a research report which predicts the use of MIMO technology in 500 million PCs, tablets, and smartphones by 2016. link
Diversity-multiplexing tradeoff (DMT)
There exists a fundamental tradeoff between diversity and multiplexing in a MIMO system (Zheng and Tse, 2003).
Other applications
Given the nature of MIMO, it is not limited to wireless communication. It can be used for wire line communication as well. For example, a new type of DSL technology (Gigabit DSL) has been proposed based on Binder MIMO Channels.Sampling theorem in MIMO systems
An important question which attracts the attention of engineers and mathematician is how to use the multi-output signals at the receiver to recover the multi-input signals at the transmitter. In Shang, Sun and Zhou (2007), sufficient and necessary conditions are established to guarantee the complete recovery of the multi-input signals..
See also
- Channel bondingChannel bondingChannel bonding is a computer networking arrangement in which two or more network interfaces on a host computer are combined for redundancy or increased throughput....
- Mimax
- Single-frequency networkSingle-frequency networkA single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
(SFN) - WiMAX MIMOWiMAX MIMOWiMAX MIMO refers to the use of Multiple-input multiple-output communications technology on WiMAX, which is the technology brand name for the implementation of the standard IEEE 802.16.-WiMAX:...
- wifiWIFIWIFI is a radio station broadcasting a brokered format. Licensed to Florence, New Jersey, USA, the station is currently operated by Florence Broadcasting Partners, LLC.This station was previously owned by Real Life Broadcasting...
Spatial techniques
- Antenna diversityAntenna diversityAntenna diversity, also known as space diversity, is any one of several wireless diversity schemes that uses two or more antennas to improve the quality and reliability of a wireless link. Often, especially in urban and indoor environments, there is no clear line-of-sight between transmitter and...
- BeamformingBeamformingBeamforming is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in the array in a way where signals at particular angles experience constructive interference and while others experience destructive...
- Channel state informationChannel state informationIn wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
- Dirty paper coding (DPC)
- PrecodingPrecodingPrecoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
- Space–time block codeSpace–time block codeSpace–time block coding is a technique used in wireless communications to transmit multiple copies of a data stream across a number of antennas and to exploit the various received versions of the data to improve the reliability of data-transfer...
- Space–time codeSpace–time codeA space–time code is a method employed to improve the reliability of data transmission in wireless communication systems using multiple transmit antennas...
- Spatial multiplexingSpatial multiplexingSpatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
- Multi-user MIMOMulti-user MIMOIn radio, multi-user MIMO is a set of advanced MIMO, multiple-input and multiple-output , technologies that exploit the availability of multiple independent radio terminals in order to enhance the communication capabilities of each individual terminal...
- 802.11
- 802.16
Web sites
- GEDOMIS® (GEneric hardware DemOnstrator for MIMO Systems)
- NIST UWB-MIMO Channel Propagation Measurements in the 2-8 GHz Spectrum
- D. Gesbert, M. Kountouris, R. W. Heath, Jr., C.-B. Chae, and T. Salzer, Shifting the MIMO Paradigm: From Single User to Multiuser Communications, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 36–46, Oct., 2007
- Links to suggested readings in MIMO - WCSP Group — University of South Florida (USF)
- Introduction to Wireless MIMO - Theory and Applications
- Introduction to Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (covers OFDM and MIMO radio configurations)
- Introduction to MIMO
- Computerworld QuickStudy MIMO
- Developing Strategies for MIMO Testing
- Meeting The Test Challenges Of 4G LTE
- The Basics Of OFDM
- MIMO: The Future Of Wireless: Test Challenges For WiMAX, HSPA+, And LTE
- OFDM Will Soon Be Dominant Form Of Digital Modulation
- The challenges of moving to MIMO systems
- RF test system tackles 4 x 4 MIMO signals
- Increasing Mobile Systems Raises RF Test Throughput Issues
- The Role Of EVM Measurements In Characterizing Amplifier Modulation Performance
- Industry Views: 4G Systems Bring New Design And Testing Challenges
- Test System Pushes MIMO Standards Into The Spotlight
- Instruments test MIMO data transmissions
- Literature review of MIMO
Books
- Claude Oestges, Bruno Clerckx, "MIMO Wireless Communications : From Real-world Propagation to Space-time Code Design," Academic, 2007.07.16, 448p, ISBN : 0123725356

