
Spatial Correlation
Encyclopedia
Theoretically, the performance of wireless communication systems can be improved by having multiple antennas
at the transmitter and the receiver. The idea is that if the propagation channel
s between each pair of transmit and receive antennas are statistically independent and identically distributed, then multiple independent channels with identical characteristics can be created by precoding
and be used for either transmitting multiple data streams
or increasing the reliability
(in terms of bit error rate). In practice, the channels between different antennas are often correlated and therefore the potential multi-antenna gains may not always be obtainable. This is called spatial correlation as it can be interpreted as a correlation between a signal's spatial direction and the average received signal gain.
between the transmitter and receiver that represents clear spatial channel characteristics. In urban cellular systems, this is seldom the case as base stations
are located on rooftops while many users are located either indoors or at streets far from base stations. Thus, there is a non-line-of-sight multipath propagation channel between base stations and users, describing how the signal is reflected at different obstacles on its way from the transmitter to the receiver. However, the received signal may still have a strong spatial signature in the sense that stronger average signal gains are received from certain spatial directions.
Spatial correlation means that there is a correlation between the received average signal gain and the angle of arrival
of a signal.
Rich multipath propagation decreases the spatial correlation by spreading the signal such that multipath components are received from many different spatial directions. Short antenna separations increase the spatial correlation as adjacent antennas will receive similar signal components. The existence of spatial correlation has been experimentally validated.
Spatial correlation is often said to degrade the performance of multiantenna systems
and put a limit on the number of antennas that can be effectively squeezed into a small device (as a mobile phone
). This seems intuitive as spatial correlation decreases the number of independent channels that can be created by precoding
, but is not true for all kinds of channel knowledge
as described below.
flat-fading channel with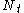 transmit antennas and
transmit antennas and  receive antennas (MIMO), the propagation channel is modeled as
receive antennas (MIMO), the propagation channel is modeled as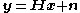
where and
and  are the
are the  receive and
receive and 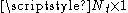 transmit vectors, respectively. The
transmit vectors, respectively. The  noise vector is denoted
noise vector is denoted  . The
. The  th element of the
th element of the  channel matrix
channel matrix  describes the channel from the
describes the channel from the  th transmit antenna to the
th transmit antenna to the  th receive antenna.
th receive antenna.
When modeling spatial correlation it is useful to employ the Kronecker model, where the correlation between transmit antennas and receive antennas are assumed independent and separable. This model is reasonable when the main scattering appears close to the antenna arrays and has been validated by both outdoor and indoor measurements.
With Rayleigh fading
, the Kronecker model means that the channel matrix can be factorized as
where the elements of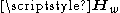 are independent and identically distributed as circular symmetric complex Gaussian with zero-mean and unit variance. The important part of the model is that
are independent and identically distributed as circular symmetric complex Gaussian with zero-mean and unit variance. The important part of the model is that  is pre-multiplied by the receive-side spatial correlation matrix
is pre-multiplied by the receive-side spatial correlation matrix  and post-multiplied by transmit-side spatial correlation matrix
and post-multiplied by transmit-side spatial correlation matrix 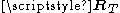 .
.
Equivalently, the channel matrix can be expressed as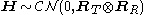
where denotes the Kronecker product
denotes the Kronecker product
.
of the correlation matrices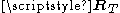 and
and  . Each eigenvector represents a spatial direction of the channel and its corresponding eigenvalue describes the average channel/signal gain in this direction. For the transmit-side matrix
. Each eigenvector represents a spatial direction of the channel and its corresponding eigenvalue describes the average channel/signal gain in this direction. For the transmit-side matrix 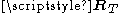 it describes the average gain in a spatial transmit direction, while it describes a spatial receive direction for
it describes the average gain in a spatial transmit direction, while it describes a spatial receive direction for  .
.
High spatial correlation is represented by large eigenvalue spread in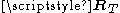 or
or 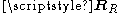 , meaning that some spatial directions are statistically stronger than others.
, meaning that some spatial directions are statistically stronger than others.
Low spatial correlation is represented by small eigenvalue spread in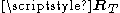 or
or 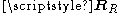 , meaning that almost the same signal gain can be expected from all spatial directions.
, meaning that almost the same signal gain can be expected from all spatial directions.
 or
or 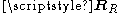 ) has an impact on the performance of a multiantenna
) has an impact on the performance of a multiantenna
system. This impact can be analyzed mathematically by majorization of vectors with eigenvalues.
In information theory
, the ergodic channel capacity
represents the amount of information that can be transmitted reliably. Intuitively, the channel capacity
is always degraded by receive-side spatial correlation as it decreases the number of (strong) spatial directions that the signal is received from. This makes it harder to perform diversity combining
.
The impact of transmit-side spatial correlation depends on the channel knowledge
. If the transmitter is perfectly informed or is uninformed, then the more spatial correlation there is the less the channel capacity
. However, if the transmitter has statistical knowledge (i.e., knows and
and  ) it is the other way around – spatial correlation improves the channel capacity
) it is the other way around – spatial correlation improves the channel capacity
since the dominating effect is that the channel uncertainty decreases.
The ergodic channel capacity
measures the theoretical performance, but similar results have been proved for more practical performance measures as the error rate.
MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
at the transmitter and the receiver. The idea is that if the propagation channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
s between each pair of transmit and receive antennas are statistically independent and identically distributed, then multiple independent channels with identical characteristics can be created by precoding
Precoding
Precoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
and be used for either transmitting multiple data streams
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
or increasing the reliability
Diversity combining
Diversity combining is the technique applied to combine the multiple received signals of a diversity reception device into a single improved signal.- Various techniques :Various diversity combining techniques can be distinguished:...
(in terms of bit error rate). In practice, the channels between different antennas are often correlated and therefore the potential multi-antenna gains may not always be obtainable. This is called spatial correlation as it can be interpreted as a correlation between a signal's spatial direction and the average received signal gain.
Existence of spatial correlation
In an ideal communication scenario, there is a line-of-sight pathLine-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
between the transmitter and receiver that represents clear spatial channel characteristics. In urban cellular systems, this is seldom the case as base stations
Base station
The term base station can be used in the context of land surveying and wireless communications.- Land surveying :In the context of external land surveying, a base station is a GPS receiver at an accurately-known fixed location which is used to derive correction information for nearby portable GPS...
are located on rooftops while many users are located either indoors or at streets far from base stations. Thus, there is a non-line-of-sight multipath propagation channel between base stations and users, describing how the signal is reflected at different obstacles on its way from the transmitter to the receiver. However, the received signal may still have a strong spatial signature in the sense that stronger average signal gains are received from certain spatial directions.
Spatial correlation means that there is a correlation between the received average signal gain and the angle of arrival
Angle of arrival
Angle of arrival measurement is a method for determining the direction of propagation of a radio-frequency wave incident on an antenna array...
of a signal.
Rich multipath propagation decreases the spatial correlation by spreading the signal such that multipath components are received from many different spatial directions. Short antenna separations increase the spatial correlation as adjacent antennas will receive similar signal components. The existence of spatial correlation has been experimentally validated.
Spatial correlation is often said to degrade the performance of multiantenna systems
MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
and put a limit on the number of antennas that can be effectively squeezed into a small device (as a mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
). This seems intuitive as spatial correlation decreases the number of independent channels that can be created by precoding
Precoding
Precoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
, but is not true for all kinds of channel knowledge
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
as described below.
Mathematical description
In a narrowbandNarrowband
In radio, narrowband describes a channel in which the bandwidth of the message does not significantly exceed the channel's coherence bandwidth. It is a common misconception that narrowband refers to a channel which occupies only a "small" amount of space on the radio spectrum.The opposite of...
flat-fading channel with
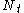 transmit antennas and
transmit antennas and  receive antennas (MIMO), the propagation channel is modeled as
receive antennas (MIMO), the propagation channel is modeled as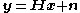
where
 and
and  are the
are the  receive and
receive and 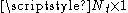 transmit vectors, respectively. The
transmit vectors, respectively. The  noise vector is denoted
noise vector is denoted  . The
. The  th element of the
th element of the  channel matrix
channel matrix  describes the channel from the
describes the channel from the  th transmit antenna to the
th transmit antenna to the  th receive antenna.
th receive antenna.When modeling spatial correlation it is useful to employ the Kronecker model, where the correlation between transmit antennas and receive antennas are assumed independent and separable. This model is reasonable when the main scattering appears close to the antenna arrays and has been validated by both outdoor and indoor measurements.
With Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices.Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium will vary randomly, or fade, according to a...
, the Kronecker model means that the channel matrix can be factorized as

where the elements of
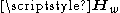 are independent and identically distributed as circular symmetric complex Gaussian with zero-mean and unit variance. The important part of the model is that
are independent and identically distributed as circular symmetric complex Gaussian with zero-mean and unit variance. The important part of the model is that  is pre-multiplied by the receive-side spatial correlation matrix
is pre-multiplied by the receive-side spatial correlation matrix  and post-multiplied by transmit-side spatial correlation matrix
and post-multiplied by transmit-side spatial correlation matrix 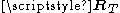 .
.Equivalently, the channel matrix can be expressed as
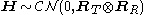
where
 denotes the Kronecker product
denotes the Kronecker productKronecker product
In mathematics, the Kronecker product, denoted by ⊗, is an operation on two matrices of arbitrary size resulting in a block matrix. It gives the matrix of the tensor product with respect to a standard choice of basis. The Kronecker product should not be confused with the usual matrix...
.
Spatial correlation matrices
Under the Kronecker model, the spatial correlation depends directly on the eigenvalue distributionsEigenvalue, eigenvector and eigenspace
The eigenvectors of a square matrix are the non-zero vectors that, after being multiplied by the matrix, remain parallel to the original vector. For each eigenvector, the corresponding eigenvalue is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled when multiplied by the matrix...
of the correlation matrices
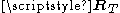 and
and  . Each eigenvector represents a spatial direction of the channel and its corresponding eigenvalue describes the average channel/signal gain in this direction. For the transmit-side matrix
. Each eigenvector represents a spatial direction of the channel and its corresponding eigenvalue describes the average channel/signal gain in this direction. For the transmit-side matrix 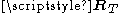 it describes the average gain in a spatial transmit direction, while it describes a spatial receive direction for
it describes the average gain in a spatial transmit direction, while it describes a spatial receive direction for  .
.High spatial correlation is represented by large eigenvalue spread in
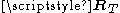 or
or 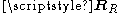 , meaning that some spatial directions are statistically stronger than others.
, meaning that some spatial directions are statistically stronger than others.Low spatial correlation is represented by small eigenvalue spread in
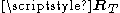 or
or 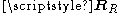 , meaning that almost the same signal gain can be expected from all spatial directions.
, meaning that almost the same signal gain can be expected from all spatial directions.Impact on performance
The spatial correlation (i.e., the eigenvalue spread in or
or 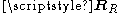 ) has an impact on the performance of a multiantenna
) has an impact on the performance of a multiantennaMIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
system. This impact can be analyzed mathematically by majorization of vectors with eigenvalues.
In information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
, the ergodic channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
represents the amount of information that can be transmitted reliably. Intuitively, the channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
is always degraded by receive-side spatial correlation as it decreases the number of (strong) spatial directions that the signal is received from. This makes it harder to perform diversity combining
Diversity combining
Diversity combining is the technique applied to combine the multiple received signals of a diversity reception device into a single improved signal.- Various techniques :Various diversity combining techniques can be distinguished:...
.
The impact of transmit-side spatial correlation depends on the channel knowledge
Channel state information
In wireless communications, channel state information refers to known channel properties of a communication link. This information describes how a signal propagates from the transmitter to the receiver and represents the combined effect of, for example, scattering, fading, and power decay with...
. If the transmitter is perfectly informed or is uninformed, then the more spatial correlation there is the less the channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
. However, if the transmitter has statistical knowledge (i.e., knows
 and
and  ) it is the other way around – spatial correlation improves the channel capacity
) it is the other way around – spatial correlation improves the channel capacityChannel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
since the dominating effect is that the channel uncertainty decreases.
The ergodic channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
measures the theoretical performance, but similar results have been proved for more practical performance measures as the error rate.
See also
- MIMOMIMOIn radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
- Diversity combiningDiversity combiningDiversity combining is the technique applied to combine the multiple received signals of a diversity reception device into a single improved signal.- Various techniques :Various diversity combining techniques can be distinguished:...
- Multipath propagation
- PrecodingPrecodingPrecoding is a generalization of beamforming to support multi-layer transmission in multi-antenna wireless communications. In conventional single-layer beamforming, the same signal is emitted from each of the transmit antennas with appropriate weighting such that the signal power is maximized at...
- Spatial multiplexingSpatial multiplexingSpatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
Further reading
- K. T. Wong & Y. I. Wu, “Spatio-Polarizational Correlation-Coefficient Function Between Receiving-Antennas in Radiowave Communications: Geometrically Modeled, Analytically Derived, Simple, Closed-Form, Explicit Formulas,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 57, no. 12, pp. 3566-3570, December 2009.

