
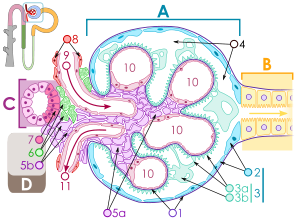
Macula densa
Encyclopedia
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
lining the wall of the distal tubule at the point of return of the nephron
Nephron
The renal tubule is the portion of the nephron containing the tubular fluid filtered through the glomerulus. After passing through the renal tubule, the filtrate continues to the collecting duct system, which is not part of the nephron....
to the vascular pole of its parent glomerulus, (glomerular vascular pole
Vascular pole
The vascular pole is a location of the glomerulus. At the vascular pole, the afferent arterioles and efferent arterioles enter the Bowman's capsule.The urinary pole is at the other end....
).
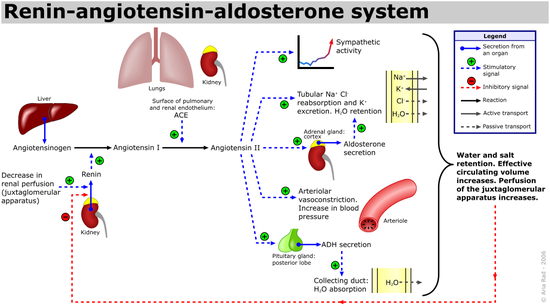
The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of sodium chloride in the distal convoluted tubule. A decrease in sodium chloride concentration initiates a signal from the macula densa that has two effects: (1) it decreases resistance to blood flow in the afferent arterioles, which increases glomerular hydrostatic pressure and helps return glomerulus filtration rate (GFR) toward normal, and (2) it increases renin
Renin
Renin , also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an enzyme that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system -- also known as the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Axis -- that mediates extracellular volume , and arterial vasoconstriction...
release from the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent and efferent arterioles, which are the major storage sites for renin.
The release of renin is an essential component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
and volume.
Histology
The cells of the macula densa are taller and have more prominent nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
than surrounding cells of the distal straight tubule (cortical thick ascending limb).
The close proximity and prominence of the nuclei cause this segment of the distal tubule wall to appear darker in microscopic preparations, hence the name macula densa.
Function
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
causes a decrease in the GFR (glomerular filtration rate) which causes more reabsorption, resulting in a decreased concentration of sodium and chloride ions in the filtrate and/or decreased filtrate flow rate. The macula densa can sense this decrease and trigger an autoregulatory response to further increase reabsorption of ions and water in order to return blood pressure to normal. Reduced blood pressure means decreased venous pressure and hence a decreased peritubular capillary pressure. This causes a smaller capillary hydrostatic pressure which causes an increased absorption of sodium ions into the vasa recta at the proximal tubule
Proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is the portion of the duct system of the nephron of the kidney which leads from Bowman's capsule to the loop of Henle.-Structure and appearance:...
. Because of this increased absorption, less NaCl is present at the distal tubule where the macula densa is located. The macula densa senses this drop in salt concentration and responds through two mechanisms: first, it triggers dilation of the renal afferent arteriole, decreasing afferent arteriole resistance and thus offsetting the decrease in glomerular hydrostatic pressure caused by the drop in blood pressure. Second, macula densa cells release prostaglandins, which triggers granular juxtaglomerular cells lining the afferent arterioles
Afferent arterioles
The afferent arterioles are a group of blood vessels that supply the nephrons in many excretory systems. They play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure as a part of the Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism....
to release renin
Renin
Renin , also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an enzyme that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system -- also known as the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Axis -- that mediates extracellular volume , and arterial vasoconstriction...
into the bloodstream. (The juxtaglomerular cells can also release renin independently of the macula densa, as they are also triggered by baroreceptors lining the arterioles, and release renin if a fall in blood pressure in the arterioles is detected.) Furthermore, activation of the sympathetic nervous system stimulates renin release through activation of beta-1 receptors.
The process triggered by the Macula densa helps keep the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) fairly steady in response to varying artery pressure, due to dilation of the afferent arterioles
Afferent arterioles
The afferent arterioles are a group of blood vessels that supply the nephrons in many excretory systems. They play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure as a part of the Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism....
and the action of Renin, which triggers constriction of the efferent arterioles, both of which increase hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus
Glomerulus
A glomerulus is a capillary tuft that is involved in the first step of filtering blood to form urine.A glomerulus is surrounded by Bowman's capsule, the beginning component of nephrons in the vertebrate kidney. A glomerulus receives its blood supply from an afferent arteriole of the renal...
.

