
Manx Runestones
Encyclopedia
Norsemen
Norsemen is used to refer to the group of people as a whole who spoke what is now called the Old Norse language belonging to the North Germanic branch of Indo-European languages, especially Norwegian, Icelandic, Faroese, Swedish and Danish in their earlier forms.The meaning of Norseman was "people...
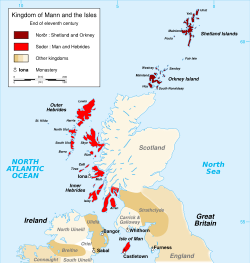
population on the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
during the Viking Age
Viking Age
Viking Age is the term for the period in European history, especially Northern European and Scandinavian history, spanning the late 8th to 11th centuries. Scandinavian Vikings explored Europe by its oceans and rivers through trade and warfare. The Vikings also reached Iceland, Greenland,...
, mostly in the 10th century. Despite its small size, the Isle of Man stands out with many Viking Age runestones, in 1983 numbering as many as 26 surviving stones, which can be compared to 33 in all of Norway. The reason why there are so many of them on the Isle of Man may be due to the merging of the immigrant Norse runestone tradition with the local Celtic tradition of raising high cross
High cross
A high cross or standing cross is a free-standing Christian cross made of stone and often richly decorated. There was a unique Early Medieval tradition in Ireland and Britain of raising large sculpted stone crosses, usually outdoors...
es.
In addition, the church contributed by not condemning the runes as pagan, but instead it encouraged the recording of people for Christian purposes. Sixteen of the stones bear the common formula, "N ... put up this cross in memory of M", but among the other ten there is also a stone raised for the benefit of the runestone raiser.
The Manx runestones are consequently similar to the Scandinavian ones, but whereas a Norwegian runestone is called "stone" in the inscriptions, even if it is in the shape of a cross, the runestones that were raised in the British isles typically call them "crosses". There are also two slabs incised with Anglo-Saxon runes at Maughold
Maughold
Saint Maughold of Man is venerated as the patron saint of the Isle of Man...
.
Br Olsen;183 (Andreas (I), MM 99)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... (þ)[an](a) : [aft] (u)(f)(a)ik : fauþur : sin : in : kautr : kar[þ]i : sunr : biarnar f(r)(a) : (k)(u)(l)(i) [:]
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... þenna ept Ófeig, fôður sinn, en Gautr gerði, sonr Bjarnar frá Kolli.
English translation:
- "... this [cross] in memory of Ófeigr, his father, but Gautr made (it), the son of Bjôrn from Kollr."
Br Olsen;184 (Andreas (II), MM 131)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- sont:ulf : hin : suarti : raisti : krus : þona : aftir : arin:biaurk * kuinu : sina (u) [*] k : au [*]: (o)ks/(b)ks
Old Norse transliteration:
- Sandulfr hinn Svarti reisti kross þenna eptir Arinbjôrgu, konu sína. ... ... ... ...
English translation:
- "Sandulfr the Black erected this cross in memory of Arinbjôrg his wife. ..."
Thorwald's Cross: Br Olsen;185A (Andreas (III), MM 128)

Rundata
The Scandinavian Runic-text Data Base is a project involving the creation and maintenance of a database of runic inscriptions. The project's goal is to comprehensively catalog runestones in a machine-readable way for future research...
dates it to 940, while Pluskowski dates it to the 11th century.
This depiction has been interpreted as the Norse pagan
Norse paganism
Norse paganism is the religious traditions of the Norsemen, a Germanic people living in the Nordic countries. Norse paganism is therefore a subset of Germanic paganism, which was practiced in the lands inhabited by the Germanic tribes across most of Northern and Central Europe in the Viking Age...
god Odin
Odin
Odin is a major god in Norse mythology and the ruler of Asgard. Homologous with the Anglo-Saxon "Wōden" and the Old High German "Wotan", the name is descended from Proto-Germanic "*Wodanaz" or "*Wōđanaz"....
, with a raven or eagle at his shoulder, being consumed by the wolf Fenrir during the events of Ragnarök
Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, Ragnarök is a series of future events, including a great battle foretold to ultimately result in the death of a number of major figures , the occurrence of various natural disasters, and the subsequent submersion of the world in water...
. Next to the image is a depiction of a large cross and another image parallel to it that has been described as Christ triumphing over Satan. These combined elements have led to the cross as being described as "syncretic art
Syncretism
Syncretism is the combining of different beliefs, often while melding practices of various schools of thought. The term means "combining", but see below for the origin of the word...
"; a mixture of pagan and Christian beliefs. Andy Orchard comments that the bird on Odin's shoulder may be either Huginn or Muninn, Odin's ravens.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- þurualtr ÷ (r)[aisti] (k)(r)(u)(s) ÷ (þ)[...]
Old Norse transliteration:
- Þorvaldr reisti kross þe[nna].
English translation:
- "Þorvaldr raised (this) cross."
Br Olsen;185B (Andreas (IV), MM 113)
This stone cross is located in the church Andreas. It is engraved with short-twig runes and it is dated to the 10th century. What remains of the message informs that it was raised in memory of someone.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- [... ...ai]s[t]i : [k]rus : þaina : aftiR ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... reisti kross þenna eptir ...
English translation:
- "... raised this cross in memory of ..."
Br Olsen;185C (Andreas (V), MM 111)

Bind rune
A bind rune is a ligature of two or more runes. They are extremely rare in Viking Age inscriptions, but are common in pre-Viking Age and in post-Viking Age inscriptions....
s.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br Page1998;9 (Andreas (VI), MM 121)
Only a fragment remains of this slab of stone that was once part of a grave. It is dated to the Viking Age and it is located in the church Andreas. Too little remains of the inscription to allow any decipherment.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ka-
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br NOR1992;6B (Andreas (VII), MM 193)
This fragment was discovered at Larivane Cottage it is a slab of stone was once part of a grave. The inscription was made in relief form, and it is presently located in the Manx Museum. What remains of the inscription cannot be read.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ...----...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br Olsen;189 (Ballaugh, MM 106)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- oulaibr ÷ liu(t)ulbs| |sunr : r[ai](s)[ti k]rs * þ-na : ai(f)(t)ir * ...-b : sun [s]in
Old Norse transliteration:
- Áleifr/Óleifr Ljótulfs sonr reisti kross þ[e]nna eptir [Ul]f, son sinn.
English translation:
- "Áleifr/Óleifr, Ljótulfrs son raised this cross in memory of Ulfr, his son."
Br Olsen;190A (Balleigh)
These fragments of a stone cross are found at Balleigh, and they are dated to the Viking Age. Only traces of runes remain and they cannot be read.Latin transliteration:
- ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br Olsen;190B (Braddan (I), MM 112)
This stone cross is located in the church Braddan. The inscription consists of short-twig runes and they are dated to 930-950. It was raised in memory of a man.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- (þ)(u)(r)... : raisti : krus : þono : ift : ufaak : sun : krinais
Old Norse transliteration:
- Þorsteinn reisti kross þenna ept Ófeig, son Krínáns.
English translation:
- "Þorsteinn raised this cross in memory of Ófeigr, the son of Krínán."
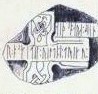
Br Olsen;191A (Braddan (II), MM 138)
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... ...(n) roskitil : uilti : i : triku : aiþsoara : siin
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... [e]n Hrossketill vélti í tryggu eiðsvara sinn.
English translation:
- "... but Hrosketill betrayed the faith of his sworn confederate."
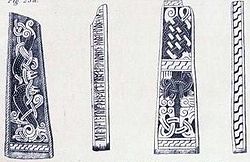
Br Olsen;191B (Braddan (III), MM 136)
Runemaster
A runemaster or runecarver is a specialist in making runestones.Most early medieval Scandinavians were probably literate in runes, and most people probably carved messages on pieces of bone and wood. However, it was difficult to make runestones, and in order to master it one also needed to be a...
is identified as man named Thorbjörn, who also made Br Olsen;193A, below. It has been badly damaged since it was recorded.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- utr : risti : krus : þono : aft : fro(k)(a) [: f](a)(þ)[ur sin : in :] (þ)[urbiaurn : ...]
Old Norse transliteration:
- Oddr reisti kross þenna ept Frakka, fôður sinn, en Þorbjôrn ...
English translation:
- "Oddr raised this cross in memory of Frakki, his father, but ... ..."
Br Olsen;193A (Braddan (IV), MM 135)

Runemaster
A runemaster or runecarver is a specialist in making runestones.Most early medieval Scandinavians were probably literate in runes, and most people probably carved messages on pieces of bone and wood. However, it was difficult to make runestones, and in order to master it one also needed to be a...
Thorbjörn, like Br Olsen;191B, above. It was made in memory of a son.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- þurlibr : nhaki : risti : krus : þono : aft [:] fiak : s(u)[n] (s)in : (b)ruþur:sun : habrs × {IHSVS}
Old Norse transliteration:
- Þorleifr Hnakki reisti kross þenna ept Fiak, son sinn, bróðurson Hafrs. {
}
English translation:
- "Þorleifr the Neck raised this cross in memory of Fiak, his son, Hafr's brothers son. {
}"
Br Page1998;20 (Braddan (V), MM 176)
This fragment of a runestone is located in Manx Museum. It is probably from the Viking Age, but as of 2006, it had not yet been analysed.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br NOR1992;6A (Braddan (VI), MM 200)
This runestone consists of a fragment of slate. It is dated to the Viking Age and it is located in Manx Museum. The only message that remains consists of "made".Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ...---r--nr * kirþi * ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... gerði ...
English translation:
- "... made ..."
gerði would also translate into modern Swedish as gjorde or English did ... The meaning of the words made or did depends on the original context of the sentence as a whole (or at least the words surrounding this single word) , which here appears lost.
The current use of the Swedish word gjorde is much more closely related to did than the word made. Which is intended is impossible to say here.
Br Olsen;193B (MM 118)
This stone cross is found in the church Bride. The inscription consists of short-twig runes and it is dated to between 930 and 950. It was raised in memory of a wife.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- [t]ruian : sur [t]u(f)kals : raisti krs þina : a(f)[t] aþmiu... : kunu si[n...]
Old Norse transliteration:
- Druian, sonr Dufgals, reisti kross þenna ept Aþmiu[l], konu sín[a].
English translation:
- "Druian, Dufgal's son raised this cross in memory of Aþmiu[l], his wife."
Br Olsen;194 (MM 141)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- A ...(a) sunr × raisti × if(t) [k](u)[i](n)(u) (s)(i)(n)(a) ×
- B murkialu × m...
- C × uk ik at × auk raþ ik r...t ×
- D a=læns
- E kru...
- F isu krist
- G þuriþ × raist × rune... ×
Old Norse transliteration:
- A ... sonr reisti ept konu sína
- B Myrgjôl ...
- C Hygg ek at ok ræð ek r[é]tt.
- D Alleins.
- E Kro[ss]
- F Jésu Krist
- G Þúríð reist rúna[r].
English translation:
- A "...'s son raised (this) in memory of his wife"
- B "Myrgjôl ..."
- C "I examine (the runes) and I interpret (them) rightly.(?)"
- D "in agreement(?)"
- E "Cross"
- F "Jesus Christ"
- G "Þúríð carved the runes."
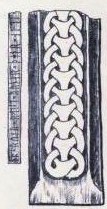
Br Olsen;199 (German (I), MM 107)
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... in o(s)(r)(u)(þ)(r) : raist : runar : þsar × ¶ ----- -
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... En Ásrøðr reist rúnar þessar. ... ...
English translation:
- "... and Ásrøðr carved these runes. ... ..."
Br Olsen;200A (German (II), MM 140)
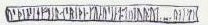
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... ... ...(u)s * þense * efter * asriþi * kunu sina * (t)(u)(t)ur * ut... ...-
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... ... [kr]oss þenna eptir Ástríði, konu sína, dóttur Odd[s]. ...
English translation:
- "... ... this cross in memory of Ástríðr, his wife, Oddr's daughter ..."
Br Olsen;200B (MM 127)
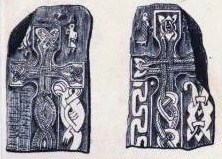
Jurby
Jurby is a parish in Micheal Sheading in the Isle of Man and has, according to the 2006 census 659 , residents.It is largely an agricultural district on the north-north-western coast of the island but also has an industrial park on the old RAF Jurby Airfield.The parish is one of three divisions of...
and the short-twig runes are dated to the second half of the 10th century. It has been badly damaged since it was recorded. One of the figures depicted on the cross holds a small sword in his right hand and an Alpine horn in his left while a raven flies overhead. It has been suggested that this figure represents the Norse pagan deity Heimdall
Heimdall
In Norse mythology, Heimdallr is a god who possesses the resounding horn Gjallarhorn, owns the golden-maned horse Gulltoppr, has gold teeth, and is the son of Nine Mothers...
holding the Gjallarhorn
Gjallarhorn
In Norse mythology, Gjallarhorn is a horn associated with the god Heimdallr and the wise being Mímir...
, used to announce the coming of Ragnarök.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- [... ... ...un * si]n : in : onon : raiti ¶ --- * aftir þurb-...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... ... [s]on sinn, en annan reisti/rétti [hann](?) eptir Þor...
English translation:
- "... ... his son and raised(?) another ... in memory of Þorb-..."
Br Olsen;201 (MM 139)
This stone cross is located in Saint Trinian's chapel. The short-twig inscription is dated to the Viking Age.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- þurbiaurn : risti : krus : þ(o)-...
Old Norse transliteration:
- Þorbjôrn reisti kross þe[nna].
English translation:
- "Þorbjôrn raised this cross."
Br Olsen;202A (Maughold (I), MM 145)
This runic inscription is found on a stone slab that was used in a grave. It is located near the church Maughold. The inscription is dated to the second half of the 12th century, and it was made by the same runemaster as Br Olsen;202B. On the stone can also be seen the first half of the OghamOgham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
alphabet.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- (i)(u)an + brist + raisti + þasir + runur +¶ [f]uþor(k)(h)niastbml +
Old Norse transliteration:
- Jóan prestr reisti þessar rúnar.
English translation:
- "Jóan the priest carved these runes. Fuþorkhniastbml"
Br Olsen;202B (Maughold (II), MM 144)
This inscription is found on a slab of stone that was used in a grave. It was discovered at the upper end of the Corna valley, but is presently found at the church Maughold. The short-twig inscription is dated to the second half of the 12th century and it was made by the same runemaster as Br Olsen;202A.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- + krisþ : malaki : ok baþr(i)k : (a)þ(a)(n)man (×) ¶ ÷ [...nal] * sauþ * a... * iuan * brist * i kurnaþal *
Old Norse transliteration:
- Kristr, Malaki ok Patrik. Adamnán ... ... ... Jóan prestr í Kornadal.
English translation:
- "Christ, Malachi, and Patrick. Adamnán ... Joán the priest in Kornadalr."
Br Olsen;205A (Maughold (III), MM 133)
This fragment of a stone cross was found in Ballagilley. It is presently located at the church Maughold. It is dated to the Viking Age but only four runes remain of the inscription.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ...
English translation:
- "..."
Br Olsen;205B (Maughold (IV), MM 142)
This inscription is dated to c. 1000 and found on a slab of stone that was used in a grave, and it is located at the church Maughold. The inscription is in long-branch runes, except for the s rune, and there is reason to believe that it was made by a visitor to the Isle of Man.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- A heþin : seti : krus : þino : eftir : tutur : sino ¶ lif... ¶ lifilt
- B arni : risti : runar : þisar
- C sikuþr
Old Norse transliteration:
- A Heðinn setti kross þenna eptir dóttur sína Hlíf[hildi]. Hlífhildi.
- B Árni risti rúnar þessar.
- C Sigurðr.
English translation:
- A "Heðinn placed this cross in memory of his daughter Hlíf(hildr). Hlífhildr."
- B "Árni carved these runes."
- C "Sigurðr."
Br Page1998;21 (Maughold (V), MM 175)
This inscription is found on a slab of stone that was used in a grave. It is located in the Manx Museum. It is in short-twig runes and it is dated to the Viking Age. It was engraved in memory of a wife.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- kuan sunr × mailb---ak... + kirþi + lik+tinn i(f)tir + ¶ + kuina sina +
Old Norse transliteration:
-
, sonr gerði líkstein(?) eptir kona sína.
English translation:
- "
, son of made the tomb-stone(?) in memory of his wife."
Br Olsen;208A (Kirk Michael (I), MM 102)
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... [kru](s) : þna : af[tir : ...]
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... kross þenna eptir ...
English translation:
- "... this cross in memory of ..."
Br Olsen;208B (Kirk Michael (II), MM 101)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- × mail:brikti : sunr : aþakans : smiþ : raisti : krus : þano : fur :¶ salu : sina : sin:bruku in : kaut ׶ kirþi : þano : auk ¶ ala : i maun ×
Old Norse transliteration:
- Melbrigði, sonr Aðakáns Smiðs, reisti kross þenna fyr sálu sína synd...(?), en Gautr gerði þenna ok alla í Môn.
English translation:
- "Melbrigði, the son of Aðakán the Smith, raised this cross for his sin ... soul, but Gautr made this and all in Man."
Br Olsen;215 (Kirk Michael (III), MM 130)

Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
inscriptions on both sides.
Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- mal:lymkun : raisti : krus : þena : efter : mal:mury : fustra : si(n)e : tot(o)r : tufkals : kona : is : aþisl : ati + ¶ ...etra : es : laifa : fustra : kuþan : þan : son : ilan +
Old Norse transliteration:
-
reisti kross þenna eptir fóstra sín, dóttir Dufgals, kona er Aðísl átti. Betra er leifa fóstra góðan en son illan.
English translation:
- "
raised this cross in memory of , his foster(-mother?), Dufgal's daughter, the wife whom Aðísl owned (= was married to). (It) is better to leave a good foster-son than a wretched son."
Br Olsen;217A (Kirk Michael (IV), MM 126)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- [k](r)i(m) : risti : krus : þna : ift : rum(u)... ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- Grímr reisti kross þenna ept Hróðmu[nd] ...
English translation:
- "Grímr raised this cross in memory of Hróðmundr ... his ..."
Br Olsen;217B (Kirk Michael (V), MM 132)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- + iualfir : sunr : þurulfs : hins : rauþa : ris(t)i : krus : þono : aft : friþu : muþur : sino +
Old Norse transliteration:
-
, sonr Þórulfs hins Rauða, reisti kross þenna ept Fríðu, móður sína.
English translation:
- "
, the son of Þórulfr the Red, raised this cross in memory of Fríða, his mother."
Br Olsen;218A (Kirk Michael (VI), MM 129)

Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... (k)rims : ins : suarta ×
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... Gríms/...gríms hins Svarta.
English translation:
- "... (of) Grímr/-grímr the Black."
Br Olsen;218B (Kirk Michael (VII), MM 110)
This fragment of a stone cross is located in the church Kirk Michael. The inscription was made in short-twig runes between 930 and 950.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... runar ...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... rúnar ...
English translation:
- "... runes ..."
Br Olsen;219 (Kirk Michael (VIII), MM 123)
This fragment of a stone cross is located in the church Kirk Michael. The inscription was made during the Viking Age with short-twig runes.Latin transliteration
Runic transliteration and transcription
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription which involves transliteration of the runes into Latin letters, transcription into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation of the inscription into a modern language...
:
- ... : [ai](f)(t)(i)(r) * (m)(u)... * (u)...
Old Norse transliteration:
- ... eptir
...
English translation:
- "... in memory of
..."

