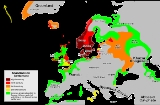
Norsemen
Encyclopedia


North Germanic languages
The North Germanic languages or Scandinavian languages, the languages of Scandinavians, make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages, a sub-family of the Indo-European languages, along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages...
branch of Indo-European languages
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
, especially Norwegian
Norwegian language
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language...
, Icelandic
Icelandic language
Icelandic is a North Germanic language, the main language of Iceland. Its closest relative is Faroese.Icelandic is an Indo-European language belonging to the North Germanic or Nordic branch of the Germanic languages. Historically, it was the westernmost of the Indo-European languages prior to the...
, Faroese
Faroese language
Faroese , is an Insular Nordic language spoken by 48,000 people in the Faroe Islands and about 25,000 Faroese people in Denmark and elsewhere...
, Swedish
Swedish language
Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish...
and Danish
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
in their earlier forms.
The meaning of Norseman was "people from the North" and was applied primarily to Nordic
Nordic
Nordic may refer to:* The Nordic countries, the northwestern European countries of Scandinavia , as well as Iceland and Finland; or a native of one of the Nordic countries...
people originating from southern and central Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
. They established states and settlements in areas which today are part of the Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands are an island group situated between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately halfway between Scotland and Iceland. The Faroe Islands are a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark proper and Greenland...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, and Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
.
Norse and Norsemen are applied to the Scandinavian population of the period from the late 8th century to the 11th century. The term "Normans" was later primarily associated with the people of Norse origin in Normandy
Normandy
Normandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, assimilated into French culture and language. The term "Finn-Galls" (i.e. Norse Vikings or Norwegians) (Gall Goidel, lit.: foreign Gaelic) was used concerning the people of Norse descent in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
and Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, who assimilated into the Gaelic
Gaels
The Gaels or Goidels are speakers of one of the Goidelic Celtic languages: Irish, Scottish Gaelic, and Manx. Goidelic speech originated in Ireland and subsequently spread to western and northern Scotland and the Isle of Man....
culture.
"In the eighth century the inrush of the Vikings in force began to be felt all over Pictland. These Vikings were pagans and savages of the most unrestrained and pitiless type. They were composed of Finn-Gall or Norwegians, and of Dubh-Gall or Danes. The latter were a mixed breed, with a Hunnish strain in them".
Viking
Viking
The term Viking is customarily used to refer to the Norse explorers, warriors, merchants, and pirates who raided, traded, explored and settled in wide areas of Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic islands from the late 8th to the mid-11th century.These Norsemen used their famed longships to...
s has been a common term for Norsemen in the early medieval period, especially in connection with raids and monastic plundering by Norsemen in Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
and Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
. Northmen was famously used in the prayer A furore normannorum libera nos domine ("From the fury of the Northmen deliver us, O Lord!"), attributed to monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
s of the English monasteries
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
plundered by Viking raids in the 8th and 9th centuries.
Other names
The Northmen were also known as Ascomanni, ashmen, by the Germans, Lochlanach (Norse) by the Irish and Dene (Danes) by the Anglo-Saxons.The Slavs, the Arabs and the Byzantins
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
knew them as the Rus'
Rus' (people)
The Rus' were a group of Varangians . According to the Primary Chronicle of Rus, compiled in about 1113 AD, the Rus had relocated from the Baltic region , first to Northeastern Europe, creating an early polity which finally came under the leadership of Rurik...
or Rhōs, probably derived from various uses of rōþs-, i.e. "related to rowing", or derived from the area of Roslagen
Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago....
in east-central Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, where most of the Norsemen who visited the Slavic lands came from. Archaeologists and historians of today believe that these Scandinavian settlements in the Slavic lands formed the names of the countries Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
.
The Slavs and the Byzantines also called them Varangians (ON
Old Norse
Old Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
: Væringjar, meaning sworn men or from Slavic варяги supposedly deriving from the root "вар"—"profit" as coming from North they would profit by trading goods and not producing them, which had a negative connotation in Slavic culture of that time), and the Scandinavian bodyguards of the Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
emperors were known as the Varangian Guard.
Modern Scandinavian usage
In the Old Norse language, the term norrœnir menn (northern men), was used to refer to the North Germanic population of Scandinavia (Swedes, Danes, Norwegians, Faroe Islanders and Icelanders), thus corresponding to the modern English name Norsemen.In the modern Scandinavian languages, no common word for Norsemen exists. In Swedish, the term nordmän is used, which corresponds to "Northmen". The Norwegians and Danish lack a word for the ancient North Germanic peoples. Usually they are simply (but incorrectly) called Vikings in both Denmark, Norway, as well as Sweden. In Norway, nordmann, and Denmark, nordmand, is the common demonym for a Norwegian. In Icelandic, Norðmaður means a man from Norway, but Norrænn maður is the term for a "North Germanic man" (or "woman"/"people"). In Faroese, Norðmaður means a man from Norway, just like in Icelandic, but the term Norrønur maður or Norrøn kvinna/fólk are the terms for the "North Germanic man" or "North Germanic woman/people" respectively.
The word nordbo however, (Sw.
Swedish language
Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish...
: nordborna, Da.
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
: nordboerne, No.
Norwegian language
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language...
: nordboerne or nordbuane in the definite
Definiteness
In grammatical theory, definiteness is a feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between entities which are specific and identifiable in a given context and entities which are not ....
plural
Plural
In linguistics, plurality or [a] plural is a concept of quantity representing a value of more-than-one. Typically applied to nouns, a plural word or marker is used to distinguish a value other than the default quantity of a noun, which is typically one...
) is used for both ancient and modern people living in the Nordic countries
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
and speaking one of the North Germanic languages. The modern people of Scandinavia also simply identify themselves as scandinavians.
See also
- ScandinaviansScandinaviansScandinavians are a group of Germanic peoples, inhabiting Scandinavia and to a lesser extent countries associated with Scandinavia, and speaking Scandinavian languages. The group includes Danes, Norwegians and Swedes, and additionally the descendants of Scandinavian settlers such as the Icelandic...
- ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
- VikingVikingThe term Viking is customarily used to refer to the Norse explorers, warriors, merchants, and pirates who raided, traded, explored and settled in wide areas of Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic islands from the late 8th to the mid-11th century.These Norsemen used their famed longships to...
- Viking AgeViking AgeViking Age is the term for the period in European history, especially Northern European and Scandinavian history, spanning the late 8th to 11th centuries. Scandinavian Vikings explored Europe by its oceans and rivers through trade and warfare. The Vikings also reached Iceland, Greenland,...
- Varangian
- Rus'Rus' (people)The Rus' were a group of Varangians . According to the Primary Chronicle of Rus, compiled in about 1113 AD, the Rus had relocated from the Baltic region , first to Northeastern Europe, creating an early polity which finally came under the leadership of Rurik...
- Swedes (Germanic tribe)
- Geats
- Gutes
- GothsGothsThe Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
- Danes (Germanic tribe)
- SwedesSwedesSwedes are a Scandinavian nation and ethnic group native to Sweden, mostly inhabiting Sweden and the other Nordic countries, with descendants living in a number of countries.-Etymology:...
- DanesDanesDanish people or Danes are the nation and ethnic group that is native to Denmark, and who speak Danish.The first mention of Danes within the Danish territory is on the Jelling Rune Stone which mentions how Harald Bluetooth converted the Danes to Christianity in the 10th century...
- NorwegiansNorwegiansNorwegians constitute both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegian people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in United States, Canada and Brazil.-History:Towards the end of the 3rd...
- IcelandersIcelandersIcelanders are a Scandinavian ethnic group and a nation, native to Iceland.On 17 June 1944, when an Icelandic republic was founded the Icelanders became independent from the Danish monarchy. The language spoken is Icelandic, a North Germanic language, and Lutheranism is the predominant religion...
- FaroeseFaroese peopleThe Faroese or Faroe Islanders are a Germanic ethnic group native to the Faeroe Islands. The Faroese are of mixed Norse and Gaelic origins.About 21,000 Faroese live in neighbouring countries, particularly in Denmark, Iceland and Norway....
- Norse-GaelsNorse-GaelsThe Norse–Gaels were a people who dominated much of the Irish Sea region, including the Isle of Man, and western Scotland for a part of the Middle Ages; they were of Gaelic and Scandinavian origin and as a whole exhibited a great deal of Gaelic and Norse cultural syncretism...
(Gall Goidel) - NormansNormansThe Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...

