Martinet dioxindole synthesis
Encyclopedia
The Martinet dioxindole synthesis is a chemical reaction
used to synthesize dioxindoles 3 from aniline
s and ester
s of mesoxalic acid 1.
will hydrolyze the remaining ester, and effect a decarboxylation
to give the desired dioxindole 3.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
used to synthesize dioxindoles 3 from aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
s and ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s of mesoxalic acid 1.

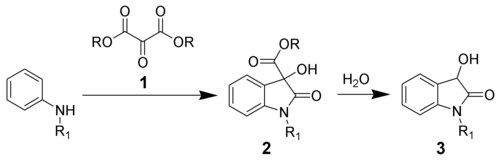
Reaction mechanism
Heating a N-substituted aniline in the presence of an ester of mesoxalic acid 1 will produce the dioxindole 2. Heating of 2 in the presence of waterWater
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
will hydrolyze the remaining ester, and effect a decarboxylation
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide . Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carbonation, the addition of CO2 to...
to give the desired dioxindole 3.

