
Mean kinetic temperature
Encyclopedia
Mean kinetic temperature (MKT) is a simplified way of expressing the overall effect of temperature
fluctuations during storage or transit of perishable goods. The MKT is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
The mean kinetic temperature can be expressed as:
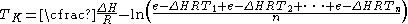
Where:
The above equation is valid only when the temperature readings are taken at the same interval. A more general form for the above equation can be expressed as:
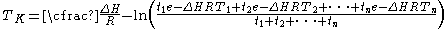
Where:
When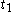 =
=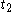 =
= =
=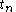 , this equation will be reduced to the former equation.
, this equation will be reduced to the former equation.
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
fluctuations during storage or transit of perishable goods. The MKT is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
The mean kinetic temperature can be expressed as:
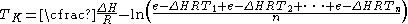
Where:
-
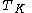 is the mean kinetic temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
is the mean kinetic temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s -
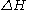 is the activation energyActivation energyIn chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
is the activation energyActivation energyIn chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
(typically within 60–100 kJ·mol-1 for solids or liquids) -
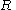 is the gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
is the gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,... -
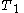 to
to 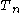 are the temperatures at each of the sample points in kelvins
are the temperatures at each of the sample points in kelvins -
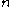 is the number of temperature sample points
is the number of temperature sample points
The above equation is valid only when the temperature readings are taken at the same interval. A more general form for the above equation can be expressed as:
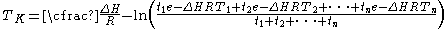
Where:
-
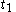 to
to 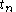 are time intervals at each of the sample points
are time intervals at each of the sample points
When
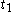 =
=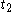 =
= =
=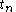 , this equation will be reduced to the former equation.
, this equation will be reduced to the former equation.

