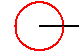
Meander (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a meander or closed meander is a self-avoiding closed curve which intersects a line a number of times. Intuitively, a meander can be viewed as a road crossing a river through a number of bridges.
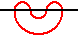
The meanders of order 2 intersect the line four times:
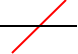
The open meander of order 2 intersects the line twice:
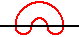
The semi-meander of order 2 intersects the ray twice:
from meandric to open meandric numbers:
Each meandric number can be bounded
by semi-meandric numbers:
For n > 1, meandric numbers are even
:
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a meander or closed meander is a self-avoiding closed curve which intersects a line a number of times. Intuitively, a meander can be viewed as a road crossing a river through a number of bridges.
Meander
Given a fixed oriented line L in the Euclidean plane R2, a meander of order n is a non-self-intersecting closed curve in R2 which transversally intersects the line at 2n points for some positive integer n. Two meanders are said to be equivalent if they are homeomorphic in the plane.Examples
The meander of order 1 intersects the line twice:The meanders of order 2 intersect the line four times:
Meandric numbers
The number of distinct meanders of order n is the meandric number Mn. The first fifteen meandric numbers are given below .- M1 = 1
- M2 = 2
- M3 = 8
- M4 = 4242 (number)42 is the natural number immediately following 41 and directly preceding 43. The number has received considerable attention in popular culture as a result of its central appearance in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy as the "Answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and...
- M5 = 262
- M6 = 1828
- M7 = 13820
- M8 = 110954
- M9 = 933458
- M10 = 8152860
- M11 = 73424650
- M12 = 678390116
- M13 = 6405031050
- M14 = 61606881612
- M15 = 602188541928
Open meander
Given a fixed oriented line L in the Euclidean plane R2, an open meander of order n is a non-self-intersecting oriented curve in R2 which transversally intersects the line at n points for some positive integer n. Two open meanders are said to be equivalent if they are homeomorphic in the plane.Examples
The open meander of order 1 intersects the line once:The open meander of order 2 intersects the line twice:
Open meandric numbers
The number of distinct open meanders of order n is the open meandric number mn. The first fifteen open meandric numbers are given below .- m1 = 1
- m2 = 1
- m3 = 2
- m4 = 3
- m5 = 8
- m6 = 1414 (number)14 is the natural number following 13 and preceding 15.In speech, the numbers 14 and 40 are often confused. When carefully enunciated, they differ in which syllable is stressed: 14 vs 40...
- m7 = 4242 (number)42 is the natural number immediately following 41 and directly preceding 43. The number has received considerable attention in popular culture as a result of its central appearance in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy as the "Answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and...
- m8 = 8181 (number)81 is the natural number following 80 and preceding 82.-In mathematics:Eighty-one is the square of 9 and the fourth power of 3. Like all powers of three, 81 is a perfect totient number. It is a heptagonal number and a centered octagonal number. It is also a tribonacci number, and an open meandric...
- m9 = 262
- m10 = 538
- m11 = 1828
- m12 = 3926
- m13 = 13820
- m14 = 30694
- m15 = 110954
Semi-meander
Given a fixed oriented ray R in the Euclidean plane R2, a semi-meander of order n is a non-self-intersecting closed curve in R2 which transversally intersects the ray at n points for some positive integer n. Two semi-meanders are said to be equivalent if they are homeomorphic in the plane.Examples
The semi-meander of order 1 intersects the ray once:The semi-meander of order 2 intersects the ray twice:
Semi-meandric numbers
The number of distinct semi-meanders of order n is the semi-meandric number Mn (usually denoted with an overline instead of an underline). The first fifteen semi-meandric numbers are given below .- M1 = 1
- M2 = 1
- M3 = 2
- M4 = 4
- M5 = 1010 (number)10 is an even natural number following 9 and preceding 11.-In mathematics:Ten is a composite number, its proper divisors being , and...
- M6 = 2424 (number)24 is the natural number following 23 and preceding 25.The SI prefix for 1024 is yotta , and for 10−24 yocto...
- M7 = 6666 (number)66 is the natural number following 65 and preceding 67.Usages of this number include:-Mathematics:*66 is a sphenic number, a triangular number, a hexagonal number, and a semi-meandric number...
- M8 = 174174 (number)174 is the natural number following 173 and preceding 175.-In mathematics:* 174 is an even number* 174 is an abundant number with the abundance of 12* 174 is a composite number* 174 is a nontotient number* 174 is an odious number...
- M9 = 504
- M10 = 1406
- M11 = 4210
- M12 = 12198
- M13 = 37378
- M14 = 111278
- M15 = 346846
Properties of meandric numbers
There is an injective functionInjective function
In mathematics, an injective function is a function that preserves distinctness: it never maps distinct elements of its domain to the same element of its codomain. In other words, every element of the function's codomain is mapped to by at most one element of its domain...
from meandric to open meandric numbers:
- Mn = m2n−1
Each meandric number can be bounded
Upper bound
In mathematics, especially in order theory, an upper bound of a subset S of some partially ordered set is an element of P which is greater than or equal to every element of S. The term lower bound is defined dually as an element of P which is lesser than or equal to every element of S...
by semi-meandric numbers:
- Mn ≤ Mn ≤ M2n
For n > 1, meandric numbers are even
Even and odd numbers
In mathematics, the parity of an object states whether it is even or odd.This concept begins with integers. An even number is an integer that is "evenly divisible" by 2, i.e., divisible by 2 without remainder; an odd number is an integer that is not evenly divisible by 2...
:
- Mn ≡ 0 (mod 2)